select correct adsorption isobars for chemisoption and physisoption respectivly ,
(where `x/m ` = extent of adsorption , T = temperature )
select correct adsorption isobars for chemisoption and physisoption respectivly ,
(where `x/m ` = extent of adsorption , T = temperature )
(where `x/m ` = extent of adsorption , T = temperature )
A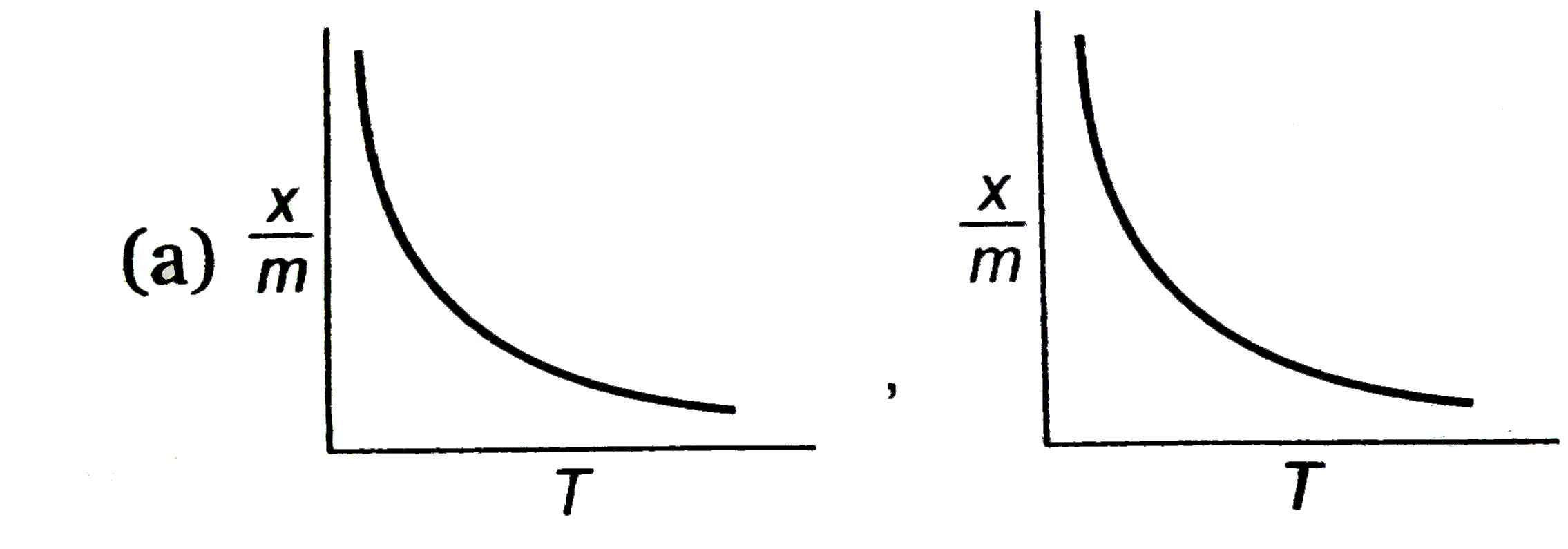
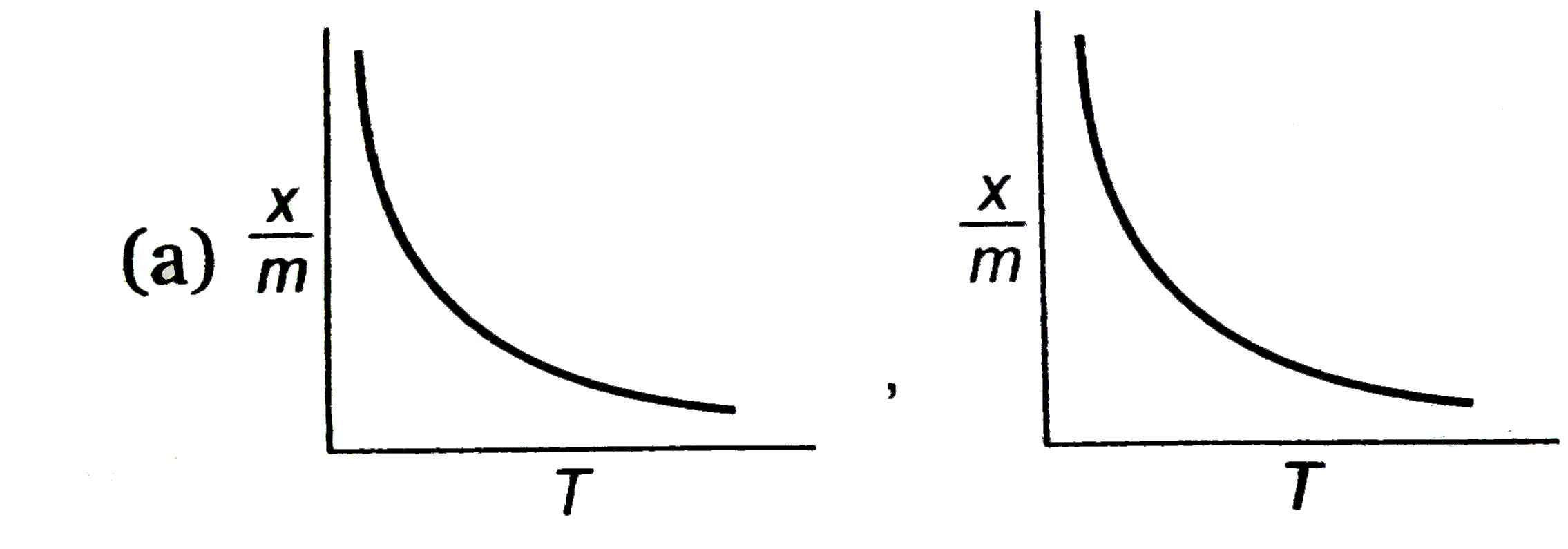
B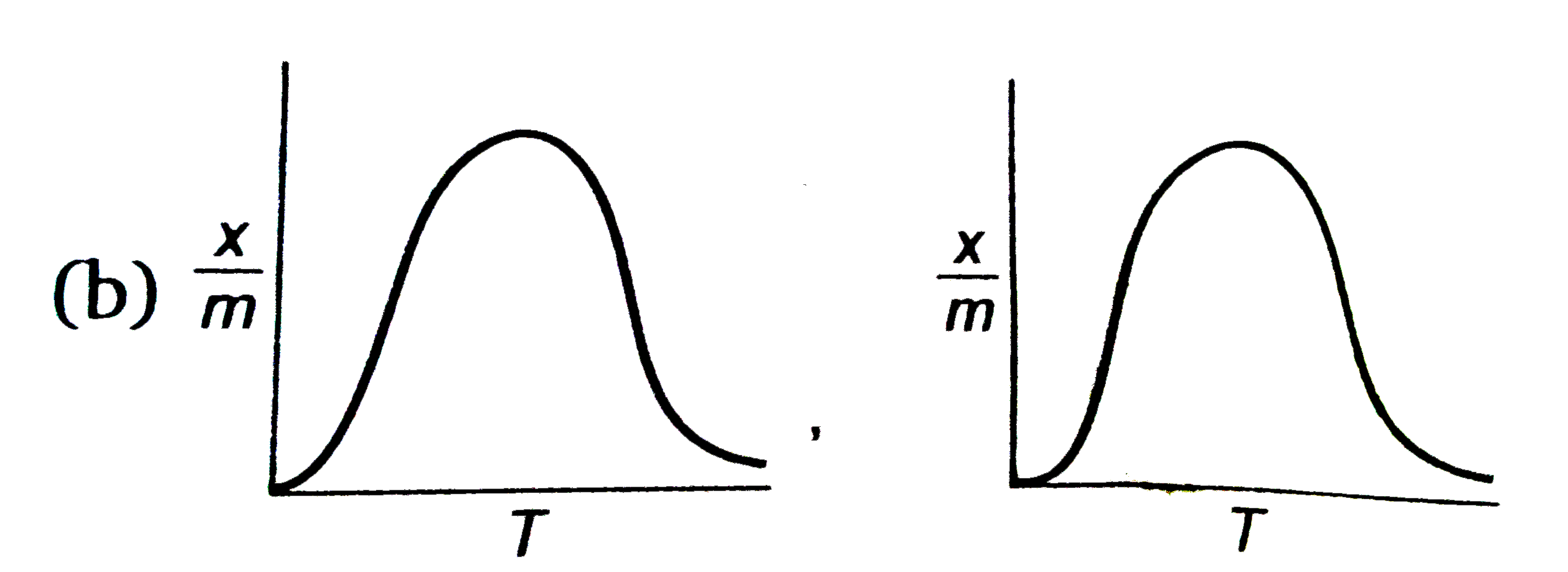

C
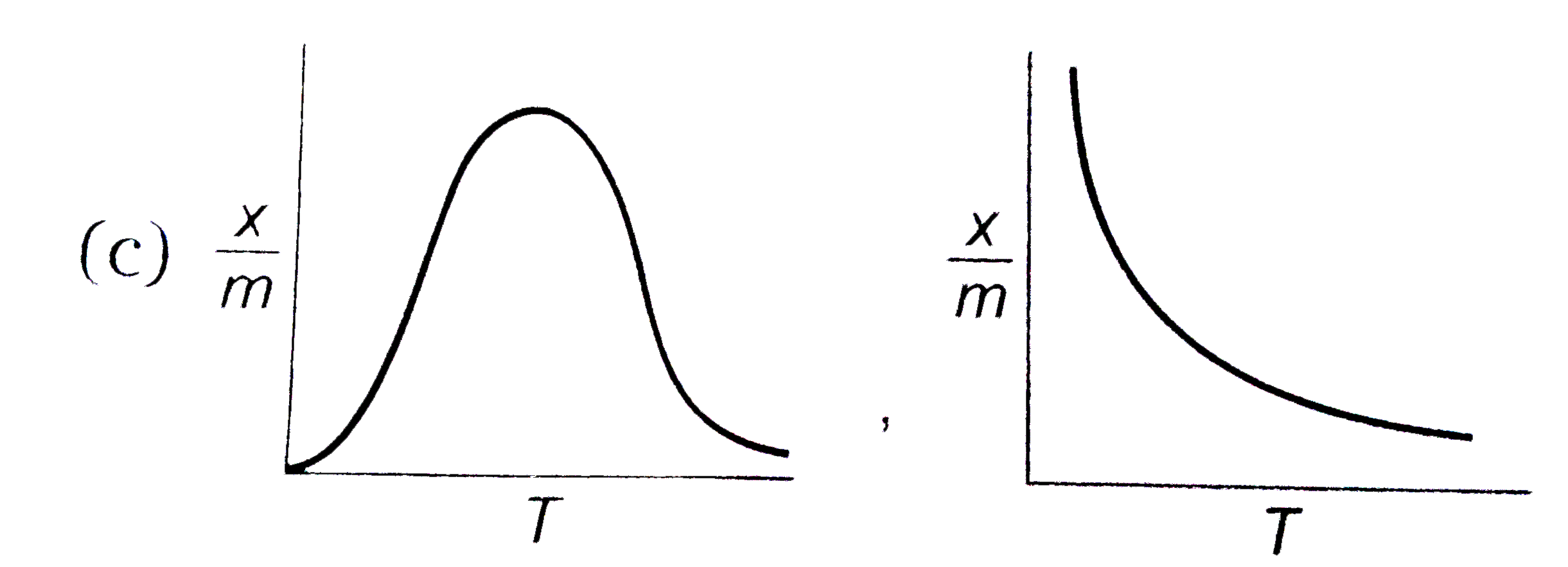
D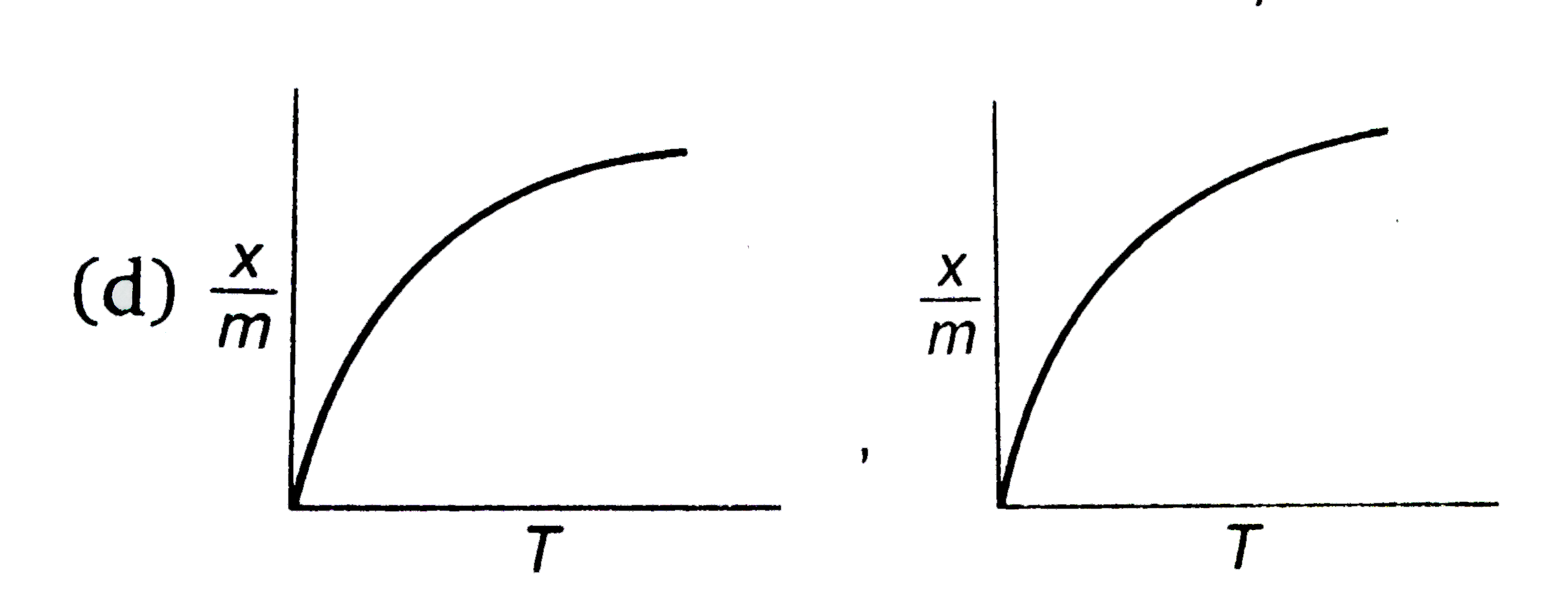
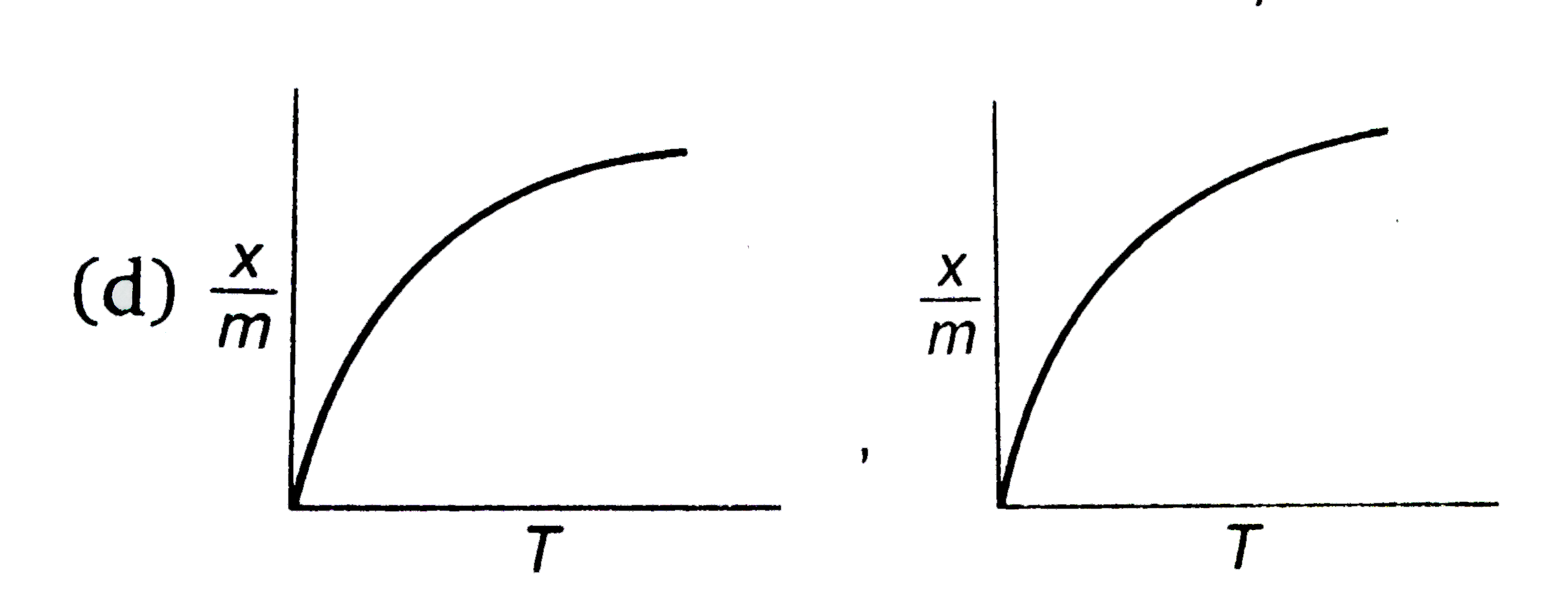
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
c
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
select the correct statement (s) : adsorption is a non - spontaneous process, surface energy deceases during the process of adsorption, adsorption takes place with decrease of entropy, in general adsorption is exothermic process.
The correct ascending order of adsorption of the following Gases on the same mass of charcoal at the same temperature and Pressure is
select the correct statement (s) : A sol is prepared by addition of excess of AgNO_(3) solution in Kl solution . The charge likely to develop on colloidal particle is positive, the effects o pressure on physical adsorption is high if temperature is low, Ultracentrifugation process is used for preparation of colloids, Gold number is the index for extent of gold plating done.
Which of the following relation is/ are correct for Langmuir adsorption isotherm? (i) x/m = constant (at high pressure) (ii) x/m = constant x p^(1//n) (at intermediate pressure) (iii) x/m = constant x p^n (at lower pressure)
each question constain STATEMENT-1(Assertion ) and STATEMENT - 2 (reason). examine the statement carefully and work the correct answer accoridng to the instructions given below : STATEMENT-1: The extent of adsorption of CO_(2) is much more higher than of H_(2) . STATEMENT-2: CO_(2)(g) has higher critical temperature and more van der Waal's force of attraction as compared to H_(2)(g) . if both the statement are TRUE and STATEMENT -2 is the correct explanation of STATEMENT - 1 , If both the statement FALSE are STATEMENT -2 is NOT the correct explanation of STATEMENT -1 , If STATEMENT -1 is TRUE and STATEMENT - 2 is FALSE , If STATEMENT -1 is FALSE and STATEMENT -2 is TRUE.
True or False : At low pressure, the extent of adsorption is directly proportional to pressure at constant temperature.
A group between x/m and the presure P of the gas at a constant temperature is called adsorption siotherm. Where x is the no. of moles of the adsorbate and m is the mass of the adsorbent. adsoption isotherms of different shaopes have been experimentally observed .. According to frundlich adosroption isthem, x//m = KP^(1//n) where K and N are constant paraments depending upon the nature of the solid and gas Inn the given isotherm select the incorrect statement : x/m proptoP^(1//n along OA, x/m proptoP^(1//n when point B is reached , x/m does not increase as rapidly with pressure along BC due to less surface area availble for adsorption .
A group between x/m and the presure P of the gas at a constant temperature is called adsorption siotherm. Where x is the no. of moles of the adsorbate and m is the mass of the adsorbent. adsoption isotherms of different shaopes have been experimentally observed .. According to frundlich adosroption isthem, x//m = KP^(1//n) where K and N are constant paraments depending upon the nature of the solid and gas Adsoption isothem of log (x/m) and log P was found of the type .
A group between x/m and the presure P of the gas at a constant temperature is called adsorption siotherm. Where x is the no. of moles of the adsorbate and m is the mass of the adsorbent. adsoption isotherms of different shaopes have been experimentally observed .. According to frundlich adosroption isthem, x//m = KP^(1//n) where K and N are constant paraments depending upon the nature of the solid and gas graph between log (x/m) and log P is a straight line a t angle 45^(@) with intercept OA as shown . hence, (x/m) at a pressure of 2 atm is :
If adsorption of a gas on a solid is limited to monolayer formation , then which of the following statement are true ? At low pressures x/m varies proportionately with P, At moderate pressures, x/m varies less than proportionately with P, At high pressure , x/m becomes independent of P, at high pressure , x/m varies more than proportionately with P.