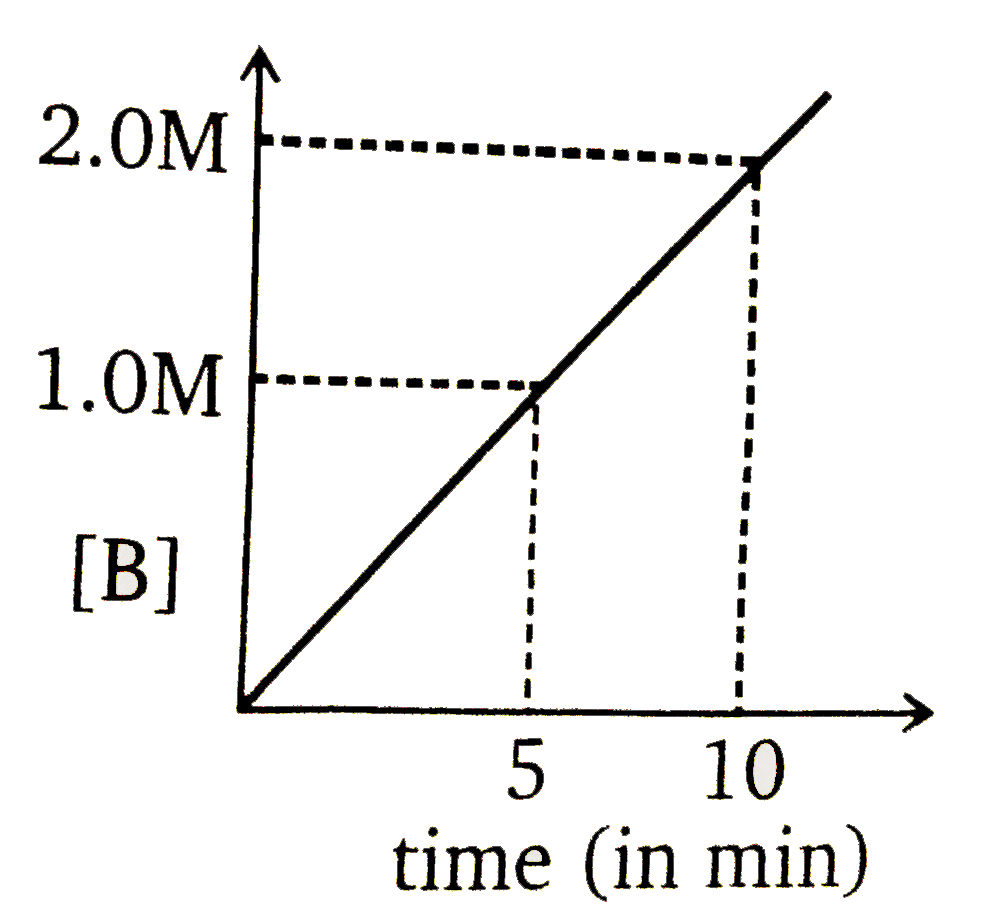
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARENDRA AWASTHI-CHEMICAL KINETIC & NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY-Level 3 - Subjective Problems
- Consider a reaction A(g)overset(k=0.1 M min^(-1))to2B(g). If initial c...
Text Solution
|
- 5A to Product In above reaction, half-life period is directly propo...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction, AiffB equilibrium constant is 1.66 and k("forward")=0....
Text Solution
|
- , At time t=0, intial mole of A is 1. Overall half time of the react...
Text Solution
|
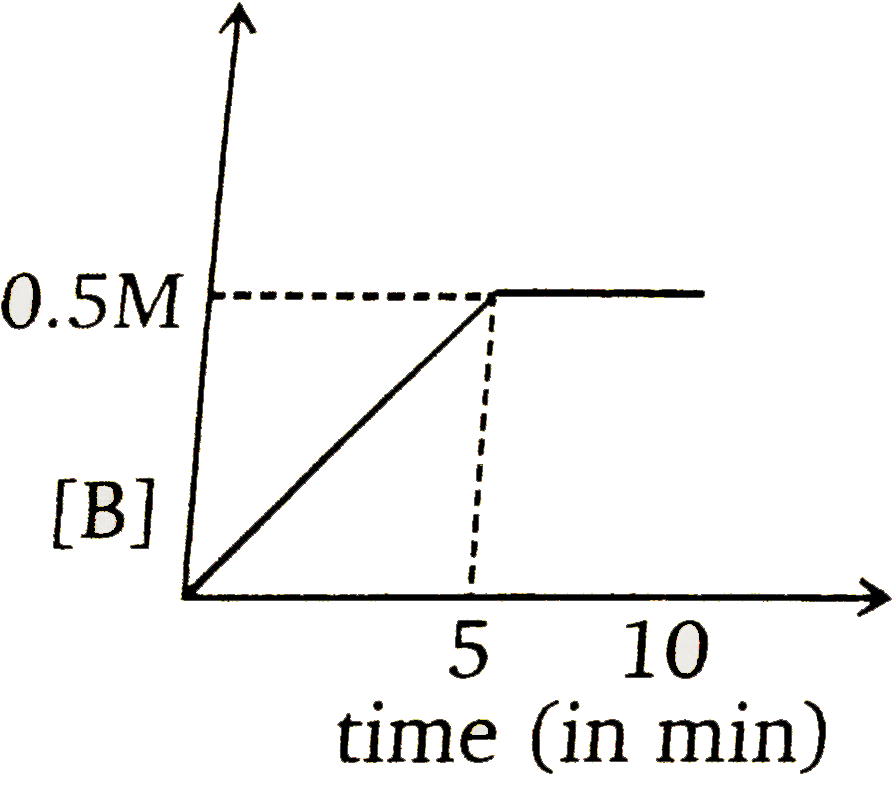 b)
b) 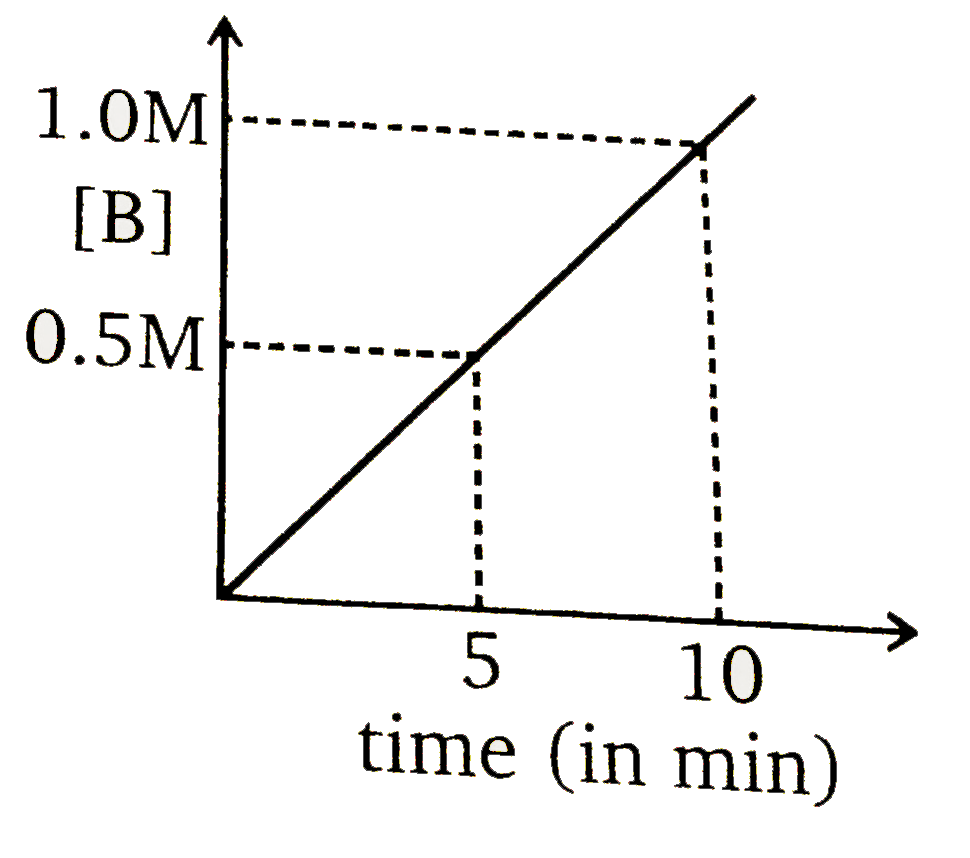
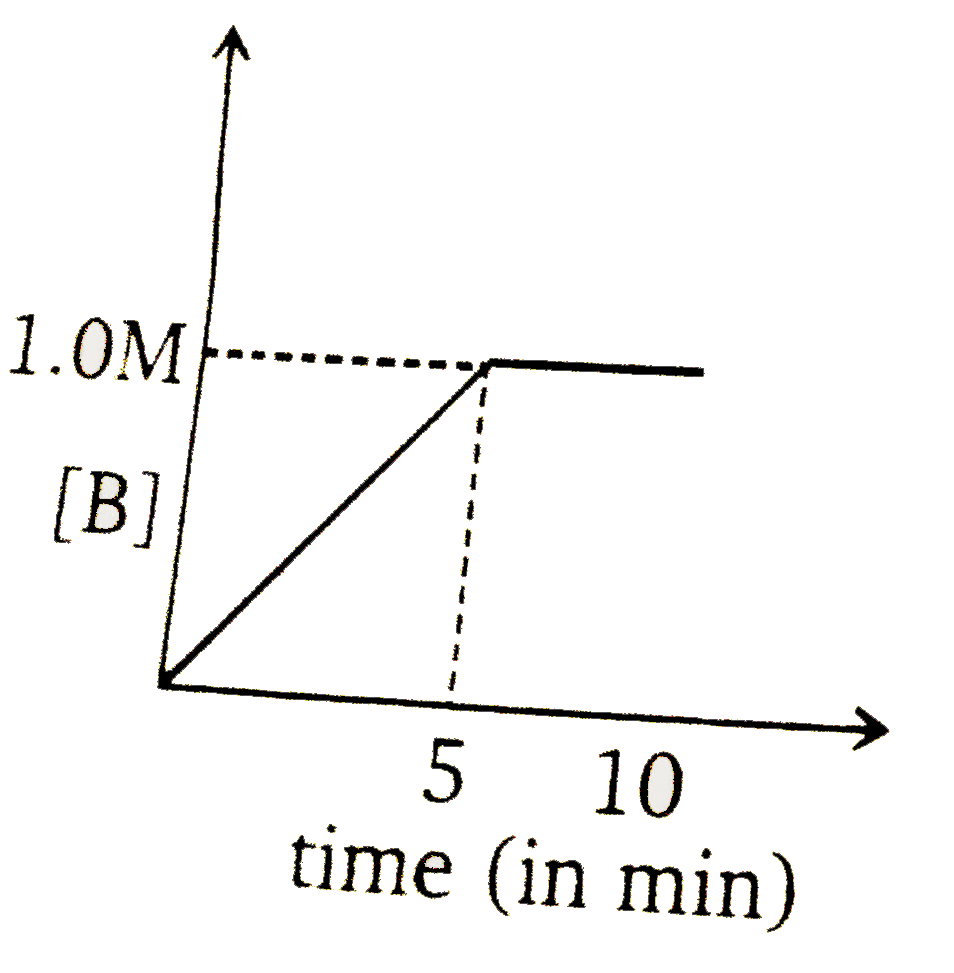 d)
d)