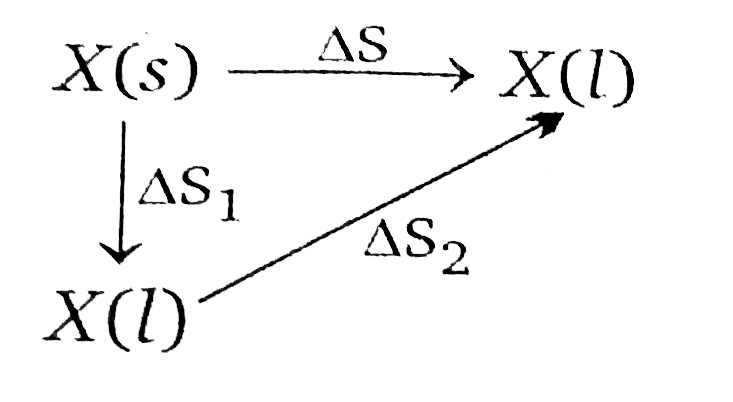A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMODYNAMICS
NARENDRA AWASTHI|Exercise Level 3 - One Or More Answers Are Correct|1 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
NARENDRA AWASTHI|Exercise Level 3 - Match The Column|2 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
NARENDRA AWASTHI|Exercise Level 2 (Q.1 To Q.30)|1 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
NARENDRA AWASTHI|Exercise Level 3 - Subjective Problems|20 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARENDRA AWASTHI-THERMODYNAMICS-Exercise
- The entropy if vaporisation of benzene is 85JK^(-1) mol^(-1). When 117...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the correct statement regarding entropy
Text Solution
|
- Calculate DeltaS for following process : underset("at" 100K)(X(s)) ...
Text Solution
|
- For a perfectly crystalline solid C(p.m.)=aT^(3), where ais constant. ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following spontaneous reaction 3X(2)(g)rarr2X(3)(g). What...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction 2H(g)rarr H(2)(g), the sign of DeltaH and DeltaS resp...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reaction. C(6)H(6)(l)+(15)/(2)O(2)(g)rarr6CO(...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reaction at temperature T : CH(2)=CH(2)(g) +...
Text Solution
|
- For a process to be spontaneous, DeltaG must be………… .
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction to occur spontaneously
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following conditions reagarding a chemical process ensure...
Text Solution
|
- The free energy change DeltaG = 0, when
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following conditions regarding a chemical process ensures...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose that a reaction has DeltaH=-40kJ and DeltaS =- 50J//K. At what...
Text Solution
|
- For isothermal expansion in case of an ideal gas :
Text Solution
|
- What is the normal boiling point of mercury? Given : DeltaH (f)^(@)...
Text Solution
|
- 19 gm of ice is converted into water at 0^(@)C and 1 atm. The entropie...
Text Solution
|
- Using the listed [DeltaG(f)^(@) values] calculate DeltaG^(@) for the r...
Text Solution
|
- From the following DeltaH^(@) and DeltaS^(@) values, predict which of ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate DeltaH(f)^(@) for Ubr(4) from the DeltaG^(@) of reaction and...
Text Solution
|