A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-LINES AND ANGLES -Exercise
- In Fig. 5.16, PA || BC || DT and AB || DC. Then, the values of a and b...
Text Solution
|
- The difference of two complementary angles is 30^(@) . Then, the angle...
Text Solution
|
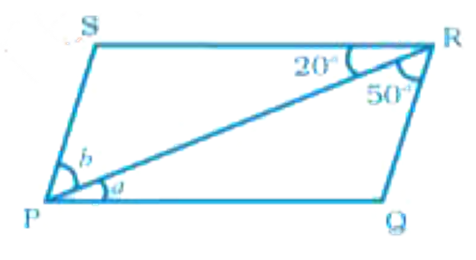
- In Fig. PQ || SR and SP || RQ. Then, angles a and b are respectively
Text Solution
|
- In Fig a and b are
Text Solution
|
- If two supplementary angles are in the ratio 1 : 2, then the bigger an...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 5.19, angleROS is a right angle and anglePOR and angleQOS a...
Text Solution
|
- Statements a and b are as given below: a : If two lines intersect, t...
Text Solution
|
- For Fig. 5.20, statements p and q are given below: p : a and b are f...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 5.21, angleAOC and angleBOC form a pair of
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 5.22, the value of a is
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 5.23, if QP || SR, the value of a is
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following figures, a and b are forming a pair of adjac...
Text Solution
|
- In a pair of adjacent angles, (i) vertex is always common, (ii) one ar...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 5.25, lines PQ and ST intersect at O. If anglePOR = 90^(@) an...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 5.26, POQ is a line, then a is equal to
Text Solution
|
- Vertically opposite angles are always
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 5.27, a = 40^(@) . The value of b is
Text Solution
|
- If an angle is 60^(@) less than two times of its supplement, then the ...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 5.28, PQ || RS. If angle1=(2a+b)^(@) and angle6=(3a–b)^(@), ...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 5.29, PQ||RS and a : b = 3 : 2. Then, f is equal to
Text Solution
|