Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HEREDITY AND VARIATION
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise Part II Questions For Assessment(Very Short Answer Type Questions) M.C.Q |5 VideosHEREDITY AND VARIATION
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise Part II Questions For Assessment(Very Short Answer Type Questions) Correct the statements, if required by changing the underlined word (s) |2 VideosHEREDITY AND VARIATION
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise Part II Questions For Practice (Very Short Answer Type Questions ) Express in one or two word (s) |2 VideosHEALTH AND DISEASES
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE (Short Answer Type II Questions )|3 VideosHUMAN REPRODUCTION
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE (Long Answer Type Questions)|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT PUBLICATION-HEREDITY AND VARIATION-Part II Questions For Practice (Short Answer Type Questions )
- Explain the phenomenon of multiple allelism and codominance taking ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the phenotype of the following (a) l^(A) i (b) ii
Text Solution
|
- A child has blood group O. If the father has blood group A and mother ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following What is the most common example of pleiot...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following How are the pleiotropic genes useful ?
Text Solution
|
- State the significance of crossingover.
Text Solution
|
- What is Chiasma ?
Text Solution
|
- What is likage? mention it's Significance.
Text Solution
|
- Write a short notes on: Crossing over
Text Solution
|
- Define multiple allelism
Text Solution
|
- During his studies on genes in Drosophila that were sex-linked, TH ...
Text Solution
|
- List three different allelic forms of gene 'I' in human . Explain th...
Text Solution
|
- A woman with blood group 'A' marries a man with blood group 'O' . Di...
Text Solution
|
- A woman with blood group 'A' marries a man with blood group 'O' . Di...
Text Solution
|
- blood group are called universal recipient.
Text Solution
|
- Explain ABO blood group?
Text Solution
|
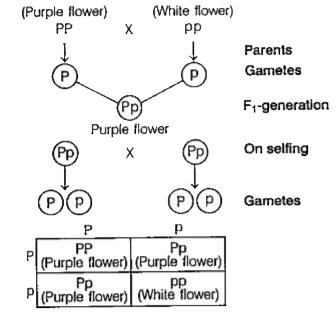
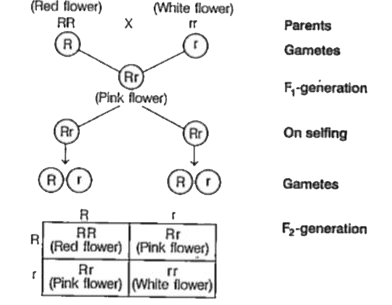
- Inheritance pattern of flower colour in garden pea plant and snapdrago...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the genetic basis of blood grouping in human population
Text Solution
|
- Can a child have blood group o if his parents have blood group A and b...
Text Solution
|
- How do genes and chromosomes share similarity from the point of view ...
Text Solution
|