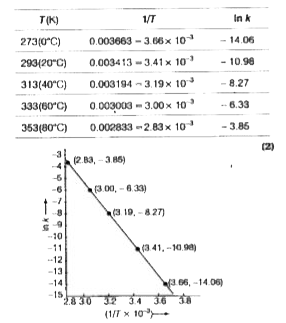
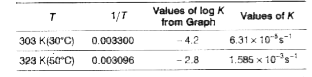Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL KINETICS
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTIONS FOR ASSESSMENT (Part IV Activation Energy and Collision Theory of Chemical Reactions ) Multiple Choice Type Questions|3 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTIONS FOR ASSESSMENT (Part IV Activation Energy and Collision Theory of Chemical Reactions ) Very Short Answer Type Questions|2 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE (Part IV Activation Energy and Collision Theory of Chemical Reactions ) Short Answer Type II Questions|6 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE (LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS) |3 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE (LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS) |2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT PUBLICATION-CHEMICAL KINETICS-QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE (Part IV Activation Energy and Collision Theory of Chemical Reactions ) Long Answer Type Questions
- Write short note on activation energy.
Text Solution
|
- The time required for 10% completion of a first order reaction at 298 ...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for rate constant of 1st order reaction. Write th...
Text Solution
|
- What is Arrhenius equation?
Text Solution
|
- For a hypothetical reaction, the mean potential energies of reactants ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant for the decomposition of N(2) O(5) at various temper...
Text Solution
|