Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELEMENTS : NITROGEN FAMILY
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE ( Short Answer Type Questions ) |17 VideosELEMENTS : NITROGEN FAMILY
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE ( Short Answer Type II Questions ) |17 VideosELEMENTS : NITROGEN FAMILY
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE ( Long Answer Type Questions ) |11 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE ( LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS) |3 VideosETHERS
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE (7 MARK)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT PUBLICATION-ELEMENTS : NITROGEN FAMILY-QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE ( Very Short Answer Type Questions )
- PH(3) , forms bubbles when passed slowly in water but NH(3) , dissolve...
Text Solution
|
- Nitrogen does not form pentahalides. Why?
Text Solution
|
- Why does R(3)P=O exist but R(3) N=O does not (R = alkyl group)? Gi...
Text Solution
|
- Why is N(2) , less reactive at room temperature?
Text Solution
|
- Mention the conditions required to maximise the yield of ammonia.
Text Solution
|
- How does ammonia react with a solution of Cu^(2+) ?
Text Solution
|
- The products obtained when ammonia is reacted with excess of chlorine ...
Text Solution
|
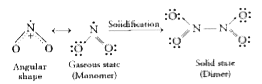
- Why is NO(2) paramagnetic in gaseous state but the solid obtained on c...
Text Solution
|
- Most stable form of phosphorus is .......
Text Solution
|
- Write the structural difference between white phosphorus and red phosp...
Text Solution
|
- Which allotrope of phosphorus is more reactive and why?
Text Solution
|
- What happens when white phosphorus is heated with conc. NaOH solution ...
Text Solution
|
- Why does PCI3, fumes in moist air ?
Text Solution
|
- What happens when PCl(5) is heated ?
Text Solution
|
- What is the basicity of H(3)PO(3) ?
Text Solution
|
- What happens when H(3)PO(3) is heated ?
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following chemical reaction. Ca(3)P(2) + H(2) O rarr
Text Solution
|
- Account for the following. H(3)PO(2) is a stronger reducing agent th...
Text Solution
|
- What is the basicity of H(3)PO(4) ?
Text Solution
|