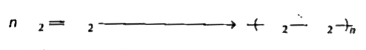Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
EXAMINATION PAPER 2018
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise GROUP C|7 VideosEXAMINATION PAPER 2018
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise GROUP C|7 VideosETHERS
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE (7 MARK)|3 VideosF-BLOCK ELEMENTS
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE (LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS) |2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT PUBLICATION-EXAMINATION PAPER 2018-GROUP B
- What happens when calcium açetate is dry distilled ?
Text Solution
|
- Give two difference between crystalline and amorphous solids.
Text Solution
|
- What are antibiotics? Writedown the name of two antibiotics.
Text Solution
|
- Write the IUPAC name of the following compounds . (a) [Co(NH(3))(6)]...
Text Solution
|
- With an example, explain roasting.
Text Solution
|
- 50 ml ofN/10 NaOH. solution, 100 ml of N/5NaOH solution and 500ml of N...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why HCl is a gas and HF is a liquid at room temperature.
Text Solution
|
- How can you convert ethanol to ethene ?
Text Solution
|
- What are tranquilisers?
Text Solution
|
- Prove that for a 1st order reaction, the time taken for 99% completion...
Text Solution
|
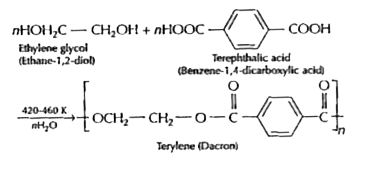
- What are addition and condensation polymerisation? Give one example of...
Text Solution
|
- What is a semiconductor? What aren-type and p-type semiconductors?
Text Solution
|
- Explain why transition metal ions are usually coloured.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the amphoteric behaviour of amino acids.
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between multimolecular and macromolecular colloids.
Text Solution
|
- Boiling point of water is 100^@C. Calculate the boiling point of an aq...
Text Solution
|
- What is lanthanide contraction? Write any two of its consequences.
Text Solution
|
- FeSO4, solution mixed with (NH4)2SO4, solution in 1:1 molar ratio give...
Text Solution
|
- Why phenol is acidic in nature ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain the Hofnann bromamide reaction with one example.
Text Solution
|