Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
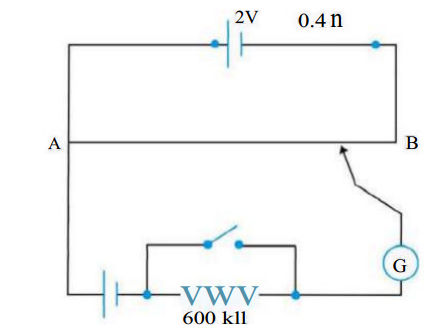
- Figure 3.33 shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal re...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resista...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resista...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resista...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resista...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resista...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र में एक वोल्ट्मीटर दर्शाए गया है जिसमे एक 2.0V और आंतरिक प्रतिरो...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र में एक वोल्ट्मीटर दर्शाए गया है जिसमे एक 2.0V और आंतरिक प्रतिरो...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र में एक वोल्ट्मीटर दर्शाए गया है जिसमे एक 2.0V और आंतरिक प्रतिरो...
Text Solution
|