Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
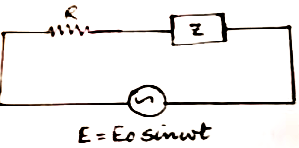
- An alternating voltage E=E0 sin omegat is applied to a circuit contain...
Text Solution
|
- The voltage and current in a series AC circuit are given by V = V0 cos...
Text Solution
|
- In a black box of unknown elements (L or R or any other combination), ...
Text Solution
|
- एक प्रत्यावर्ती धारा परिपथ में धारा i = i(0) sin (omegat-pi//2) प्रवा...
Text Solution
|
- The values of current and voltage in an AC circuits are respectively I...
Text Solution
|
- Analternating voltage E= E0 sin omegat is applied to a circuit contain...
Text Solution
|
- Analternating voltage E= E0 sin omegat is applied to a circuit contain...
Text Solution
|
- In the AC circuit shown, E=E(0)sin(omegat+phi)andi=i(0)sin(omegat+phi+...
Text Solution
|
- The voltage and current in a series AC circuit are given by V = V0 cos...
Text Solution
|