Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Find the values of m for which roots of equation x^(2)-mx+1=0 are less...
Text Solution
|
- Find the set of all values of a for which the roots of the equation x^...
Text Solution
|
- Find the equation of whose roots is greater by unity than the roots...
Text Solution
|
- find the set of value of m for which exactly one root of the equation ...
Text Solution
|
- The number of integral values of 'm' less than 50, so that the roots o...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the quadratic equationx^2-mx+1=0 with two roots alphaand bet...
Text Solution
|
- If x=2 and x=3 are roots of the equation 3x^(2)-mx+2n=0, then find the...
Text Solution
|
- यदि x=2 और x=3 समीकरण 3x^(2)-mx+2n=0 के मूल हैं, तो m और n के मान ज्ञा...
Text Solution
|
- The values of a for which one root of the equation, x^(2)+(2a+1)x+(a-2...
Text Solution
|
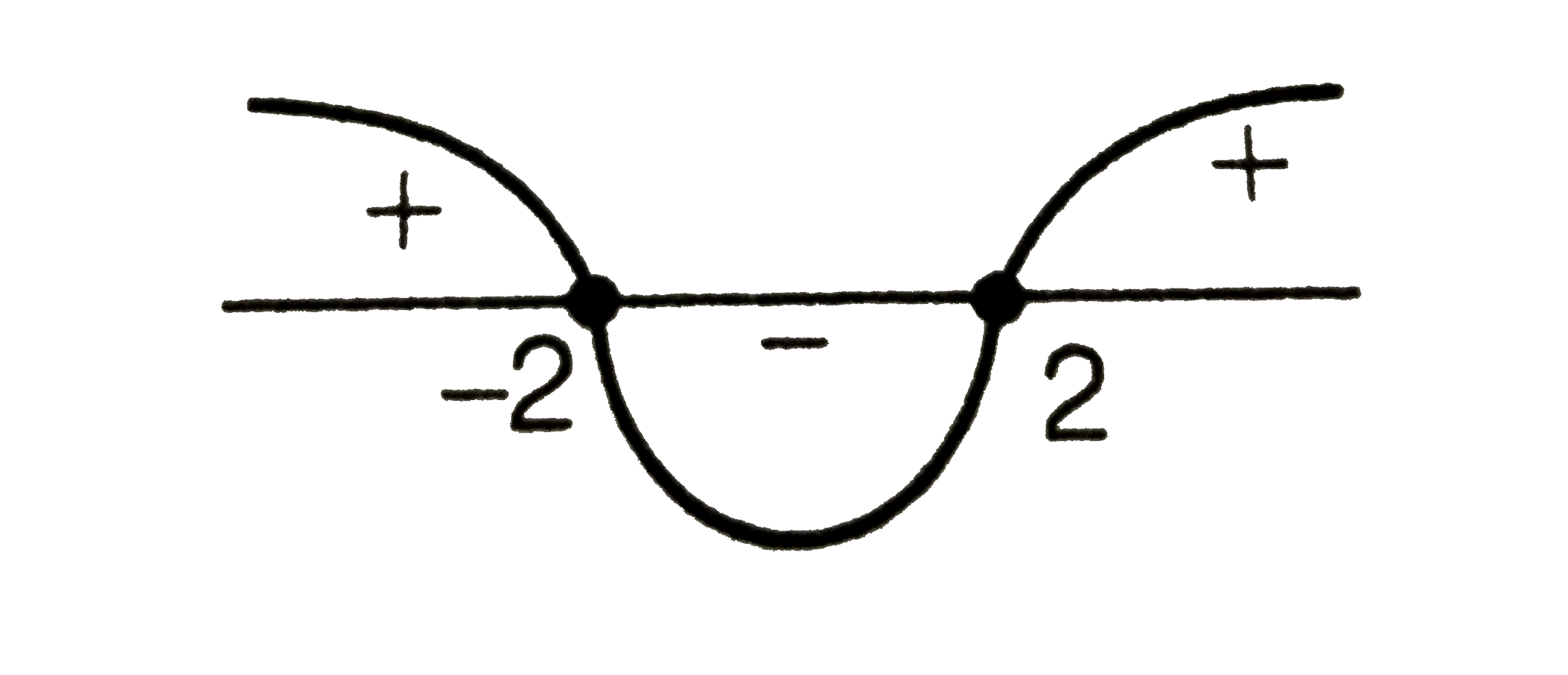 ltBrgt (i) Consider `Dge0(-m)^(2)-4.1.4ge0`
ltBrgt (i) Consider `Dge0(-m)^(2)-4.1.4ge0`