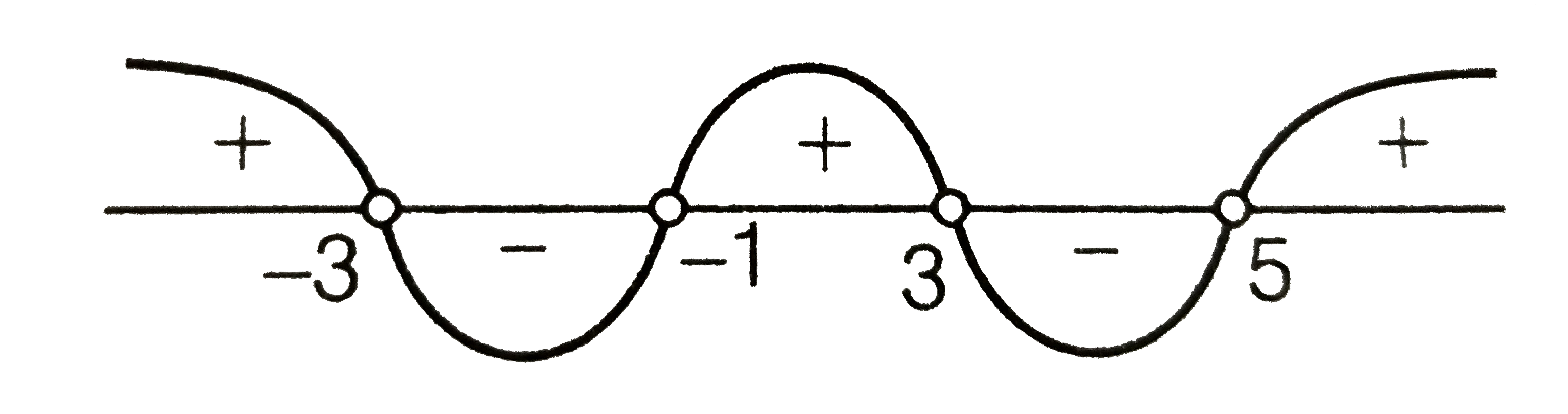
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Find the valuesof m for which exactly one root of the equation x^(2)-2...
Text Solution
|
- find the set of value of m for which exactly one root of the equation ...
Text Solution
|
- find all the possible values of k for which exactly one root of the qu...
Text Solution
|
- if the roots of the quadratic equation (4p - p^(2) - 5)x^(2) - 2mx ...
Text Solution
|
- If exactly one root of the quadratic equation x ^(2) -(a+1 ) +2a =0 li...
Text Solution
|
- Find the values of the parameter a for which the roots of the quadrati...
Text Solution
|
- If number of integeral values of 'm' for which exactly one root of the...
Text Solution
|
- if the roots of the quadratic equation (4p - p^(2) - 5)x^(2) - 2mx ...
Text Solution
|
- If x=2 and x=3 are roots of the equation 3x^(2)-2mx+2n=0, find the val...
Text Solution
|