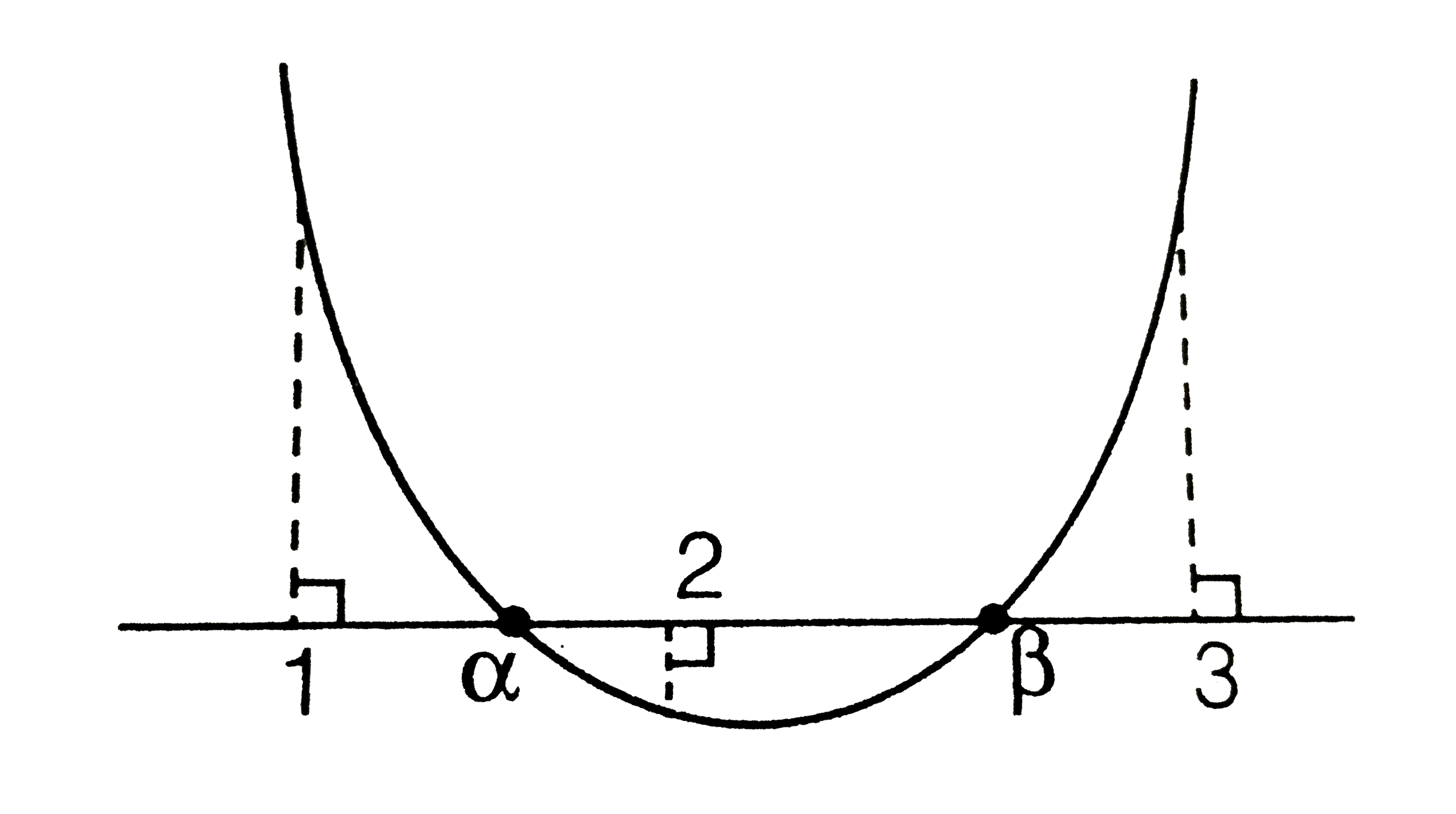
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- If alpha, beta be the roots of 4x^(2) - 16x + c = 0, c in R such that ...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha and beta (alpha lt beta) are the roots of the equation x^(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- If 0 lt a lt b lt c and the roots alpha, beta of the equation ax ^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- If 0 lt alpha lt beta lt (pi)/(2), prove that, tan alpha-tan beta lt a...
Text Solution
|
- If 0 lt c lt b lt a and the roots alpha, beta the equation cx^(2)+bx+a...
Text Solution
|
- IF alpha , beta are the roots of x^2+bx+c=0, gamma,delta are the roots...
Text Solution
|
- Let a, b, c in R be such that a + b + c lt 0, a - b + c lt 0 and c g...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha and beta (alpha lt beta) are the roots of the equation x^(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha, beta be the roots of 4x^2-17x+lambda=0, lambda in R such th...
Text Solution
|