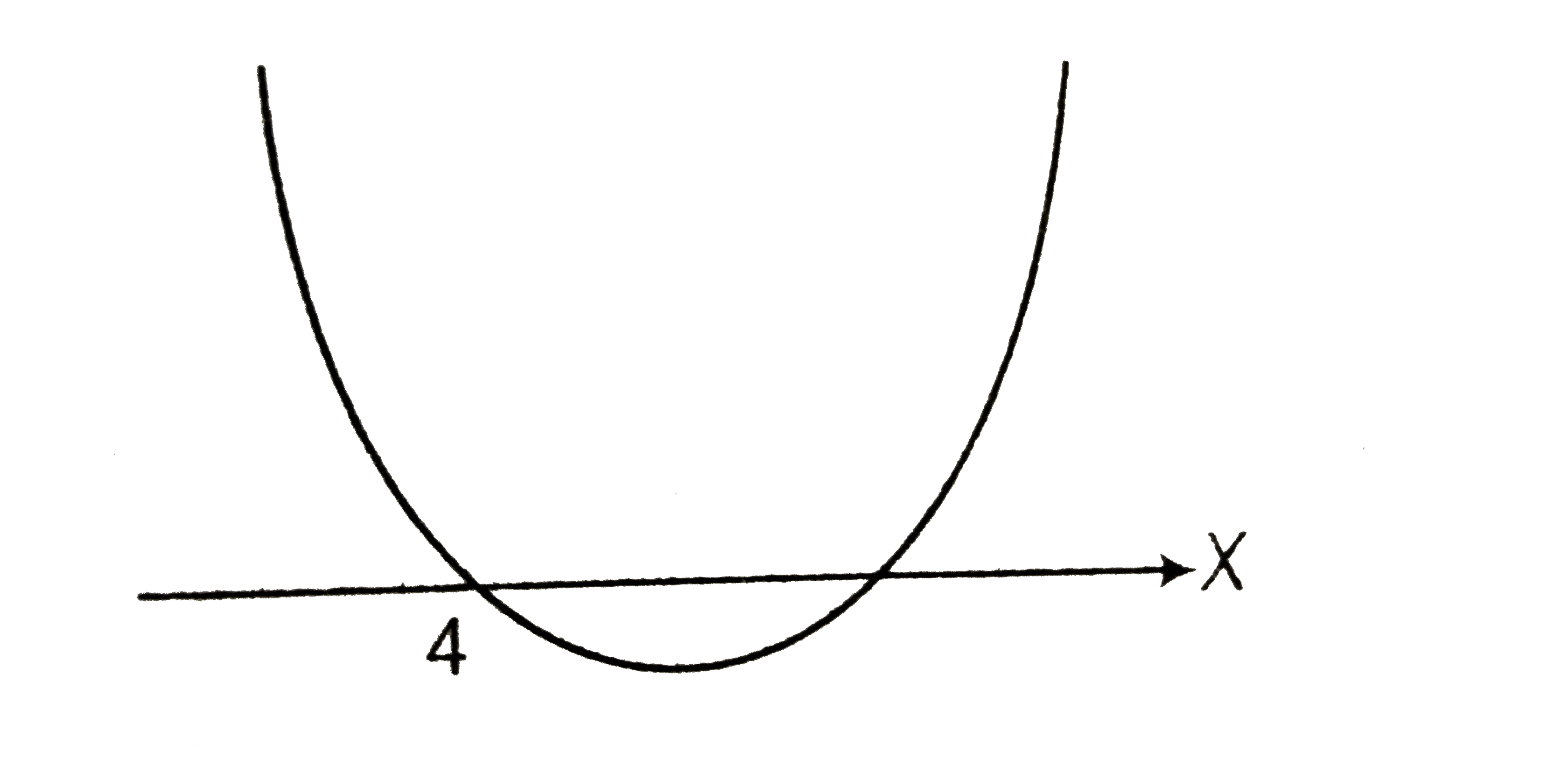
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The smallest value of k, for which both the roots of the equation, x^2...
Text Solution
|
- The smallest value of k, for which both the roots of the equation,x^(2...
Text Solution
|
- The smallest value of k for which both the roots of the equation x^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- For what real values of k the equation 9x^(2)+8Kx+16=0 have real and e...
Text Solution
|
- The smallest value of k for which both the roots of the equation x^2-8...
Text Solution
|
- The value of k for which the equation (k-2) x^(2) + 8x + k + 4 = 0 has...
Text Solution
|
- The number of values (s) of k , for which both the roots of the equati...
Text Solution
|
- If lambda is a smallest possible integral value of k, for which roots ...
Text Solution
|
- The smallest value of a for which both the roots of the equation x^(2)...
Text Solution
|