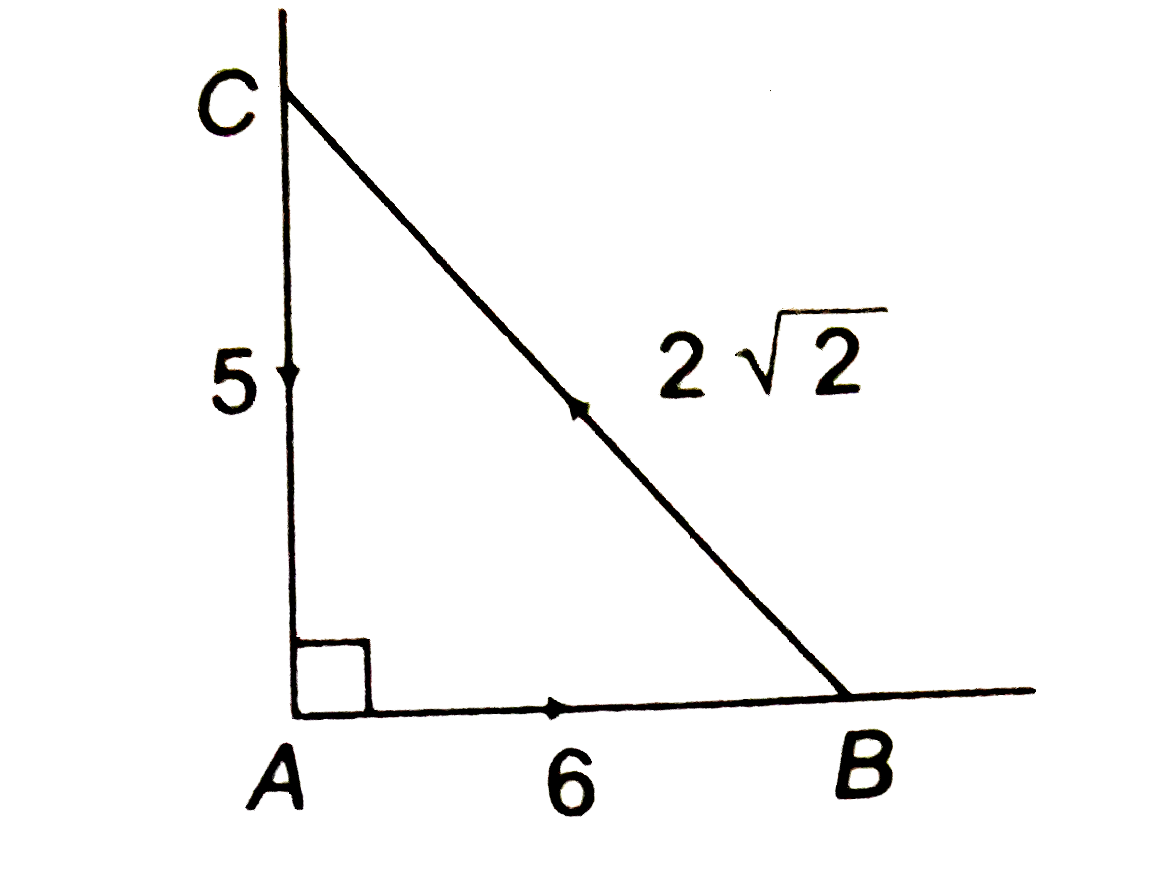
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- ABC is an isosceles triangle right angled at A. forces of magnitude 2s...
Text Solution
|
- ABC is triangle,right angled at A.The resultant of the forces acting a...
Text Solution
|
- Forces proportional to AB , BC and 2 CA act along the slides of a tria...
Text Solution
|
- Three equla force, each of magnitude P, act along the side AB, BC, and...
Text Solution
|
- Forces proportional to AB, BC & 2 CA act along the sides of triangle A...
Text Solution
|
- ABC is isosceles triangle, right angled at A. The resultant of the for...
Text Solution
|
- ABC एक समकोण त्रिभुज है -Q आवेश पर बल के परिमाण की गणना कीजिए।
Text Solution
|
- A current carrying loop in the form of a right angle isosceles triangl...
Text Solution
|
- Delta ABC , But is a right angle. The forces along the AB and AC whose...
Text Solution
|