A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- ABCDEF is a regular hexagon in the x-y plance with vertices in the ant...
Text Solution
|
- In a regular hexagon ABCDEF,vec AE
Text Solution
|
- Let ABCDEF be a regular hexagon whose centre is at the origin.(A,B,C,D...
Text Solution
|
- Let ABCDEF be a regular hexagon with vertices in the anticlockwise sen...
Text Solution
|
- In the regular hexagon shown in Fig. 3.51, vecAB + vecBC + vecCD+ ve...
Text Solution
|
- a and b form the consecutive sides of a regular hexagon ABCDEF.
Text Solution
|
- The value of vec(AB)+vec(BC)+vec(DA)+vec(CD)is
Text Solution
|
- In a quadrilateral ABCD, vecAB+vecBC+ vecCD is:
Text Solution
|
- vecAB+vecBC+vecDA+vecCD என்பது
Text Solution
|
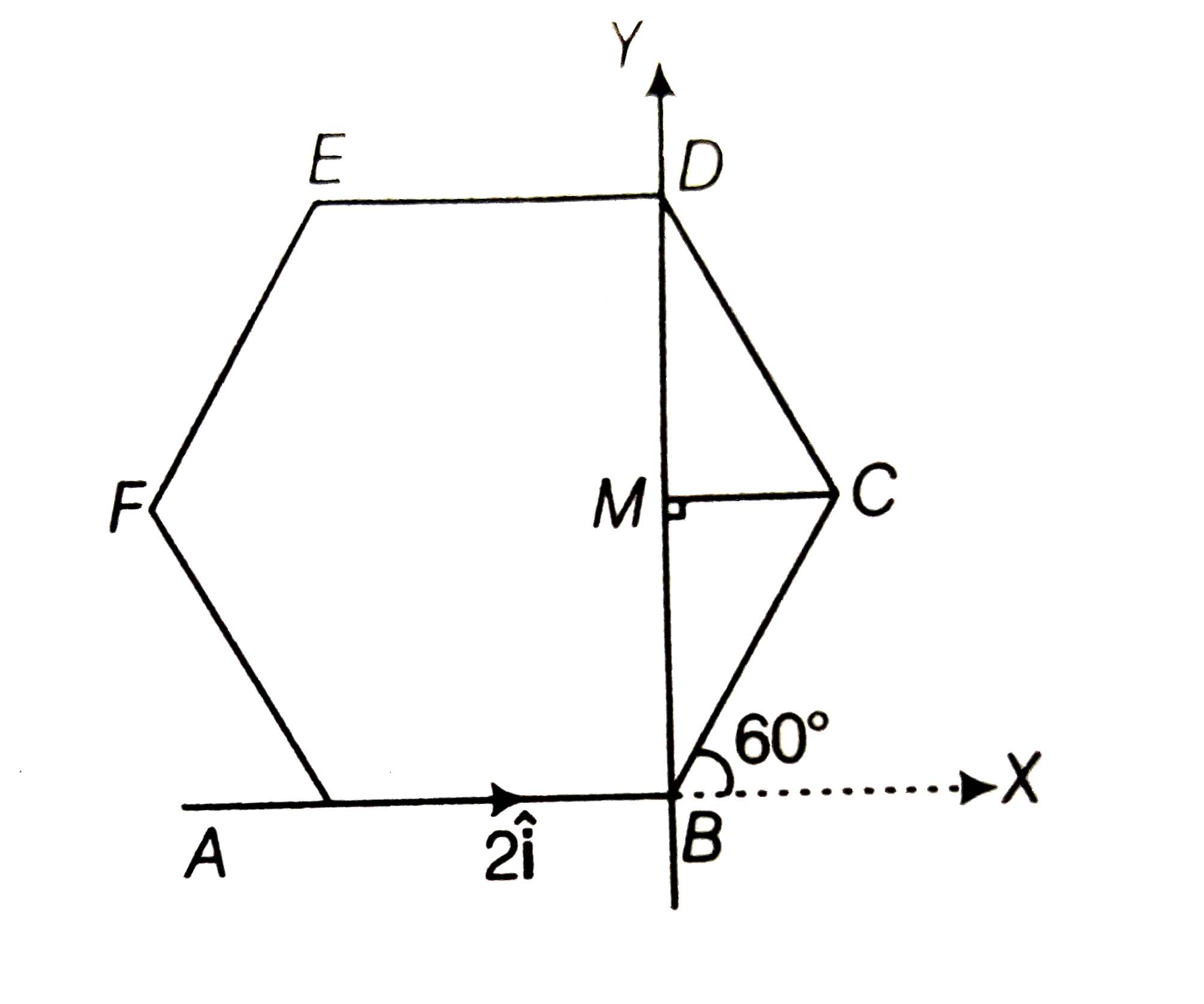 AB is along the X-axis and BD is along the Y-axis.
AB is along the X-axis and BD is along the Y-axis.