Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
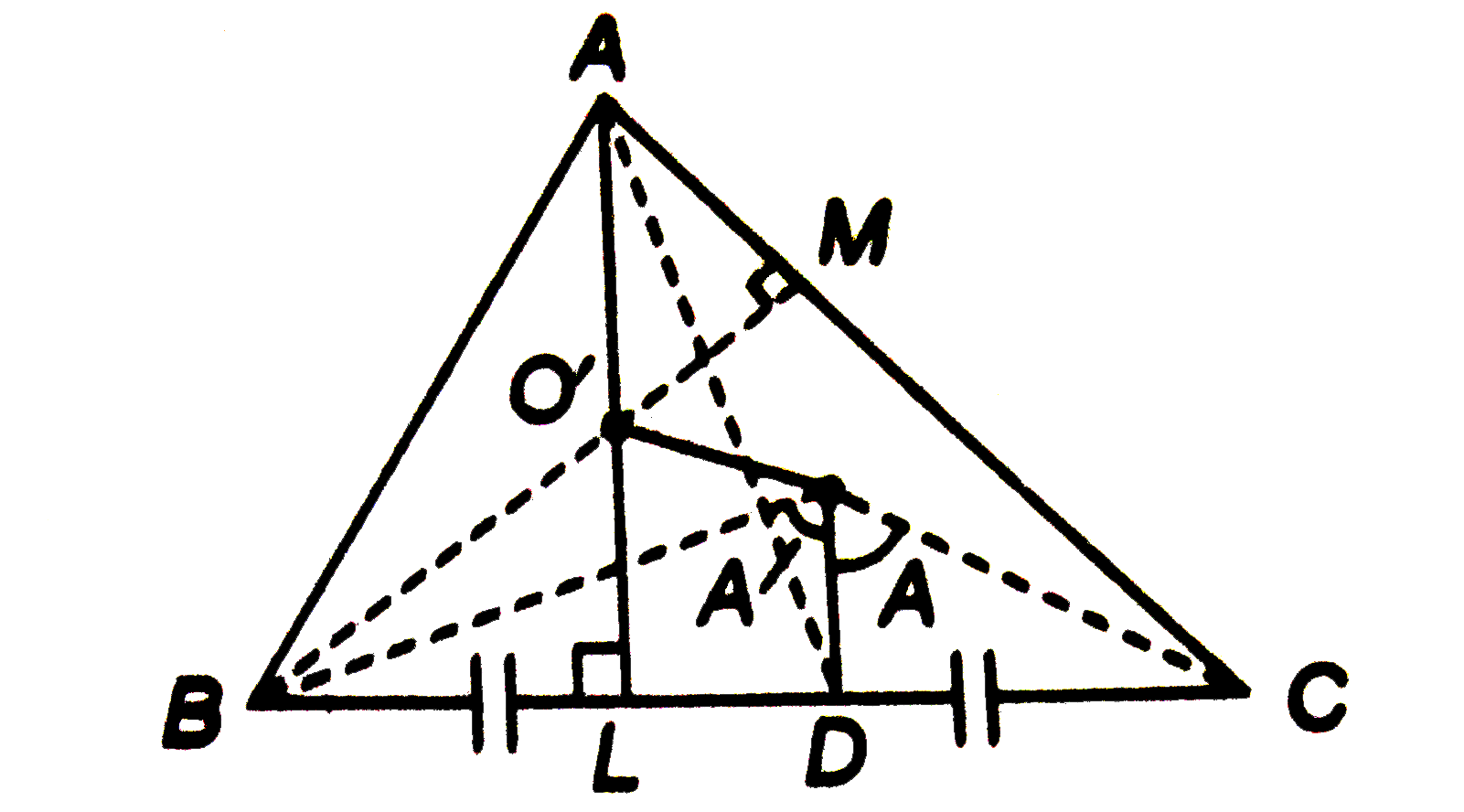
- If O is the circumcentre and O' the orthocenter of DeltaABC prove that...
Text Solution
|
- Let O be an interior point of DeltaABC such that bar(OA)+2bar(OB) + 3b...
Text Solution
|
- If S is circumcentre, O is orthocentre of DeltaABC, then vec(SA)+vec(...
Text Solution
|
- Let O be any point in the interior of DeltaABC, prove that : AB+BC+C...
Text Solution
|
- if D,E and F are the mid-points of the sides BC,CA and AB respectively...
Text Solution
|
- DeltaABC में, O एक आन्तरिक बिन्दु है। सिद्ध कीजिए कि : AB+BC+CAlt2(OA+...
Text Solution
|
- If S is circumcentre and 'O' is orthocentre of Delta ABC, then match t...
Text Solution
|
- Let O be an interior point of DeltaABC such that bar(OA)+2bar(OB) + ...
Text Solution
|
- Let O be an interior point of DeltaABC such that bar(OA)+2bar(OB) + ...
Text Solution
|