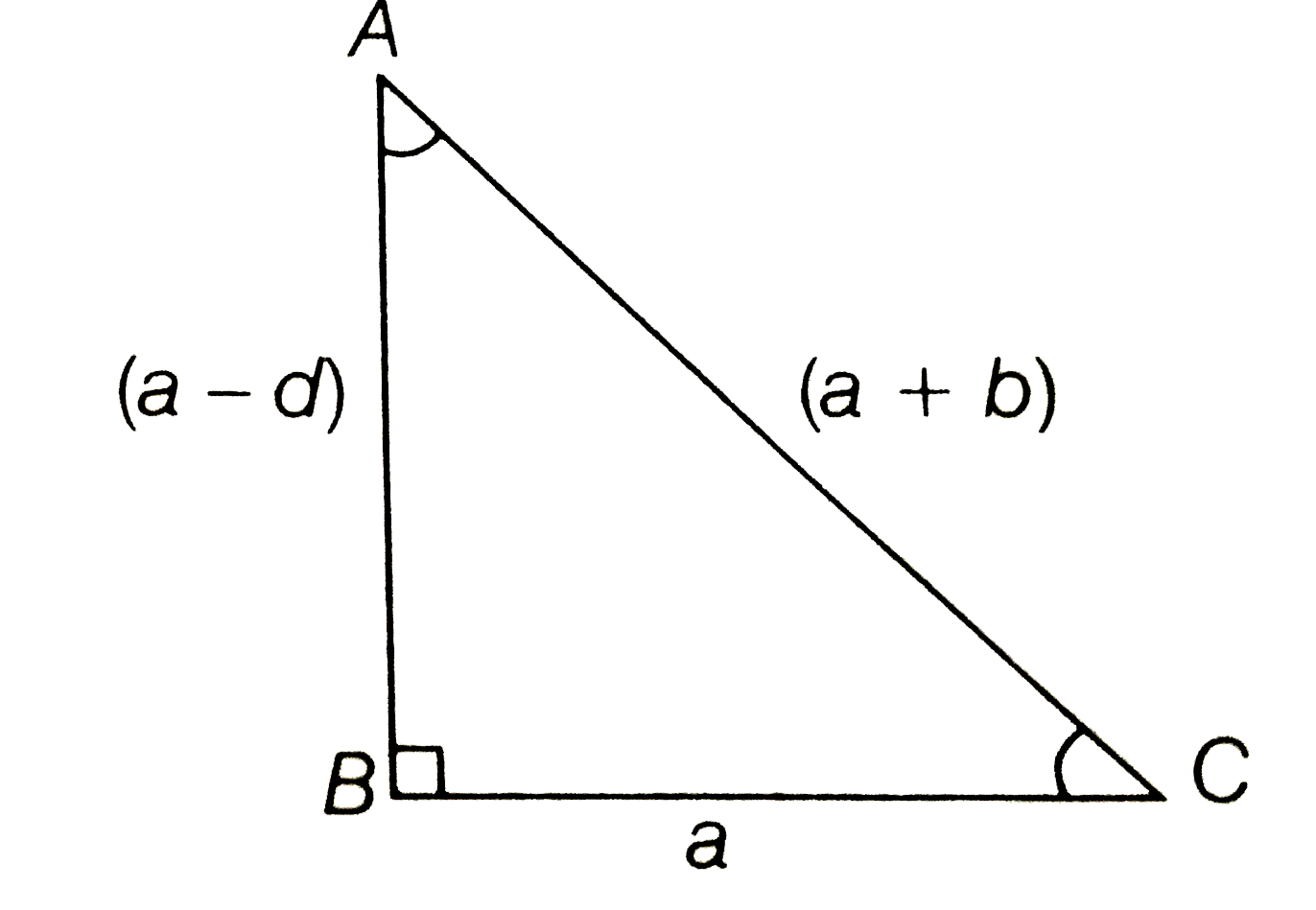
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- If the lengths of sides of right angled triangle are in A.P then the s...
Text Solution
|
- If the sides of a right-angled triangle are in A.P., then the sines of...
Text Solution
|
- If the sides of a angled triangle are in A.P then the sines of the acu...
Text Solution
|
- If the sides of right angled triangle are in G.P then the cosines of t...
Text Solution
|
- If the sides of a triangle are in A.P. and the greatest angle of the ...
Text Solution
|
- If the side of a right-angled triangled are in A.P., then tangents of ...
Text Solution
|
- If the length of sides of right angled triangle are in A.P., then the ...
Text Solution
|
- Fill in the blanks: A right triangle cannot have an ……..angle. The ac...
Text Solution
|
- If the angles of a right angled triangle are in A.P then the sides are...
Text Solution
|