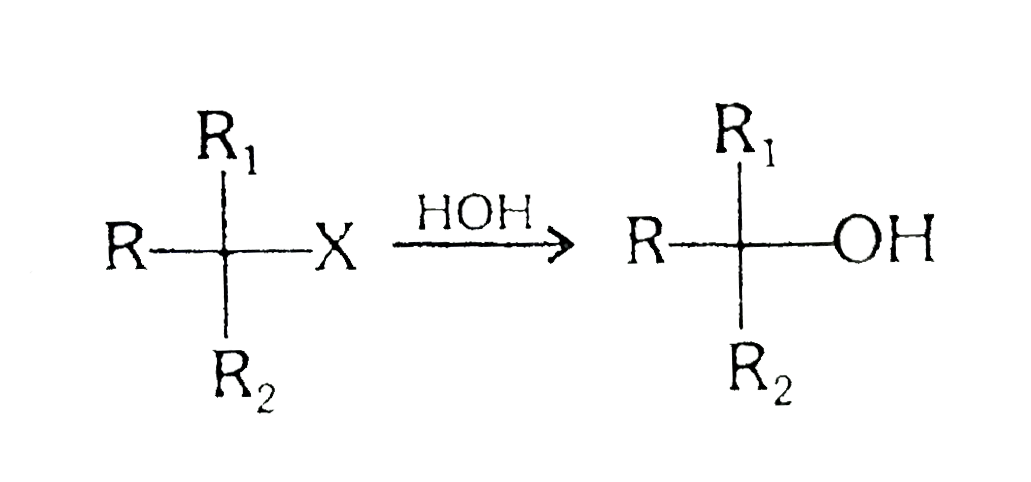
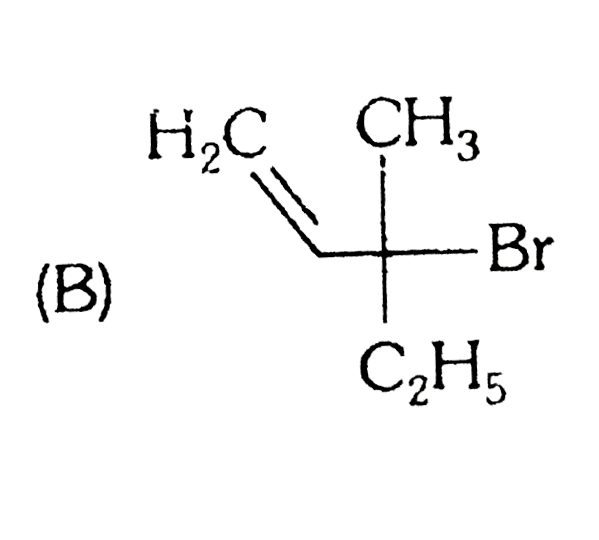
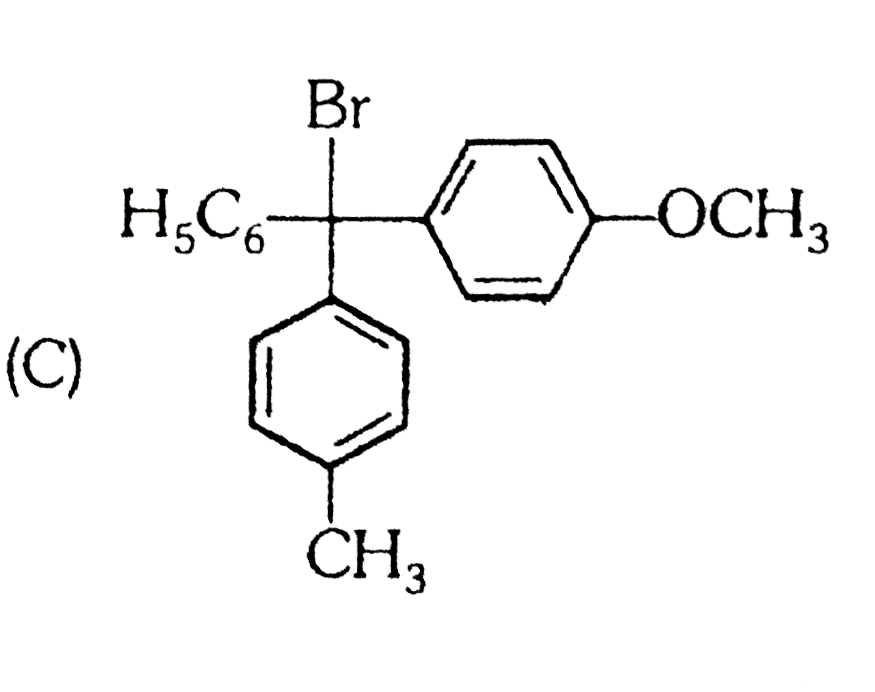
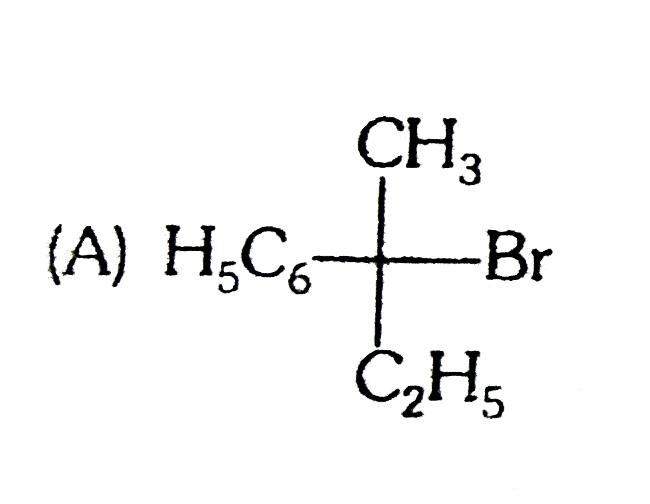A
B
C
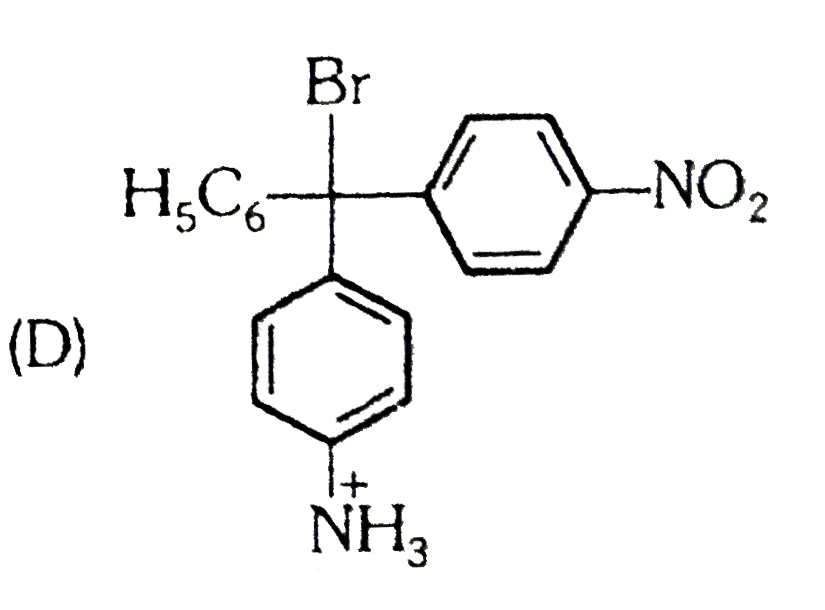
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution reaction is mainly of two types: S...
Text Solution
|
- In S(N^(1)) reaction an optically active substrates mainly gives
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution reaction is mainly of two types: S...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution reaction is mainly of two types: S...
Text Solution
|
- Aliphatic nucleophilic substitution is mainly of two type S(N^(1))" an...
Text Solution
|
- Aliphatic nucleophilic substitution is mainly of two type S(N^(1))" an...
Text Solution
|
- Aliphatic nucleophilic substitution is mainly of two type S(N^(1))" an...
Text Solution
|
- Alkylhalides have polar C-X bond and undergo nucleophilic substitution...
Text Solution
|
- Alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions in which hal...
Text Solution
|