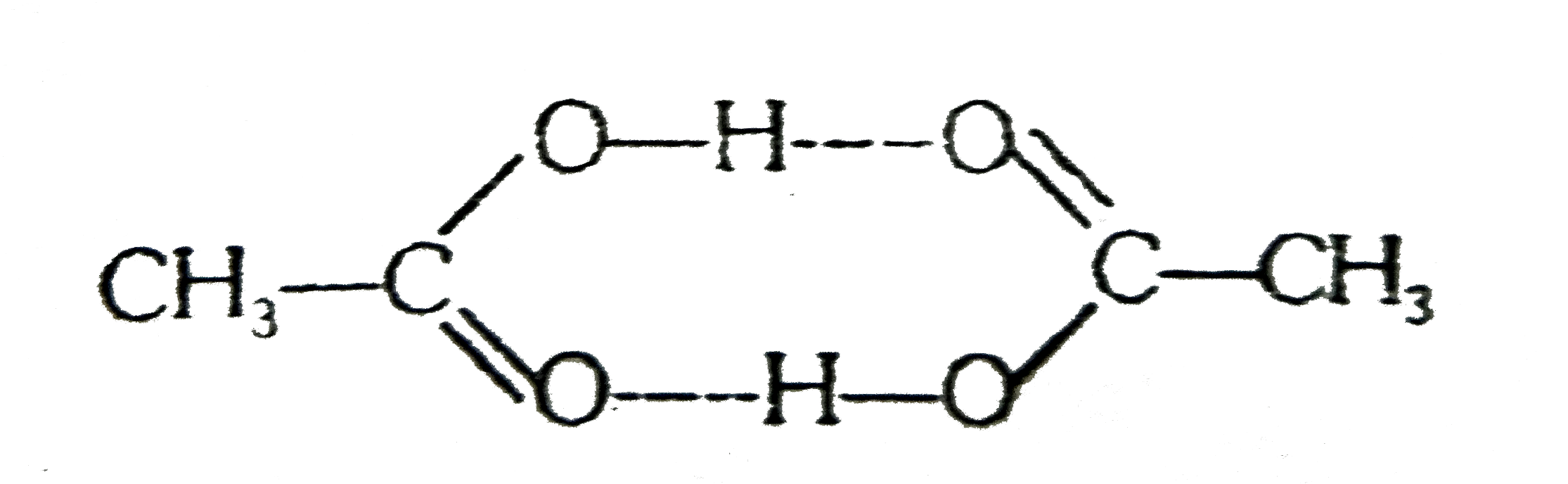
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Determination of the molar mass of acetic acid in benzene using freezi...
Text Solution
|
- From a measurement of the freezing point depression of benzene, the mo...
Text Solution
|
- Determination of the molar mass of acetic acid in benzene using freezi...
Text Solution
|
- Determination of the molar mass of acetic acid in benzene using freezi...
Text Solution
|
- (A) The molecular weight of acetic acid determined by depression in fr...
Text Solution
|
- Define boiling point. Write the formula to determine molar mass of a s...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion. The molecular weight of acetic acid determined by depressio...
Text Solution
|
- Determination of the molar mass of acetic acid in benzene using freezi...
Text Solution
|
- The depression in the freezing point of a benzene solution containing ...
Text Solution
|