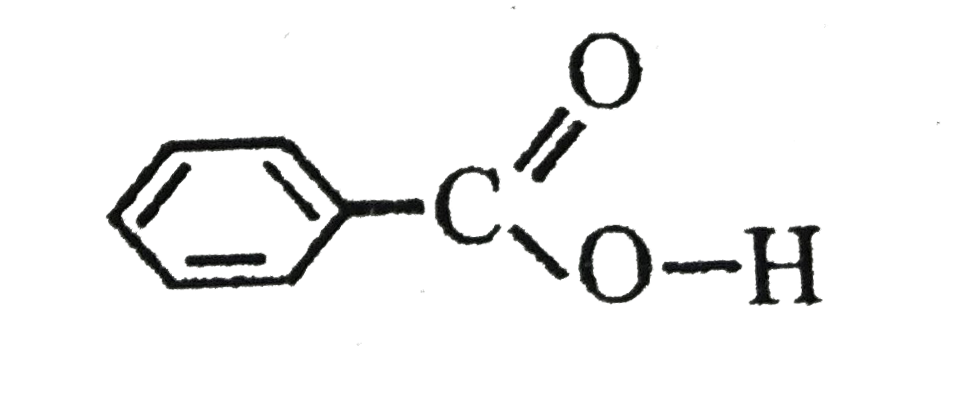
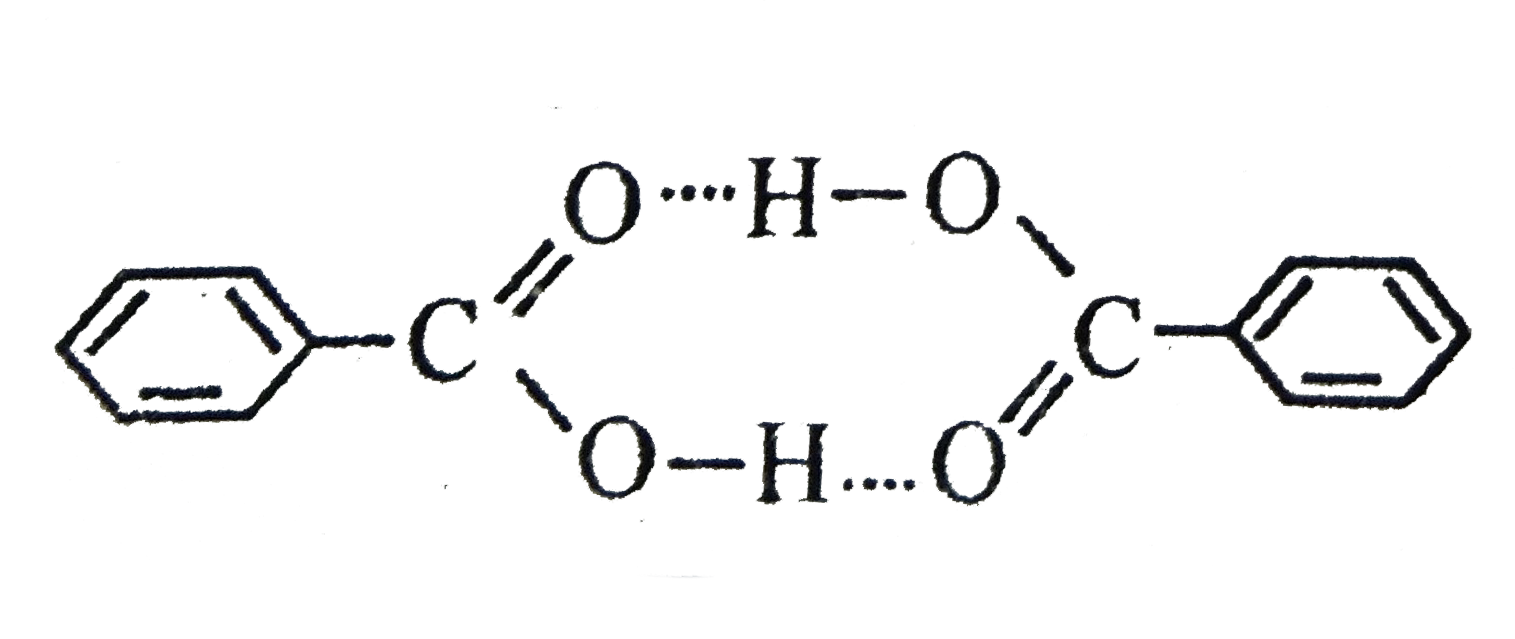
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- 1.22 g of benzoic acid is dissolved in (i) 100g acetone (K(b) for acet...
Text Solution
|
- 12.2 g of benzoic acid is dissolved in (i) 1 kg acetone (K(b) = 1.9 K ...
Text Solution
|
- 12.2 g of benzoic acid (Mw=122) in 100 g benzene has depression in fre...
Text Solution
|
- 1.22 g of benzoic acid is dissolved in acetone and benzene separately....
Text Solution
|
- Benzoic acid dissolved in benzene shows a molecular weight of:
Text Solution
|
- 1.22 g of benzoic acid is dissolved in (i) 100g acetone (K(b) for acet...
Text Solution
|
- 1.22 g of benzoic acid is dissolved in 100 g of acetone and 100 g of a...
Text Solution
|
- Benzoic acid dissolved in benzene shows
Text Solution
|
- 0.3 ग्राम बेन्जोइक अम्ल 20 ग्राम बेंजीन में घुला हुआ है इस व...
Text Solution
|