Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS
ALLEN |Exercise Exercise 4 A (Surface Tension)|5 VideosELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS
ALLEN |Exercise Exercise 4 A (Fluid Statics)|13 VideosELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS
ALLEN |Exercise Exercise 3 (Comprehension based questions)|23 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-V B|19 VideosERROR AND MEASUREMENT
ALLEN |Exercise Part-2(Exercise-2)(B)|22 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -ELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS-Exercise 4 A (Elasticity)
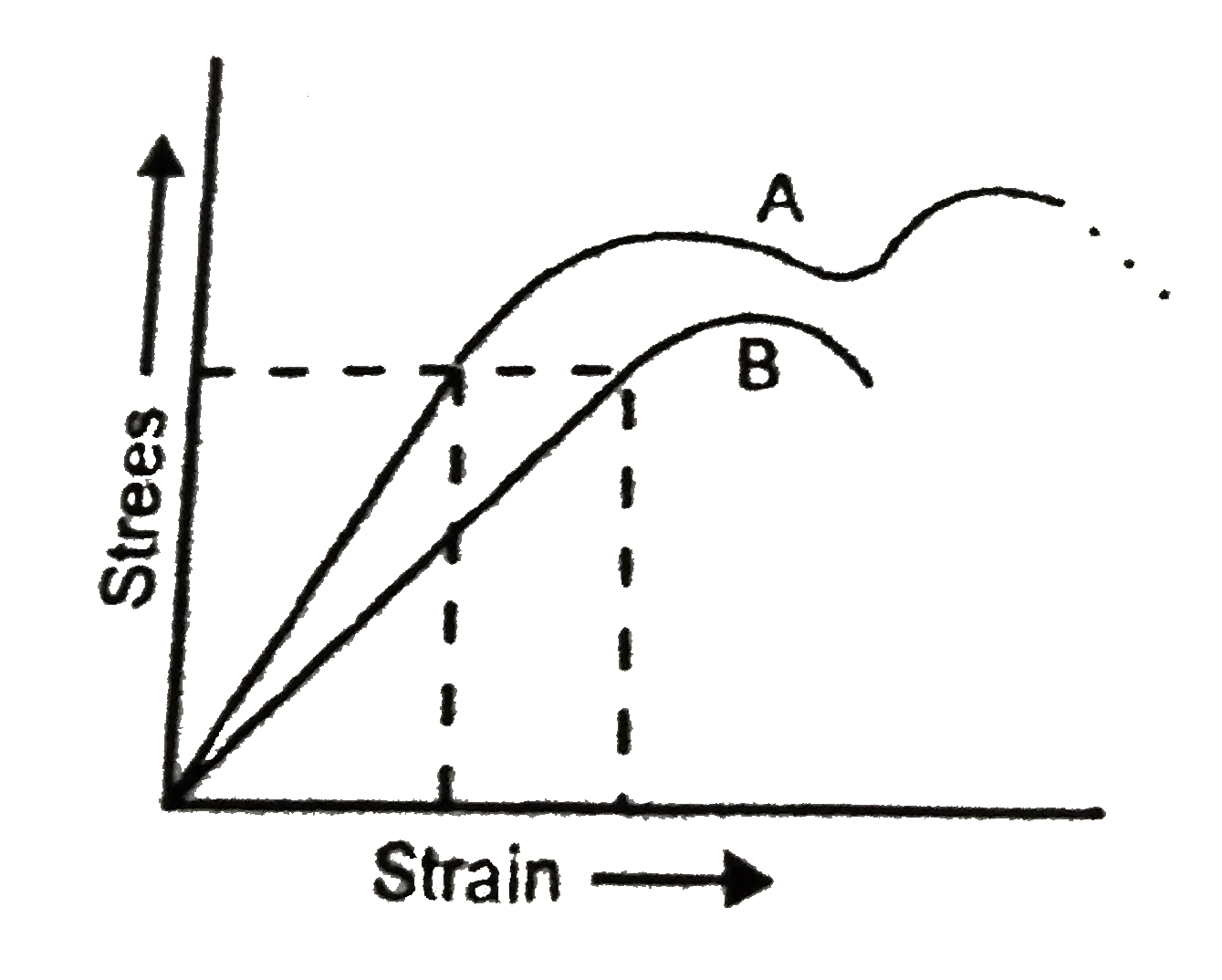
- In the figure shown the straing versus stress graph for two values of...
Text Solution
|
- Two different types of rubber are found to have the stress-strain curv...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum stress that can be applied to the material of a wire used ...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires of diameter 0.25 cm, one made of steel and other made of bra...
Text Solution
|
- A steel rope has length L area of cross-section A young's modulus Y [d...
Text Solution
|
- If a compressive force of 3.0xx10^(4)N is exerted on the end of a 20 c...
Text Solution
|
- A light rod AC of length 2.00 m is suspended from the ceiling horizont...
Text Solution
|