A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -GRAVITATION-EXERCISE 4
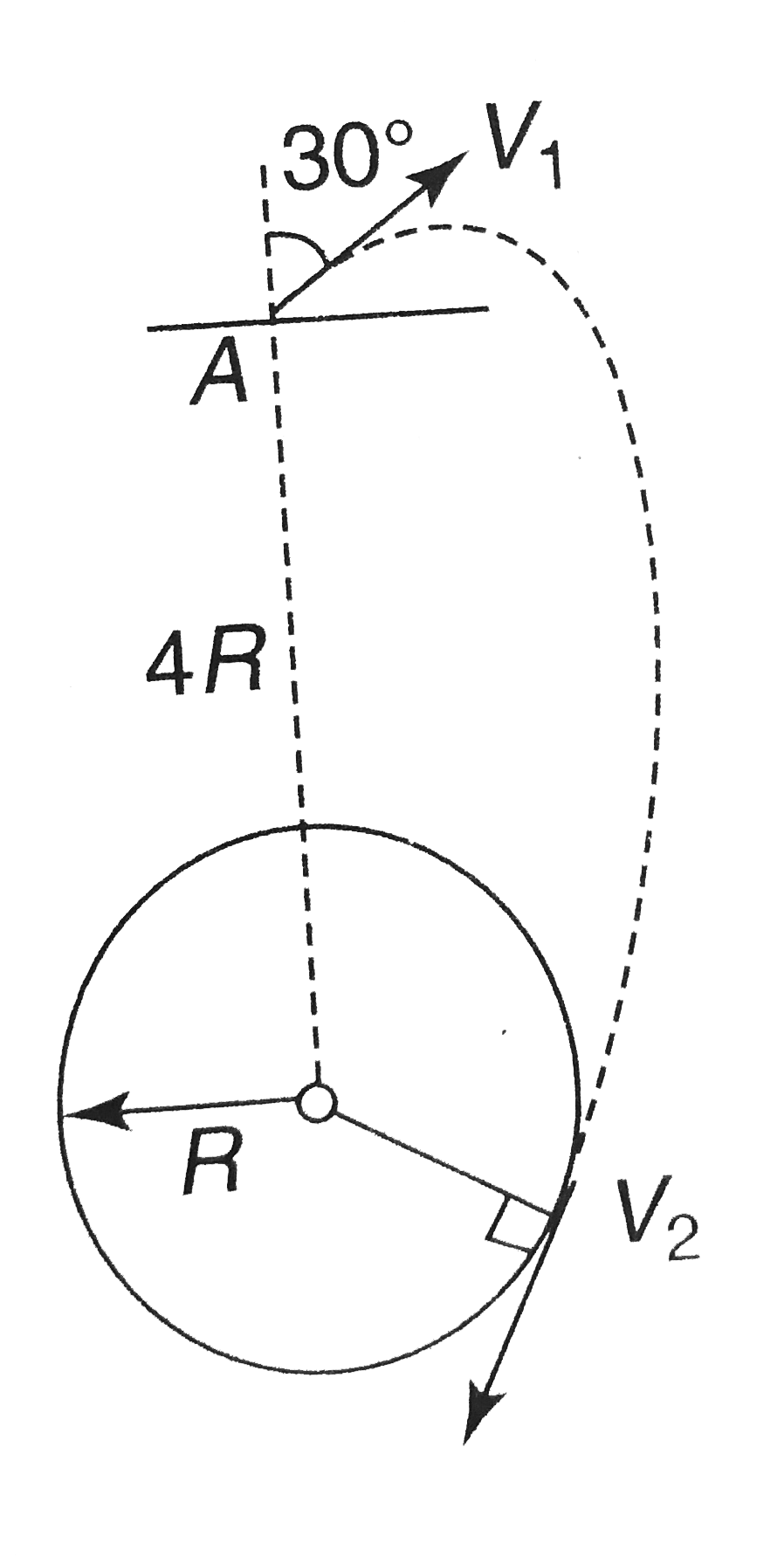
- A particle is projected from point A, that is at a distance 4R form th...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : The difference in the value of acceleration due to gravity...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1: Two satellites A & B are in the same orbit around the ear...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A geostationary satellite rotates in a direction from west...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1: The acceleration of a particle near the earth surface dif...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1: Kepler's law of areas is equivalent to the law of conserv...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : For circular orbits, the law of periods is T^(2) prop r^(3...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : If rotation of earth about its own axis is suddenly stops ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : If the earth stops rotating about its axis, the value of t...
Text Solution
|
- The gravitational potential energy is maximum at :
Text Solution
|