An object is at the top of a smooth sphere which is kept fixed. As object slides down after being given a negligible side push, magnitude of acceleration of object during its motion till it reaches ground.
An object is at the top of a smooth sphere which is kept fixed. As object slides down after being given a negligible side push, magnitude of acceleration of object during its motion till it reaches ground.


A
Increases and then decreaes
B
Decreases then becomes constant
C
Increases and then becomes constant
D
Continously increases.
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
C
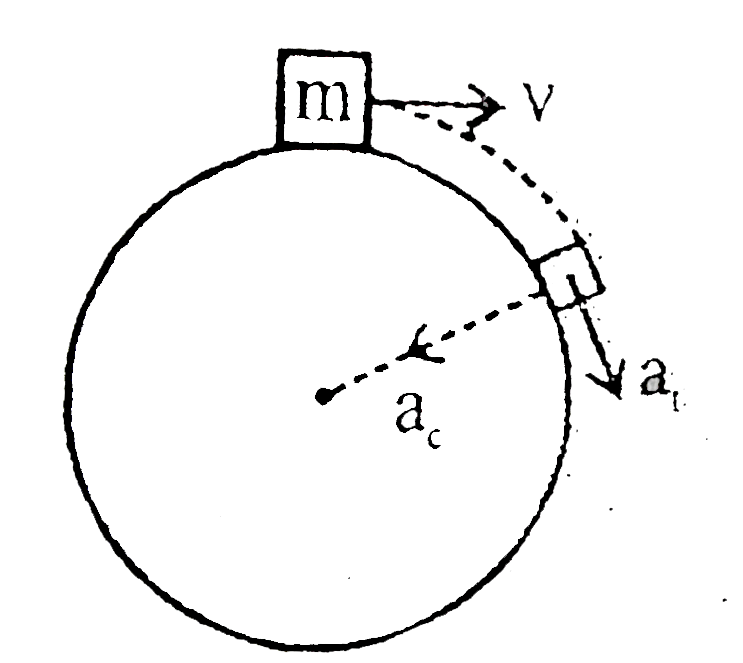
Up to when block have contact with sphere its net `a_("net")=sqrt(a_(t)^(2)+a_(c)^(2))` increases `v uparrow` after that acceleration of block will be only acceleration due to gravity.


Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
During uniform circular motion of object out of (i) magnitude of velocity (ii) magnitude of force (iii) acceleration (iv) momentum vector is not constant.
A stone is tied to an elastic string of negligible mass and spring constant k. The unstretched length of the string is L and has negligible mass. The other end of the string is fixed to a nail at a point P. Initially the stone is at the same level as the point P. The stone is dropped vertically from point P. (a) Find the distance 'y' from the top when the mass comes to rest for an instant, for the first time. (b) What is the maximum velocity attained by the stone in this drop ? (c) What shall be the nature of the motion after the stone has reached its lowest point ?
An object of mass m is released from rest at a height h above the surface of a table. The object slides along the inside of the loop. The loop track consisting of a ramp and a circular loop of radius R shown in the figure. Assume that the track is frictionless. When the object is at the top of the circular track it pushes against the track with a force equal to three times its weight. What height was the object dropped from?
A small particle of mass m is fixed to the perimeter of a ring of same mass and radius r. The system comprising of particle and ring is placed on a horizontal plane. Friction is negligible on horizontal plane. Initially particle is at top most point, then the system is released from rest. Answer next two question when the particle is at the same height as the centre of ring aftr being released from top most point. Assume that the ring stays in vertical plane during its motion under consideration Mark the CORRECT option(s):
A small particle of mass m is fixed to the perimeter of a ring of same mass and radius r. The system comprising of particle and ring is placed on a horizontal plane. Friction is negligible on horizontal plane. Initially particle is at top most point, then the system is released from rest. Answer next two question when the particle is at the same height as the centre of ring aftr being released from top most point. Assume that the ring stays in vertical plane during its motion under consideration Mark the CORRECT option(s):-
A given object takes n times as much time to slide down a 45^(@) rough incline as it takes to slide down a perfectly smooth 45^(@) incline. The coefficeint of kinetic friction between the object and the incline is given by:
An object A is kept fixed at the point x= 3 m and y = 1.25 m on a plank p raised above the ground . At time t = 0 the plank starts moving along the +x direction with an acceleration 1.5 m//s^(2) . At the same instant a stone is projected from the origin with a velocity vec(u) as shown . A stationary person on the ground observes the stone hitting the object during its downward motion at an angle 45(@) to the horizontal . All the motions are in the X -Y plane . Find vec(u) and the time after which the stone hits the object . Take g = 10 m//s
Assertion :- To observe the motion of planets, the sun may be assumed to be an inertial frame. Reason :- For practical purpose a frame of reference may be considered as inertial if it’s acceleration is negligible w.r.t. the acceleration of the object to be observed.