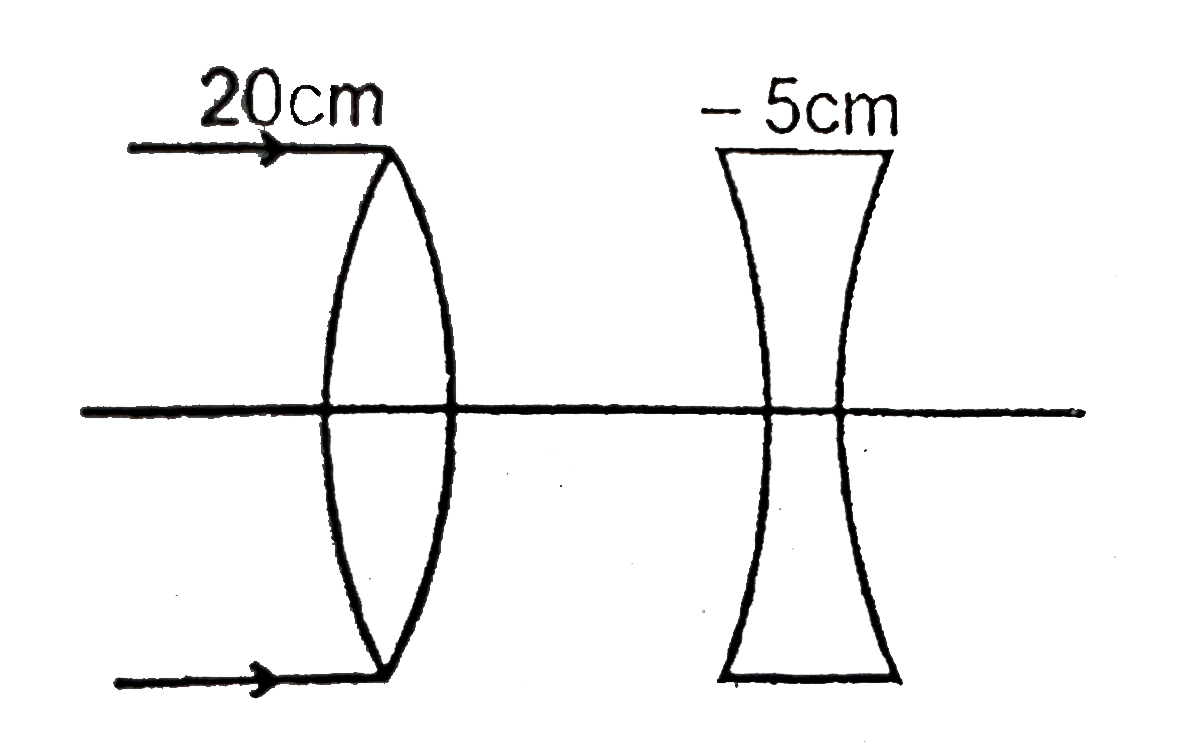A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -TEST PAPERS-PAPER 2
- The dispersive powers of two materials are 0.30 & 0.28. They are used ...
Text Solution
|
- Assume standard notations used for dispersion and deviation is a prism...
Text Solution
|
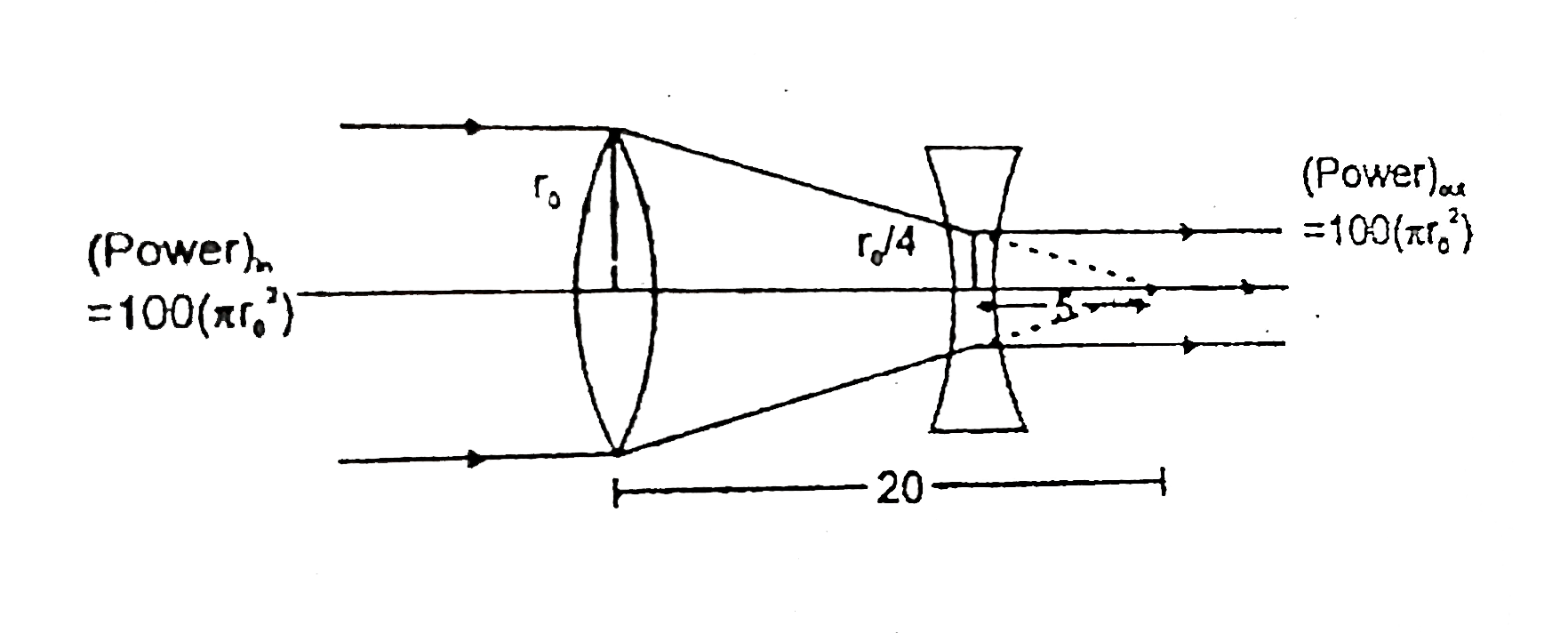
- In the figure shown a converging lens and a diverging lens of focal le...
Text Solution
|
- From the figure shown establish a relation between mu(1),mu(2),mu(3).
Text Solution
|
- Two point objects are placed on principal axis of a thin converging le...
Text Solution
|
- A ray R(1) is incident on the plane surface of the glass slab (kept in...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: A positively charged rod is held near a neutral conducting ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion:A point charge q is placed near an arbitrary shaped solid co...
Text Solution
|
- Assetrion: If a proton and electron are placed in the same uniform ele...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion:- In a given situation of arrangement of charges, an extra c...
Text Solution
|
- STATEMENT 1: The current density vec J at any point in ohmic resistor ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion:- To cells of unequal emf E(1) and E(2) having internal resi...
Text Solution
|
- Statement I : In the circuit in Fig. 7.46, both cells are ideal and of...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion:- Time constants of the cirucits shown in the figure are sam...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion:- If dipole (vecP(1)) is moved along the line normal to the ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion:- Average power consumed in an accircuit is equal to average...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion:- Electric field produced by changing magnetic field is nonc...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) : When tiny circular obstacle is placed in the path of l...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion:- In standard YDSE set up with visible light, the position o...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion:- In glass, red light travels faster than blue light. Reas...
Text Solution
|