Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-I|40 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-II|43 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-IV ASSERTION & REASON|11 VideosELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS
ALLEN |Exercise Exercise 5 B (Integer Type Questions)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -CENTRE OF MASS-EXERCISE-V B
- Spring Gun Recoil A loaded spring gun, initially at rest on a horizo...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of masses m(1) and m(2) in projectile motion have veloci...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 10 kg and 4 kg are connected by a spring of negli...
Text Solution
|
- If components of the momentum of a body along x and y-axis are p(x)=2 ...
Text Solution
|
- Two small particles of equal masses stant moving in opposite directio...
Text Solution
|
- Look at the drawing given in the figure which has been drawn with ink ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is projected from the ground with an initial spee...
Text Solution
|
- A tennis ball dropped on a barizoontal smooth surface , it because bac...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls , having linear momenta vec(p)(1) = p hat(i) and vec(p)(2) =...
Text Solution
|
- STATEMENT-l : In an elastic collision between two bodies, the relative...
Text Solution
|
- Satement-1: if there is no external torque on a body about its centre ...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass M move on a frictionless surface of an inclimed...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass M move on a frictionless surface of an inclimed...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass M move on a frictionless surface of an inclimed...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 2kg and M are at rest on an inclined plane and ar...
Text Solution
|
- A car P is moving with a uniform speed 5sqrt3 m//s towards a carriage ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m, moving in a cicular path of radius R with a cons...
Text Solution
|
- Two point masses m1 and m2 are connected by a spring of natural length...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular plate of mass M and dimension axxb is held in horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- Three objects A , B and C are kept in a straight line on a smooth hori...
Text Solution
|
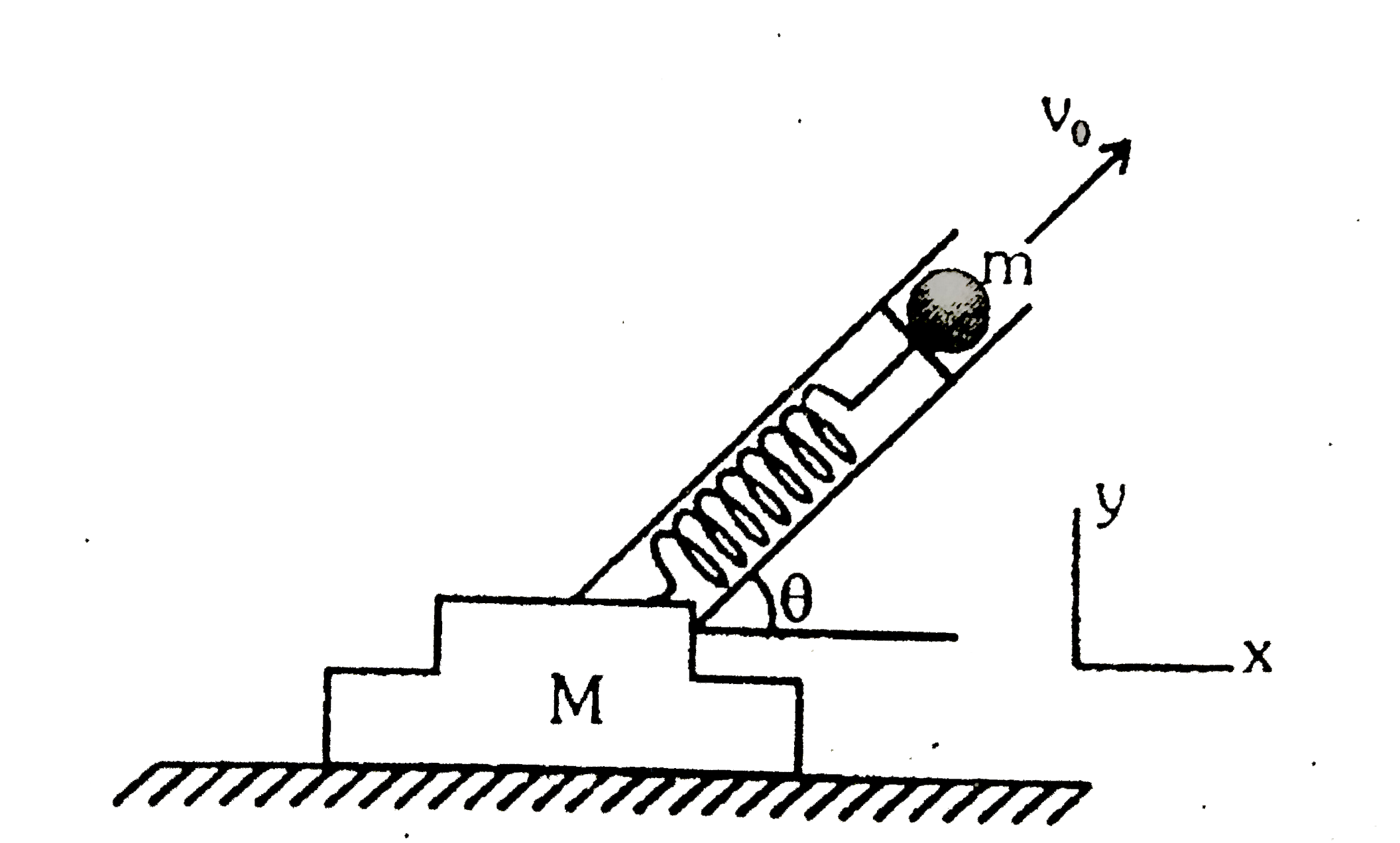
 Let the initial time be prior to firing the gun. Then `P_(x."initial") = 0`, since the system is initially at rest. After the marble has left the muzzle, the gun recoils with some speed `V_(1)`, and its final horizontal momentum is `MV_(1)`, to the left. FInding the final velocity of the marble involves a subtle point, however. Physically, the marble's accelaration is due to the force of the gun, and the gun's recoil is due to the reaction force of the marble. The gun stops accelerating once the marble leaves the barrel, so that at the instant the marble and the gun part company, the gun has its final speed `V_(f)`. At that same instant the speed of the marble relative to the gun is `v_(0)`. Hence, the final horizontal speed of the marble relative to the tablet is `v_(0) cos theta-V_(f)`. By conservation of horizontal momentum, we therefore have
Let the initial time be prior to firing the gun. Then `P_(x."initial") = 0`, since the system is initially at rest. After the marble has left the muzzle, the gun recoils with some speed `V_(1)`, and its final horizontal momentum is `MV_(1)`, to the left. FInding the final velocity of the marble involves a subtle point, however. Physically, the marble's accelaration is due to the force of the gun, and the gun's recoil is due to the reaction force of the marble. The gun stops accelerating once the marble leaves the barrel, so that at the instant the marble and the gun part company, the gun has its final speed `V_(f)`. At that same instant the speed of the marble relative to the gun is `v_(0)`. Hence, the final horizontal speed of the marble relative to the tablet is `v_(0) cos theta-V_(f)`. By conservation of horizontal momentum, we therefore have