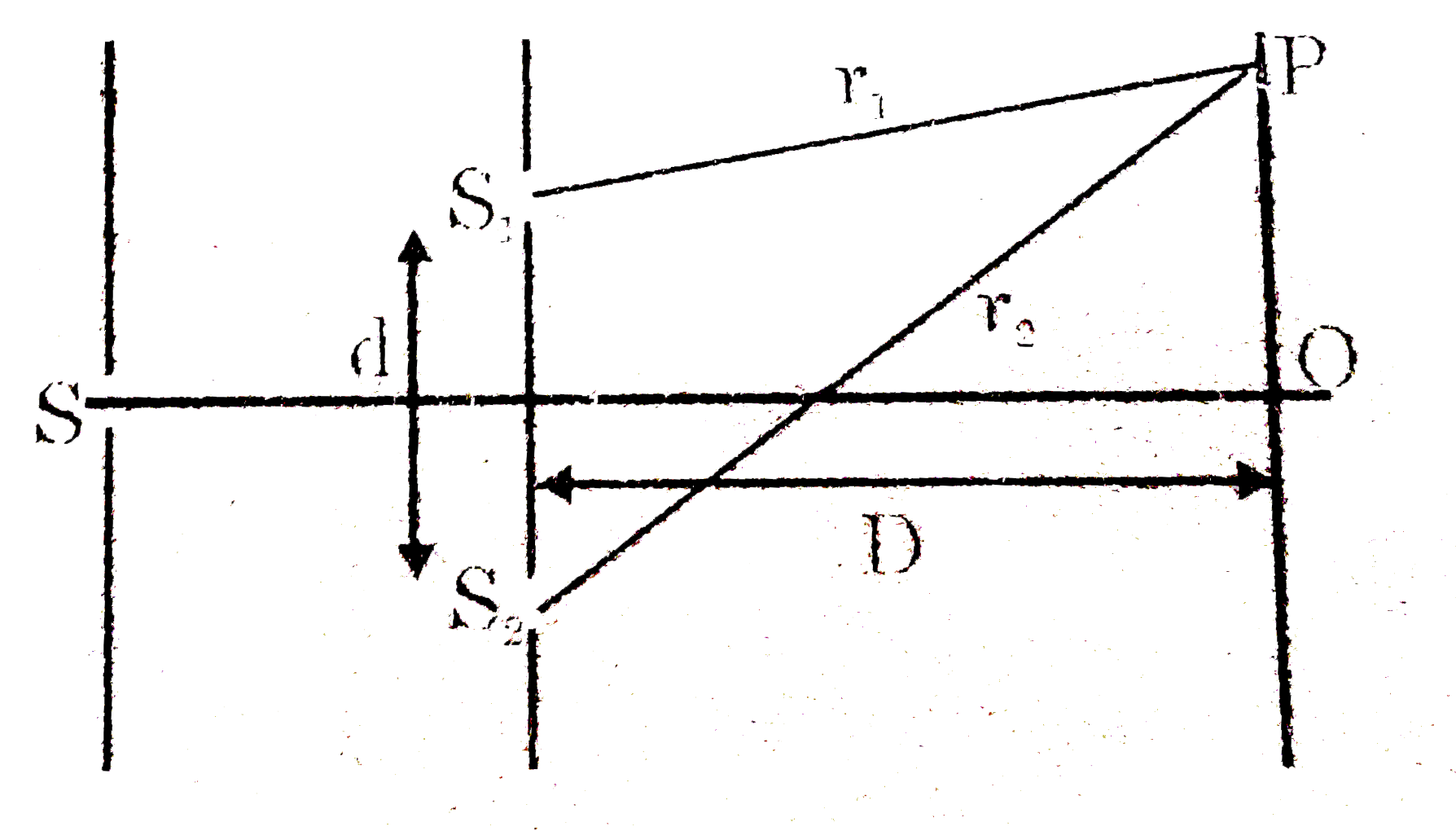
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -TEST PAPERS-Part-1 Physics
- A quantity of 2 mole of helium gas undergoes a thermodynamic process,...
Text Solution
|
- A plane wavefront A(1)B(1) is incident at a boundary A(1)B(2) as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Vessel A contains an ideal gas at a pressure 5xx10^(5) Pa and is conne...
Text Solution
|
- In a vessel, whose volume is 1l, there is a gas, which is a compound o...
Text Solution
|
- Heart leaks into a vessel, containing one mole of an ideal monoatomic ...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactive sample has a half life of 40 seconds. When its activity ...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical coherent sourc e emiting monochromatic light if same wa...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical balloon contains 1 mole of He at T(0). The balloon materia...
Text Solution
|
- Intensity of x-rays coming from an x-ray tube is plotted against wavel...
Text Solution
|
- A small marble of mass m moves in a circular orbit very close to the b...
Text Solution
|
- Two gases have the same initial pressure, volume and temperature. They...
Text Solution
|
- Two hydrogen like atoms A and B having (N)/(Z) ratio equal to 1 have a...
Text Solution
|
- Two hydrogen like atoms A and B having (N)/(Z) ratio equal to 1 have a...
Text Solution
|
- An electromagnetic wave can be represented by E = A sin (kx- omega t +...
Text Solution
|
- An electromagnetic wave can be represented by E = A sin (kx- omega t +...
Text Solution
|