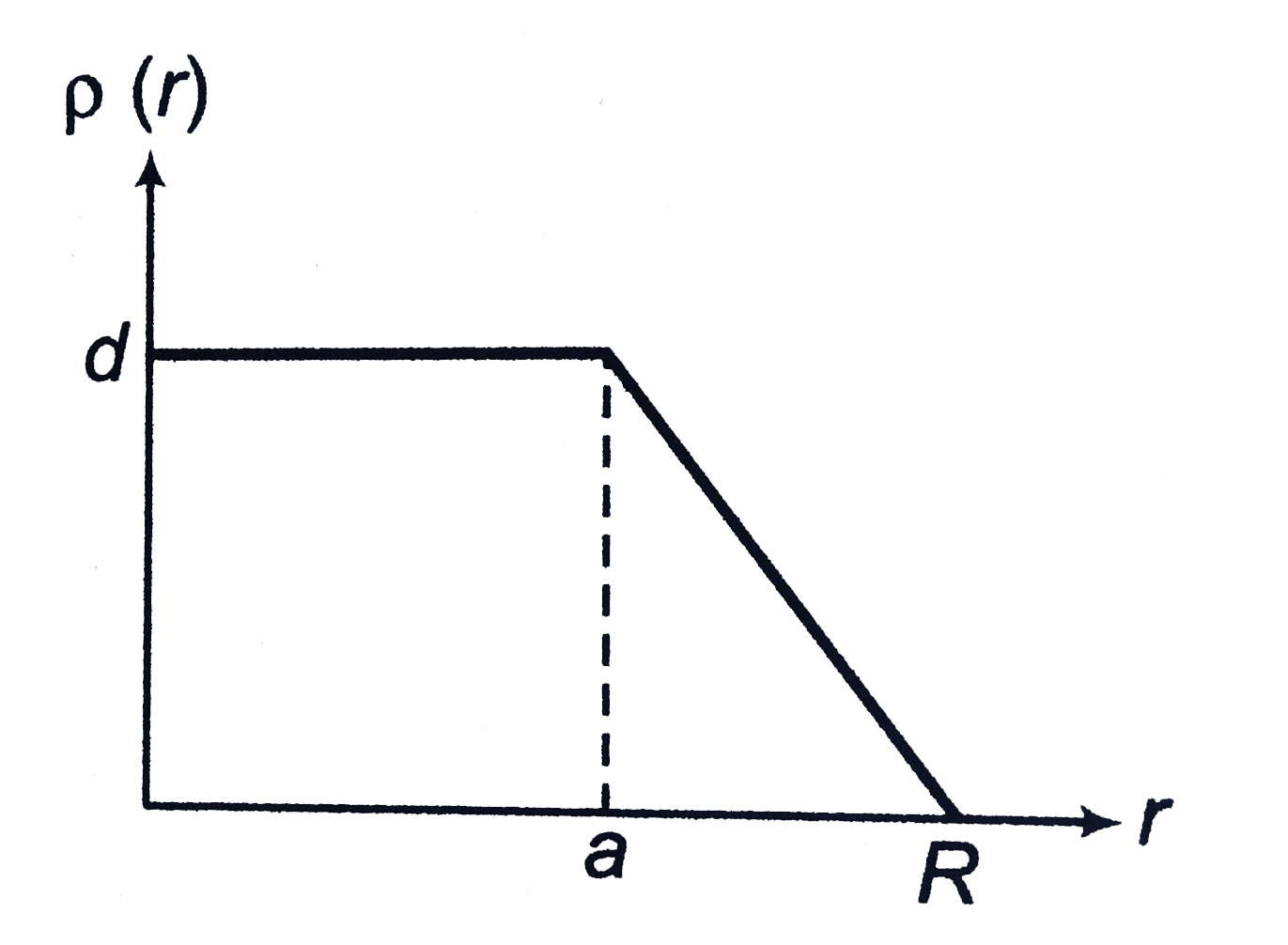
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN |Exercise SUBJECTIVE QUESTION|9 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN |Exercise PHY|68 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN |Exercise MATCH THE COLUME TYPE|1 VideosKINEMATICS (MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE AND MOTION IN A PLANE)
ALLEN |Exercise BEGINNER S BOX-7|8 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD, UNITS AND DIMENSIONS & ERRORS IN MEASUREMENT
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-IV|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems