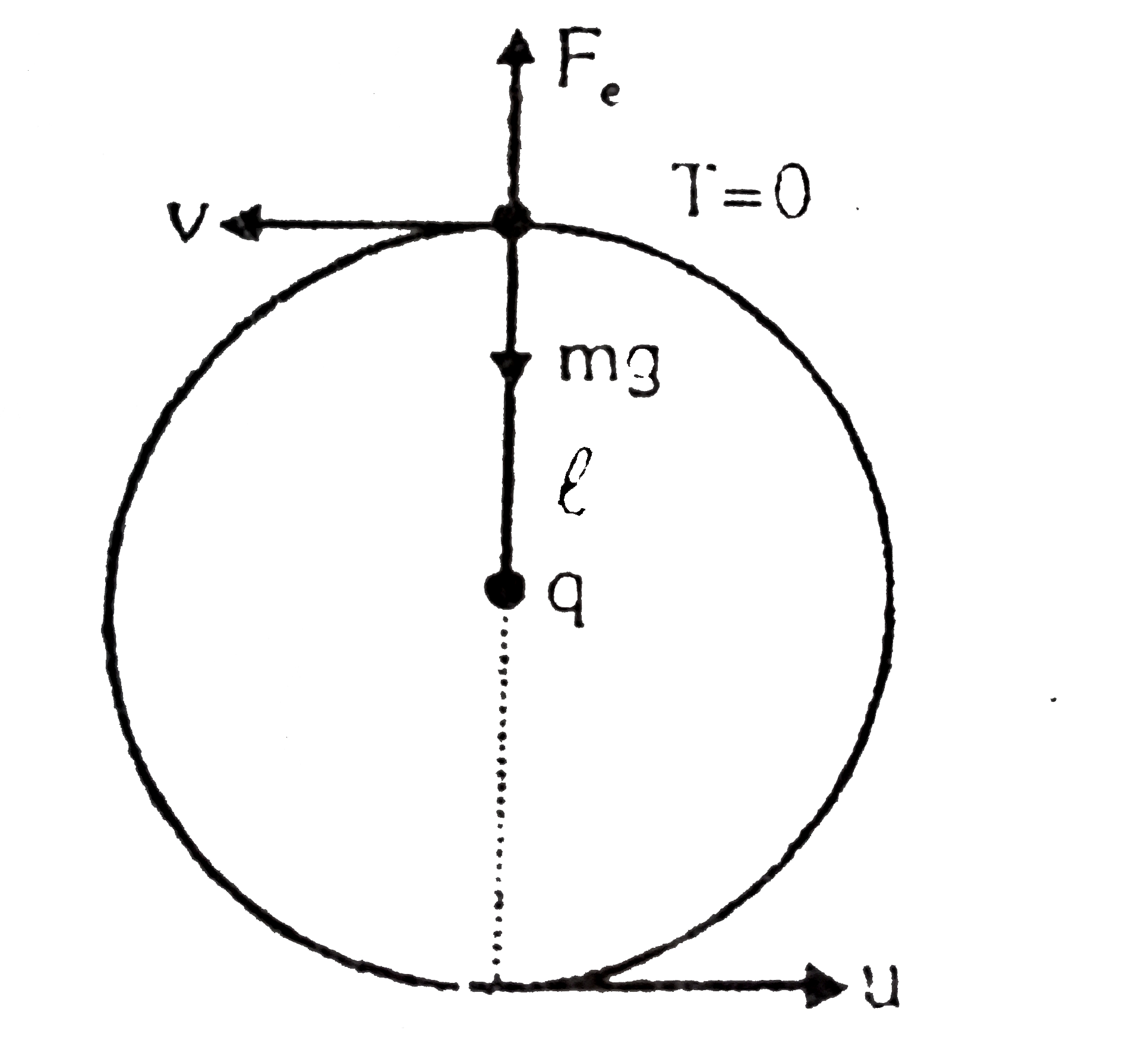
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN |Exercise PHY|68 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-1|121 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN |Exercise LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE|3 VideosKINEMATICS (MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE AND MOTION IN A PLANE)
ALLEN |Exercise BEGINNER S BOX-7|8 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD, UNITS AND DIMENSIONS & ERRORS IN MEASUREMENT
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-IV|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -MISCELLANEOUS-SUBJECTIVE QUESTION
- A conducting sphere S1 of radius r is attached to an insulating handle...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting disc of radius a and uniform positive surface charge ...
Text Solution
|
- Four point charges +8muC,-1muC,-1muC and , +8muC are fixed at the poin...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball if mass 2 xx 10^(-3) Kg having a charges of 1 mu C is su...
Text Solution
|
- Charges +q and -q are located at the corners of a cube of side as show...
Text Solution
|
- A charge +Q is fixed at the origin of the co-ordinate system while a s...
Text Solution
|
- There are two large parallel metallic plates S(1) and S(2) carrying su...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting liquid bubble of radius a and thickness t ( tltlt a) is ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of radius R has a charge Q distributed in its volume wi...
Text Solution
|