A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -TEST PAPER-Exercise (Physics)
- A constant force produces maximum velocity V on the block connected to...
Text Solution
|
- A particle with total energy E moves in one dimensional region where t...
Text Solution
|
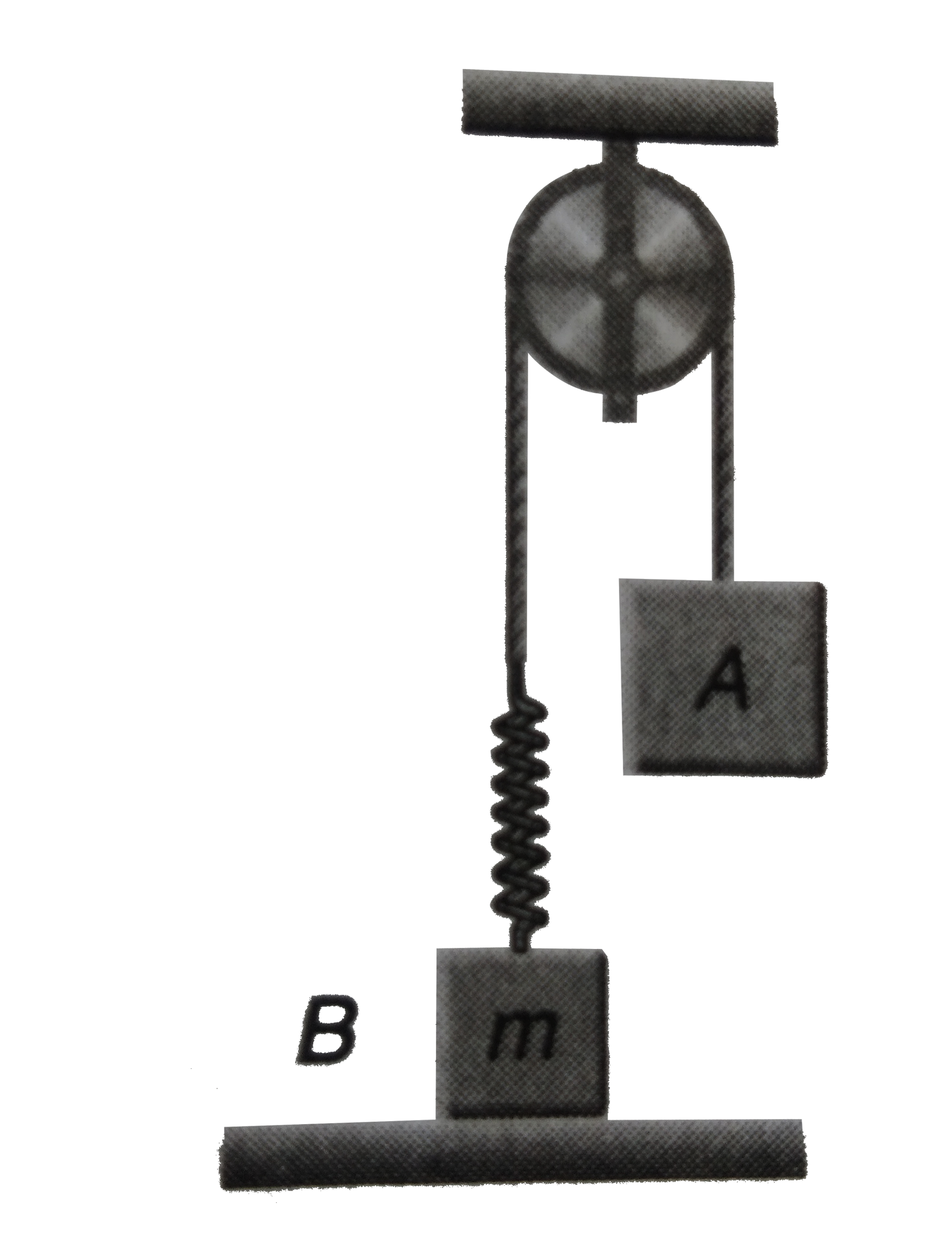
- In the figure, block A is released from rest when the spring is its na...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 2.0 kg, force to travel in the x-direction, is subjecte...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy for a force filed vecF is given by U(x,y)=cos(x+y...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 5kg moving in the X-Y plane has its potential energ...
Text Solution
|
- As a particle moves along the x-axis, it is acted upon by a conservati...
Text Solution
|
- Water is flowing in a river at 2 ms^(-1). The river is 50 m wide and h...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statemente is / are INCORRECT? (a) Mechanical...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following sketch of potential energy for a particle as a ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy of a 1 kg particle free to move along the x- axis...
Text Solution
|
- The figure below shows a graph of potential energy U(x) verses positio...
Text Solution
|
- A force F acting on a body depends on its displacement x as Fpropx^(a)...
Text Solution
|
- If vec(A)=2hat(i)+hat(j)+hat(k) and vec(B)=hat(i)+2hat(j)+2hat(k), fi...
Text Solution
|
- An insect starts from (2,3,4) and travels along (hat(i)+2hat(j)+2hat(k...
Text Solution
|
- For the given vector vec(A)=3hat(i)-4hat(j)+10hat(k), the ratio of mag...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure coefficient of friction between 5kg...
Text Solution
|
- A block is kept at the corner of two walls and force 3N is applied on ...
Text Solution
|
- A plank of mass 2 kg and length 1 m is placed on horizontal floor.A sm...
Text Solution
|
- A block is moving along y-axis with velocity vec(v)(A)=4hat(j) on a pl...
Text Solution
|
 .
.