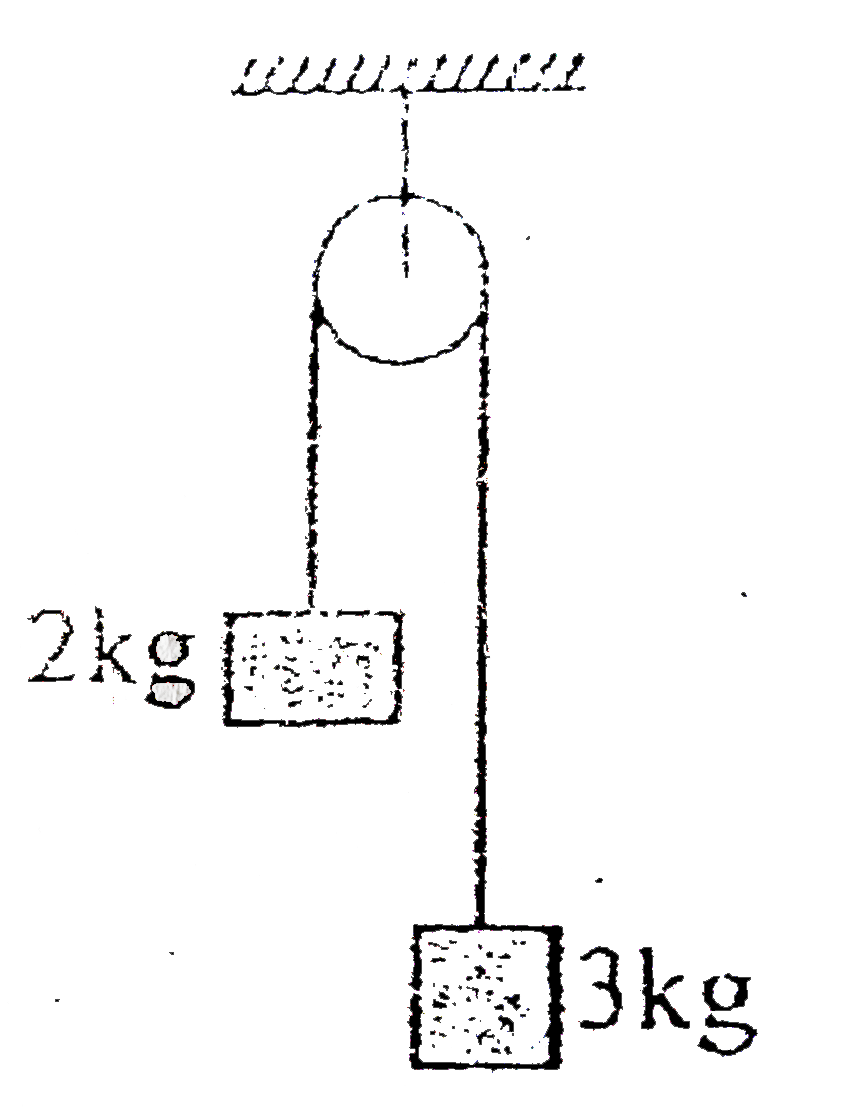A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -TEST PAPER-Exercise (Physics)
- A particle A is projected verically upwards. Another indentical partic...
Text Solution
|
- Track OABCD (as shown is figure) is smooth and fixed in vertical plane...
Text Solution
|
- In the ideal atwood machine arrangement shown, what is the change in k...
Text Solution
|
- A partical of mass 2kg is moving on the x-axis with a constant mechani...
Text Solution
|
- A chain of length L and mass m is placed upon a smooth surface. The le...
Text Solution
|
- Potential energy function along x-axis in a certain force field is giv...
Text Solution
|
- A pigeon in flight experience a force of air resistance given by F=bv^...
Text Solution
|
- A potential energy curve U(x) is shown in the figure. What value must ...
Text Solution
|
- The left end of the spring tied to a wall and at the right end is atta...
Text Solution
|
- A block weighing 40N travels down a smooth fixed curved track AB joine...
Text Solution
|
- Two atoms interact with each other according to the following force F ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy U(x) of a particle moving along x-axis is shown i...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is to move along the x-axis from x=0 to x=x(1) while a cons...
Text Solution
|
- A body with mass 2kg moves in one direction in the presence of a force...
Text Solution
|
- An escalator is used to move 5 people (60kg each) per minute from the ...
Text Solution
|
- A stone is dropped into a quiet lake and waves move in circles at the ...
Text Solution
|
- For conservative force field, vec(F)=-(delU)/(delx)hat(i)-(delU)/(dy)...
Text Solution
|
- Find the value of x(1), so that int(0)^(x(1))ydx=5
Text Solution
|
- A rocket rises vertically up from the surface of earth so that it is d...
Text Solution
|
- Find the rate of change of radius of a sphere when its radius is 4 cm ...
Text Solution
|