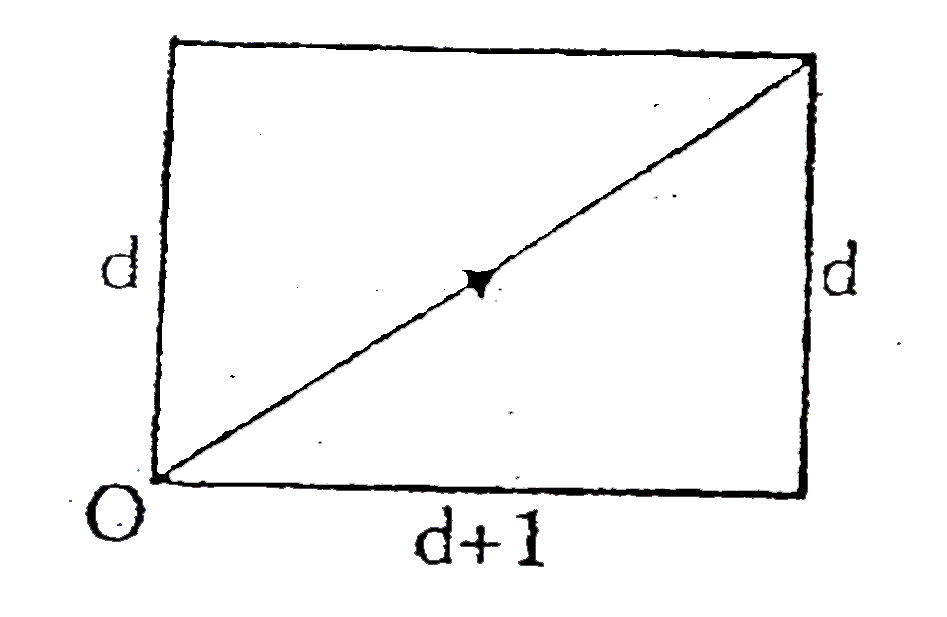
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -TEST PAPER-Exercise (Physics)
- If momentum (P), area (A) and time (T) are taken to be fundamental qun...
Text Solution
|
- In ancient time, deffernt system of units was following in which unit ...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular farm house has a 1km difference between its sides. Two f...
Text Solution
|
- The graph shown the variation with times t of the velocity v of an obj...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is released from point A. During its motion ball takes two seco...
Text Solution
|
- Velocity v//s Position graph of a particle performing curvilinear moti...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B each of weight 20N are placed on a fricti...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an At wood machine in which m(1)+m(2)=M is constant. Now ...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in the figure, Tarzan travels from one place to another by sw...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal rods joined at one end are kept on a smooth surface as shown...
Text Solution
|
- A three part rocket begins intact as a single object in distant outer ...
Text Solution
|
- A three part rocket begins intact as a single object in distant outer ...
Text Solution
|
- Five uniform circular plates, each of diameter b and mass m are laid o...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, the L-shaped shaded piece is cut from a metal plate of ...
Text Solution
|
- The centre of mass of a non uniform rod of length L whoose mass per un...
Text Solution
|
- Find the center of mass(x,y,z) of the following structure of four iden...
Text Solution
|
- A thick uniform wire is bent into the shape of the letter "U" as shown...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure four rods AB,BC,CD and DA have mass m, 2m, 3m and ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniformly thick plate in the shape of an arrow head has dimensions a...
Text Solution
|
- An object comprises of a uniform ring of radius R and its uniform chor...
Text Solution
|