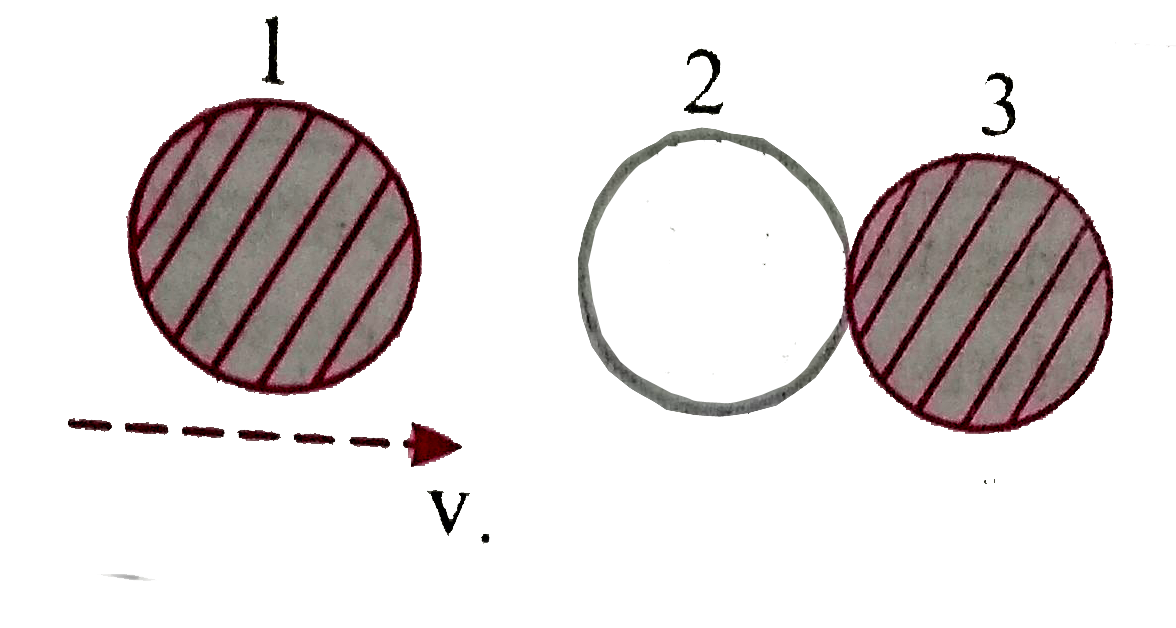
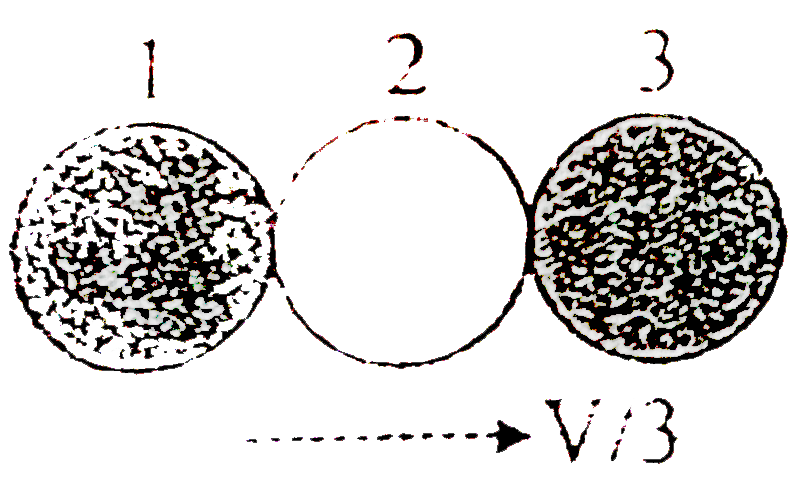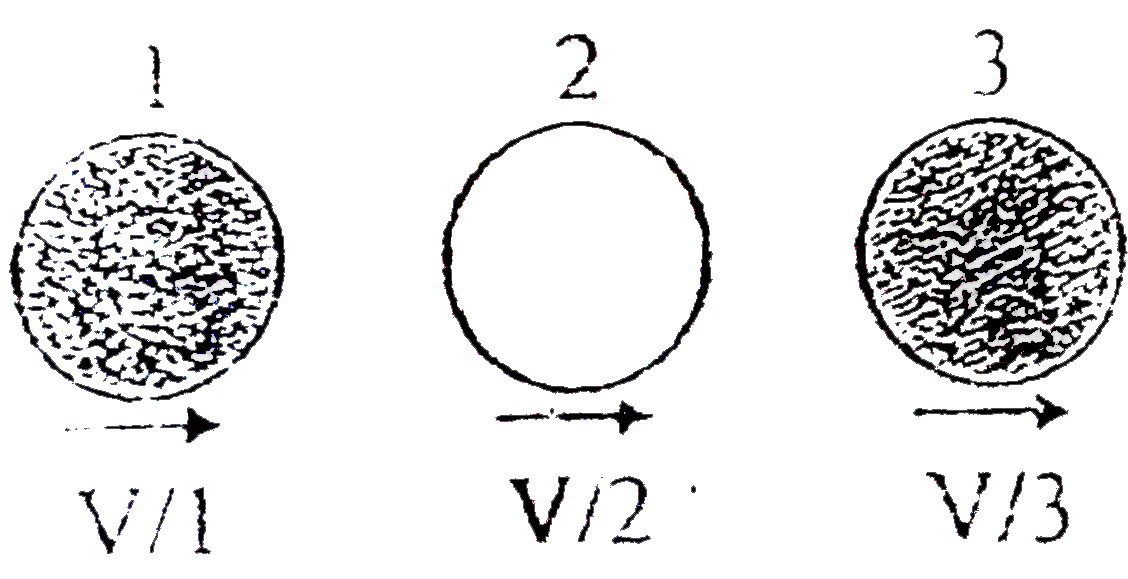A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -TEST PAPER-Exercise (Physics)
- A particle of mass 4 m which is at rest explodes into masses m, m & 2m...
Text Solution
|
- Two girls of equal mass m jump off from the border line of a stationar...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on ...
Text Solution
|
- Three different projectiles, each with the same mass, are fired with s...
Text Solution
|
- Three bodies are moving as shown below. The total kinetic energy of th...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles are projected at the same instant with speeds v(1) and v...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of equal masses moving with same collide perfectly inela...
Text Solution
|
- The linear density of a non-uniform rod of length 2m is given by lamda...
Text Solution
|
- If the volume of a sphere increases at constant rate ((dv)/(dt)=4). I...
Text Solution
|
- Potential Energy U(x) and associated force F(x) bears the relation F(x...
Text Solution
|
- Electric current in a wire is time rate of flow of charge. The charge ...
Text Solution
|
- A metal rod extends on the x-axis from x=0m to x=4m. Its linear densit...
Text Solution
|
- An airplane takes off at an angle 30^(@) with the horizontal ground tr...
Text Solution
|
- If vectors vec(A)=(hat(i)+2hat(j)+3hat(k))m and vec(B)=(hat(i)-hat(j)...
Text Solution
|
- Position of a particle moving along straight line is given by x(t)=(A)...
Text Solution
|
- Acceleration time graph of a particle moving along a straight line is ...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth sphere each of radius 5cm and weight W rest one on the othe...
Text Solution
|
- The position of a particle moving along x-axis varies with time t acco...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is moving with constant speed in a vertical circl...
Text Solution
|
- The relation between time t and distance x of a particle is given by t...
Text Solution
|