A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -TEST PAPER-Exercise (Physics)
- A thin uniform rod AB of mass 1 kg moves translationally with accelera...
Text Solution
|
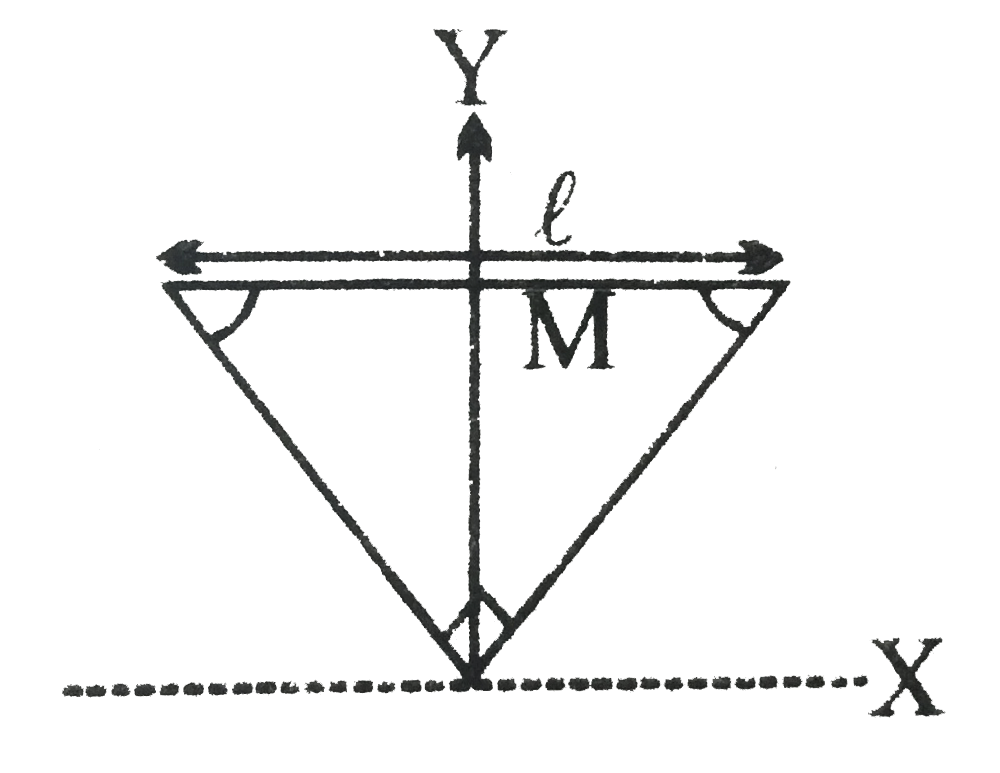
- The figure shows an isosceles triangle plate of mass M and base L. T...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows an isosceles triangle plate of mass M and base L. T...
Text Solution
|
- A pulley is connected to the ceiling of an elevator by a massless rod....
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the variation of the moment of inertia of a uniform rod, ...
Text Solution
|
- Four rigid bodies, each with the same mass and radius, are spinning fr...
Text Solution
|
- Particles of masses m,2m,3m,…….nm grams are placed on the same line at...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of the radius R is confined to roll without slipping at A and B...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder C and a hollow pipe P of same diameter are in contact...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m collides horizontally with a stationary wedge on a ro...
Text Solution
|
- Shown in the figure is a system of three particles of mass 1 kg, 2 kg ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m moving with velocity v makes head-on elastic coll...
Text Solution
|
- which of the following forces can never, under any circumstances, does...
Text Solution
|
- A body (intially at rest is falling under gravity. When it loses a gra...
Text Solution
|
- Position time graph of a particle of mass 2 kg is shown in figrure. To...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m lies on a horizontal frictionless surface and is att...
Text Solution
|
- Block A of mass 1 kg is placed on the rough surface of block B of mass...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a light spring of natural length 4m and spring constant 170...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 1 kg moves in a circular path of radius 1 m such th...
Text Solution
|
- Infinite rods of uniform mass density and length L,L/2,L/4….. Are plac...
Text Solution
|