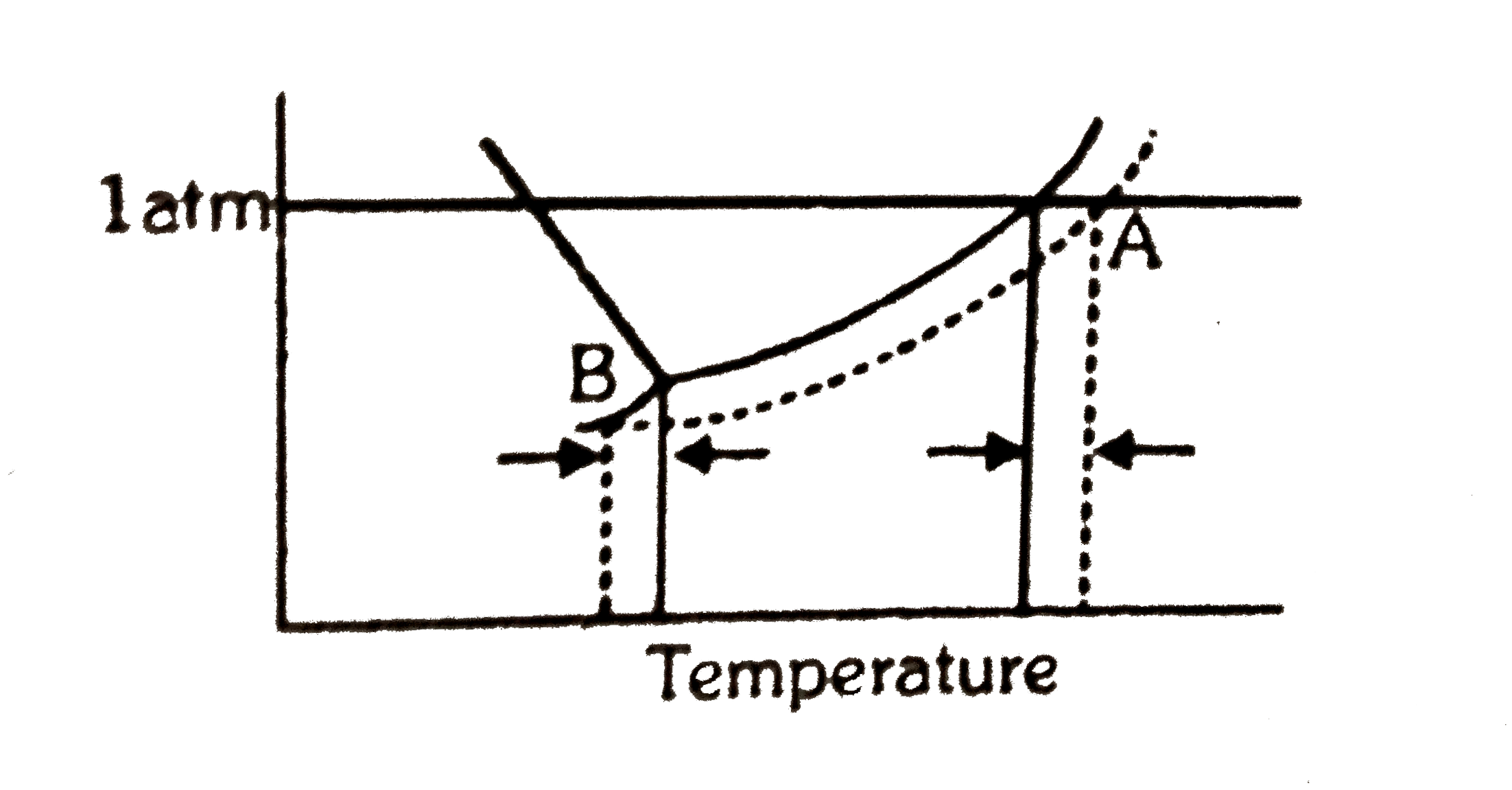
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent A is 0.80 atm when a non vo...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent A is 0.80 atm. When a non-v...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent 0.50 atm. When a non-volati...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent A is 0.80atm.When a non vol...
Text Solution
|
- If P^(@) the vapour pressure of a pure solvent and P is the vapour pre...
Text Solution
|
- At room temperature the mole fraction of a solution is 0.25 and the va...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of a pure liquid is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile ...
Text Solution
|
- A non-volatile solute (A) is dissolved in a volatile solvent (B). The ...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of pure liquid A is 0.80 atm. On mixing a non-vola...
Text Solution
|