A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-EXERCISE-2
- A ray of light of refractive index 1.4approaches the boundary surface ...
Text Solution
|
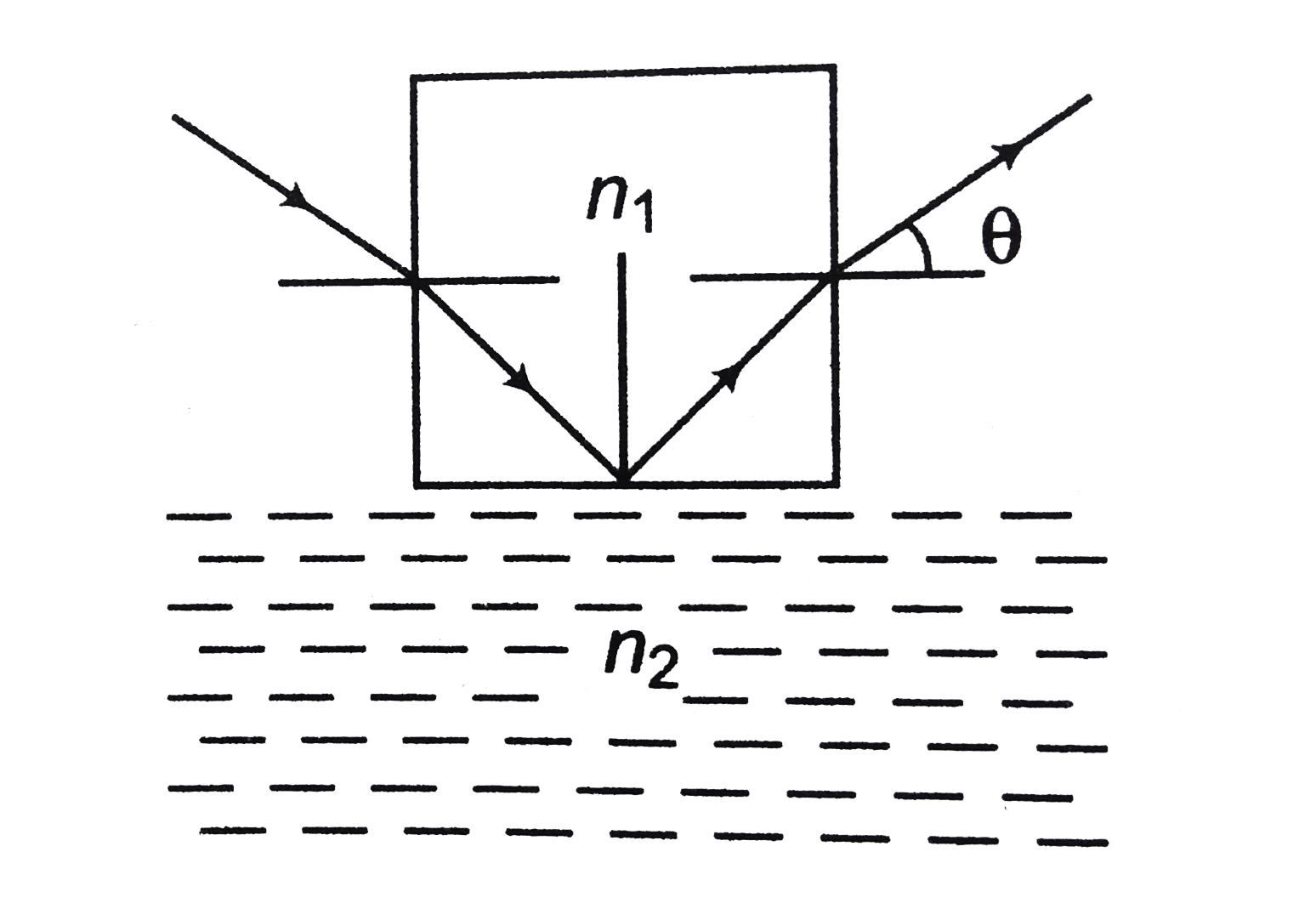
- A ray of light strikes a cubical slab surrounded by air as shown in th...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical block of glass of refractive index n1 is in contact with the...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of diameter 'd' is incident on a glass hemisphere. If the radiu...
Text Solution
|
- When the object is at distance u(1)andu(2)the images formed by the sa...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray hits the pole of a thin biconvex lens as shown in fig. The...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light passes through a prism in a principle plane the deviati...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram shows five isosceles right angled prisms.A light ray incid...
Text Solution
|
- A certain prism is found to produce a minimum of38^(@).It produces a d...
Text Solution
|
- A ray incident at an angle 53^(@) on a prism emerges at an angle 37^(@...
Text Solution
|
- A man of height 170cmwants to see his complete image in a plane mirror...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane mirrors at an angle such that a ray incident on a mirror und...
Text Solution
|
- If the equation of mirror is given by y= 2//pi "sin"pix (y gt 0 , 0 le...
Text Solution
|
- In the fig. shown consider the first reflection at the plane mirror an...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a ray incident a angle i=pi//3 of the plot drawn show...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident normally on one face of 30^(@) - 60^(@) - 9...
Text Solution
|
- A curved surface of radius R separates two medium of refractive indice...
Text Solution
|
- A curved surface of radius R separates two medium of refractive indice...
Text Solution
|
- A curved surface of radius R separates two medium of refractive indice...
Text Solution
|
- An object O is kept infront of a converging lens of focal length 30 cm...
Text Solution
|
_E01_063_S01.png)