A rod OA rotates about a horizontal axis through O with a constant anti-clockwise velocity `omega=3 rad//s.` As it pases the positions `theta=0^(@)` a small block of mass m is placed on it at a radial distacne r=450 mm If the block is observed to slip at `theta=50^(@)` the coefficient of static friction bewteen the block and the rod is (Given that ,`sin50^(@)=0766,cos 50^(@)=0.64`)
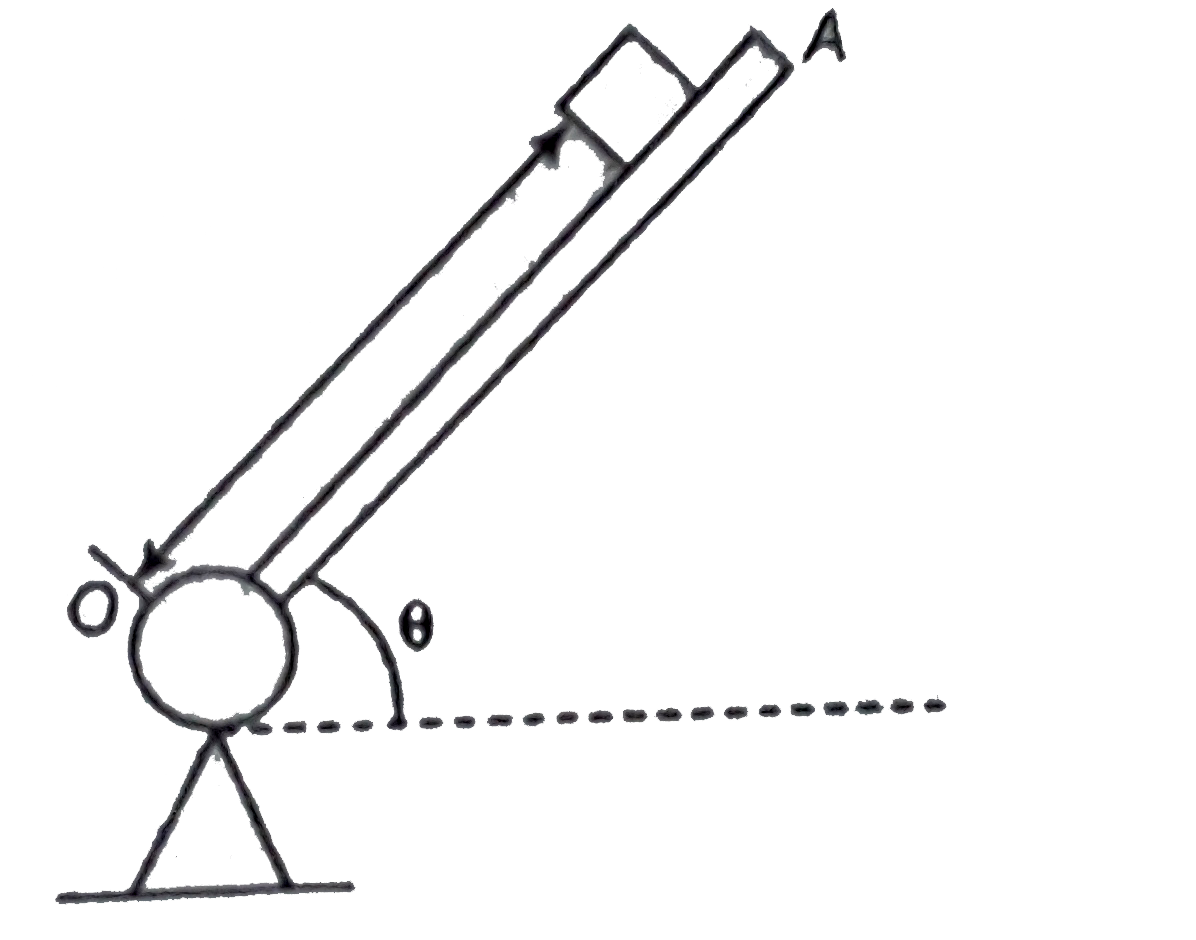
A rod OA rotates about a horizontal axis through O with a constant anti-clockwise velocity `omega=3 rad//s.` As it pases the positions `theta=0^(@)` a small block of mass m is placed on it at a radial distacne r=450 mm If the block is observed to slip at `theta=50^(@)` the coefficient of static friction bewteen the block and the rod is (Given that ,`sin50^(@)=0766,cos 50^(@)=0.64`)


Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
`mu = (3)/(16)`
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A disc of radius R=2m starts rotating wth constant angular acceleration alpha=(2rad//s^(2)) . A block of mass m=2kg is kept at a distance (R)/(2) from the centre of disc. The coeffiecient of friction between disc and block is mu_(s)=0.4,mu_(k)=0.3 . Acceleration of block when it just slips w.r.t. ground and w.r.t. disc are respectively - ( g=10ms^(-2) )
A block of mass m1 = 1 kg another mass m2 = 2 kg, are placed together (see figure) on an inclined plane with angle of inclination theta . Various values of theta are given in List I. The coefficient of friction between the block m_(1) and the plane is always zero. The coefficient of static and dynamic friction between the block m_(2) and the plane are equal to mu = 0.3 . In List II expressions for the friction on block m_(2) are given. Match the correct expression of the friction in List II with the angles given in List I, and choose the correct option. The acceleration due to gravity is denoted by g [Useful information : tan (5.5^(@)) ~~ 0.1, tan (11.5^(@)) ~~ 0.2 , tan (16.5^(@))~~ 0.3 ].
Two blocks of mass m_(1)=10kg and m_(2)=5kg connected to each other by a massless inextensible string of length 0.3m are placed along a diameter of the turntable. The coefficient of friction between the table and m_(1) is 0.5 while there is no friction between m_(2) and the table. the table is rotating with an angular velocity of 10rad//s . about a vertical axis passing through its center O . the masses are placed along the diameter of the table on either side of the center O such that the mass m_(1) is at a distance of 0.124m from O . the masses are observed to be at a rest with respect to an observed on the tuntable (g=9.8m//s^(2)) . (a) Calculate the friction on m_(1) (b) What should be the minimum angular speed of the turntable so that the masses will slip from this position? (c ) How should the masses be placed with the string remaining taut so that there is no friction on m_(1) .
A frame of reference that is accelerated with respect to an inertial frame of reference is called a non-inertial frame of reference. A coordinate system fixed on a circular disc rotating about a fixed axis with a constant angular velocity omega is an example of non=inertial frame of reference. The relationship between the force vecF_(rot) experienced by a particle of mass m moving on the rotating disc and the force vecF_(in) experienced by the particle in an inertial frame of reference is vecF_(rot)=vecF_(i n)+2m(vecv_(rot)xxvec omega)+m(vec omegaxx vec r)xxvec omega . where vecv_(rot) is the velocity of the particle in the rotating frame of reference and vecr is the position vector of the particle with respect to the centre of the disc. Now consider a smooth slot along a diameter fo a disc of radius R rotating counter-clockwise with a constant angular speed omega about its vertical axis through its center. We assign a coordinate system with the origin at the center of the disc, the x-axis along the slot, the y-axis perpendicular to the slot and the z-axis along the rotation axis (vecomega=omegahatk) . A small block of mass m is gently placed in the slot at vecr(R//2)hati at t=0 and is constrained to move only along the slot. The distance r of the block at time is
A frame of reference that is accelerated with respect to an inertial frame of reference is called a non-inertial frame of reference. A coordinate system fixed on a circular disc rotating about a fixed axis with a constant angular velocity omega is an example of non=inertial frame of reference. The relationship between the force vecF_(rot) experienced by a particle of mass m moving on the rotating disc and the force vecF_(in) experienced by the particle in an inertial frame of reference is vecF_(rot)=vecF_(i n)+2m(vecv_(rot)xxvec omega)+m(vec omegaxx vec r)xxvec omega . where vecv_(rot) is the velocity of the particle in the rotating frame of reference and vecr is the position vector of the particle with respect to the centre of the disc. Now consider a smooth slot along a diameter fo a disc of radius R rotating counter-clockwise with a constant angular speed omega about its vertical axis through its center. We assign a coordinate system with the origin at the center of the disc, the x-axis along the slot, the y-axis perpendicular to the slot and the z-axis along the rotation axis (vecomega=omegahatk) . A small block of mass m is gently placed in the slot at vecr(R//2)hati at t=0 and is constrained to move only along the slot. The distance r of the block at time is
A bullet of mass 50g moving with velocity 600m//s hits block of mass 1.0kg placed on a rough horizontal ground and comes out of the block with a velocity of 400m//s . The coefficient of friction between the block and the ground is 0.25 . Neglect loss of mass of the block as the bullet pierces through it. (a) In spite of the fact that friction acts a an external force, can you apply principle of conservation of momentum during interaction of the ullet with the block? (b) Find velocity of the block immediately after the bullet pierces through it. (c)FInd the distance the block will travel before it stops.
On a circular turn, table rotating about its center horizontally with uniform angular velocity rad/s placed two blocks of mass 1kg and 2kg, on a diameter symmetrically about center. Their separation is 1m and friction is sufficient to avoid slipping. The spring between them as shown is stretched and applied force of SN. lf f_(1) and f_(2) are values of friction on 1 kg & 2kg block respectively:-
A thin uniform metallic rod of length 0.5 m and radius 0.1 m rotates with an angular velocity 400rad/s is a horizontal plane about a vertical axis passing through one of its ends. Calculate (a) tenstion in the rod and (b) the elogation of te rod. The density of material of the rod is 10^(4)kg//m^(3) and the young's modulus is 2xx10^(11)N//m^(2)
A block of mass m = 20 kg is kept is a distance R = 1m from central axis of rotation of a round turn table (A table whose surface can rotate about central axis). Table starts from rest and rotates with constant angular acceleration, alpha = 3 rad//sec^(2) . The friction coefficient between block and table is mu = 0.5 . At time t = (x)/(30) from starting of motion (i.e. t =0) the block is just about to slip. Find the value of x (g = 10 m//s^(2))
A block with mass (M) is connected by a massless spring with stiffness constant (k) to a rigid wall and moves without friction on a horizontal surface. The block oscillates with small amplitude A about an equilibrium position (x_0). Consider two cases : (i) when the block is at (x_0) , and (ii) when the block is at x = x_0 + A . In both the cases, a particle with mass m(lt M) is softly placed on the block after which they strick to each other. Which of the following statement (s) is (are) true about the motion after the mass (m) is placed on the mass (M) ?
ALLEN -CIRCULAR MOTION-EXERCISE(S-2)
- A stone is launched upward at 45^(@) with speed v(0). A bee follow the...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving along a circular path ofradius R in such a way th...
Text Solution
|
- A rod OA rotates about a horizontal axis through O with a constant ant...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of mass m(1)=10kg and m(2)=5kg connected to each other by a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle 'P' is moving on a circular path under the action of only o...
Text Solution
|
- A thin circular wire of radius R rotatites about its vertical diameter...
Text Solution
|