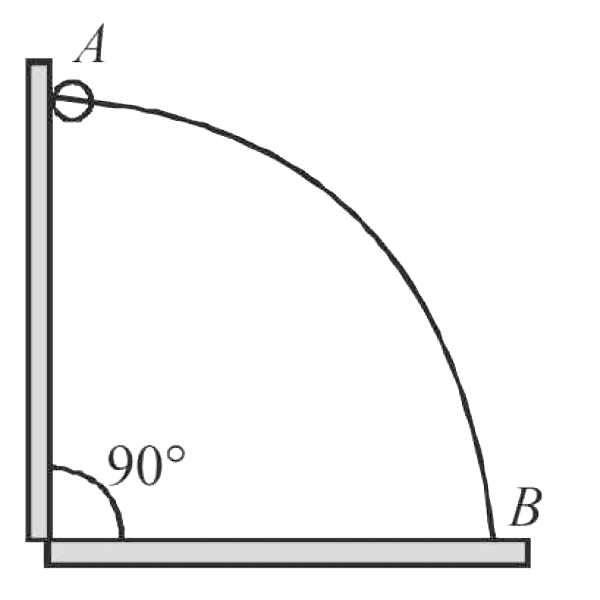
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -CIRCULAR MOTION-EXERCISE (J-A)
- A ball of mass (m) 0.5 kg is attached to the end of a string having le...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a disc rotating in the horizontal plane with a constant angul...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical discs of same radius R are rotating about their axes in ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire, which passes through the hole in a small bead, is bent in the ...
Text Solution
|
- A frame of reference that is accelerated with respect to an inertial f...
Text Solution
|
- A frame of reference that is accelerated with respect to an inertial f...
Text Solution
|