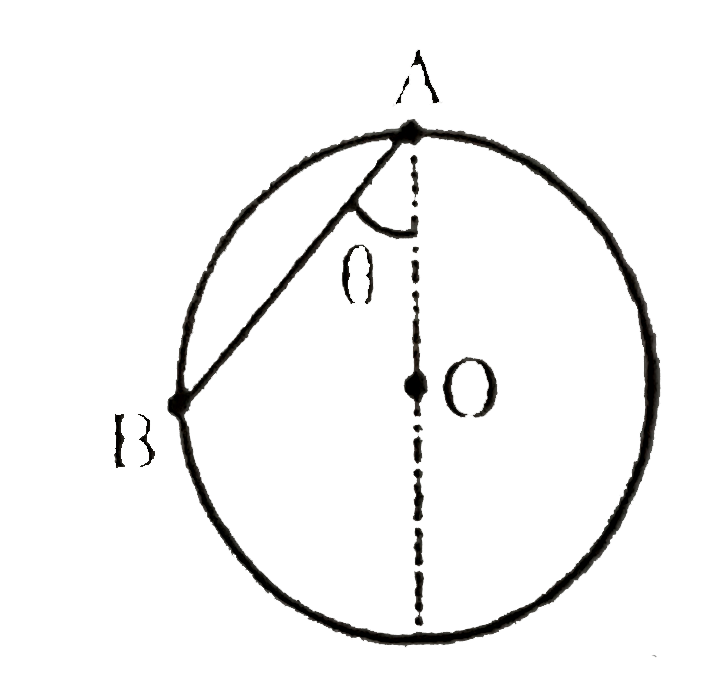
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -MOTION IN A PALNE-EXERCISE-2
- A disc in which serval grooves are cut along the chord drawn from a po...
Text Solution
|
- A body is slipping from an inclined plane of height h and length l . I...
Text Solution
|
- A bead is free to slide down a smooth wire tightly stretched between p...
Text Solution
|
- Three boys A,B and C are situated at the vertices of an equilateral tr...
Text Solution
|
- A particle start from rest and move with constant acceleration. Than v...
Text Solution
|
- In the graph shown in fig. the time is plotted along x-axis. Which qua...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is projected with velocity v making an angle of 4...
Text Solution
|
- In case of a projectile fired at an angle equally inclined to the hori...
Text Solution
|
- A cannon of mass 5m (including a shell of mass m) is at rest on a smoo...
Text Solution
|
- The range of a projectile when fired at 75^(@) with the horizontal is ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected with a velocity u making an angle theta with t...
Text Solution
|
- The speed at the maximum height of a projectile is sqrt(3)/(2) times o...
Text Solution
|
- What is the ratio of P.E. w.r.t. ground and K.E. at the top most point...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is thrown at an angle theta with the horizontal and the range i...
Text Solution
|
- A student is able to throw a ball vertically to maximum height of 40m....
Text Solution
|
- Three projectile A, B and C are thrwon from the same point in the same...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile is thrown with an initial velocity of (a hati +b hatj) ms...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of a projectile is y=sqrt(3)x-(gx^(2))/(2) the angle of...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of projectile is y=16x-(x^(2))/(4) the horizontal range i...
Text Solution
|
- If a projectile is fired at an angle theta with the vertical with velo...
Text Solution
|