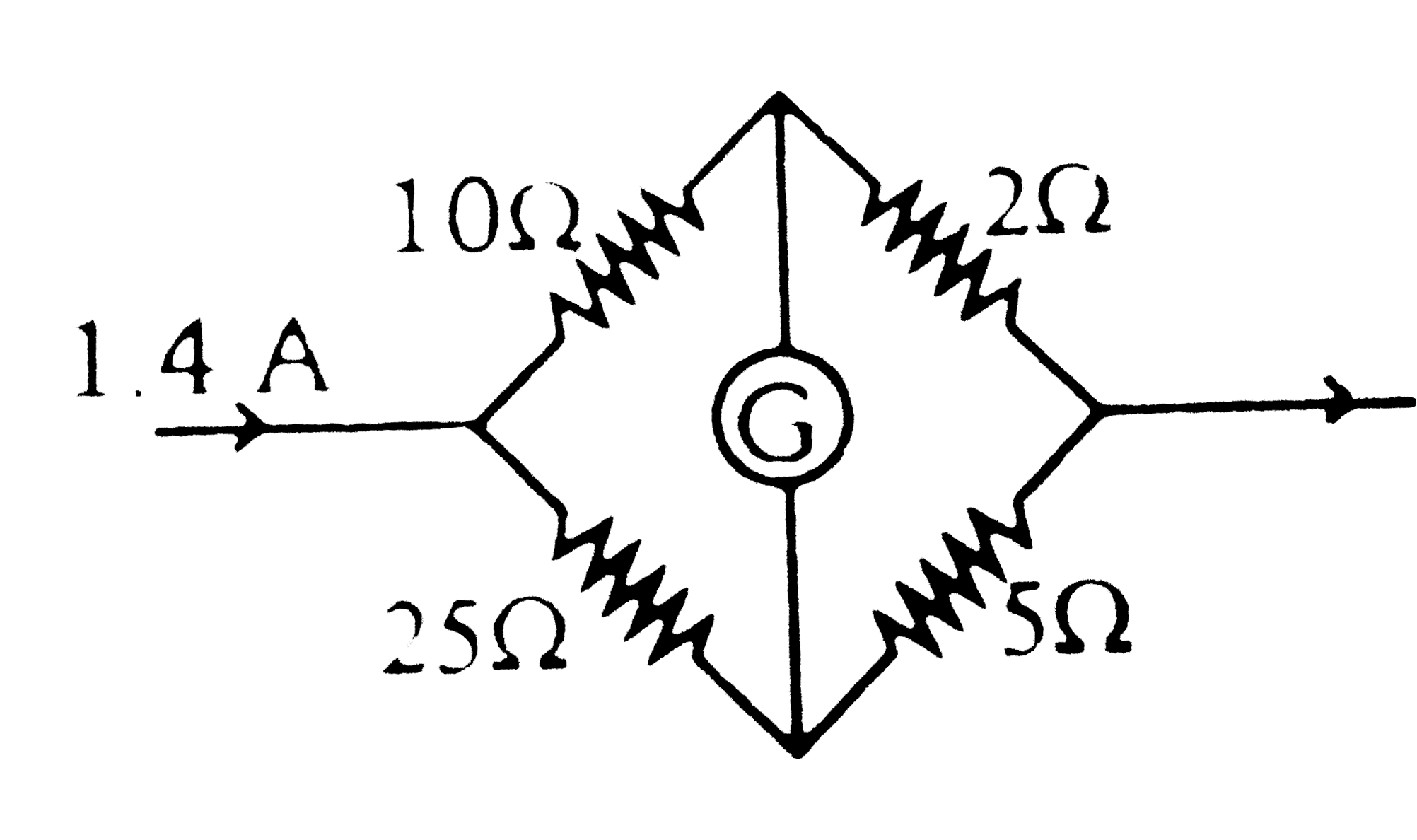
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Calculate the current flows through resistance 2Omega.
Text Solution
|
- A current of 1 A is passed through two resistances 1Omega and 2Omega c...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown figure, bridge is balanced, the current flowing through 2...
Text Solution
|
- Resistance of a Galvanometer coil is 8Omega and 2Omega Shunt resistanc...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, current through the resistance2Omega isi1 an...
Text Solution
|
- एक गैल्वेनोमीटर का 8 Omega प्रतिरोध है। इसमें 2Omega का शंट प्रतिरोध ...
Text Solution
|
- A cell supplies a current of 0.9 A through a 1 Omega resistor and a cu...
Text Solution
|
- 1A current is passed through a parallel combination of 8Omega resistan...
Text Solution
|
- 1 ampere current flows in the circuit shown in Fig. If each 4Omega In ...
Text Solution
|