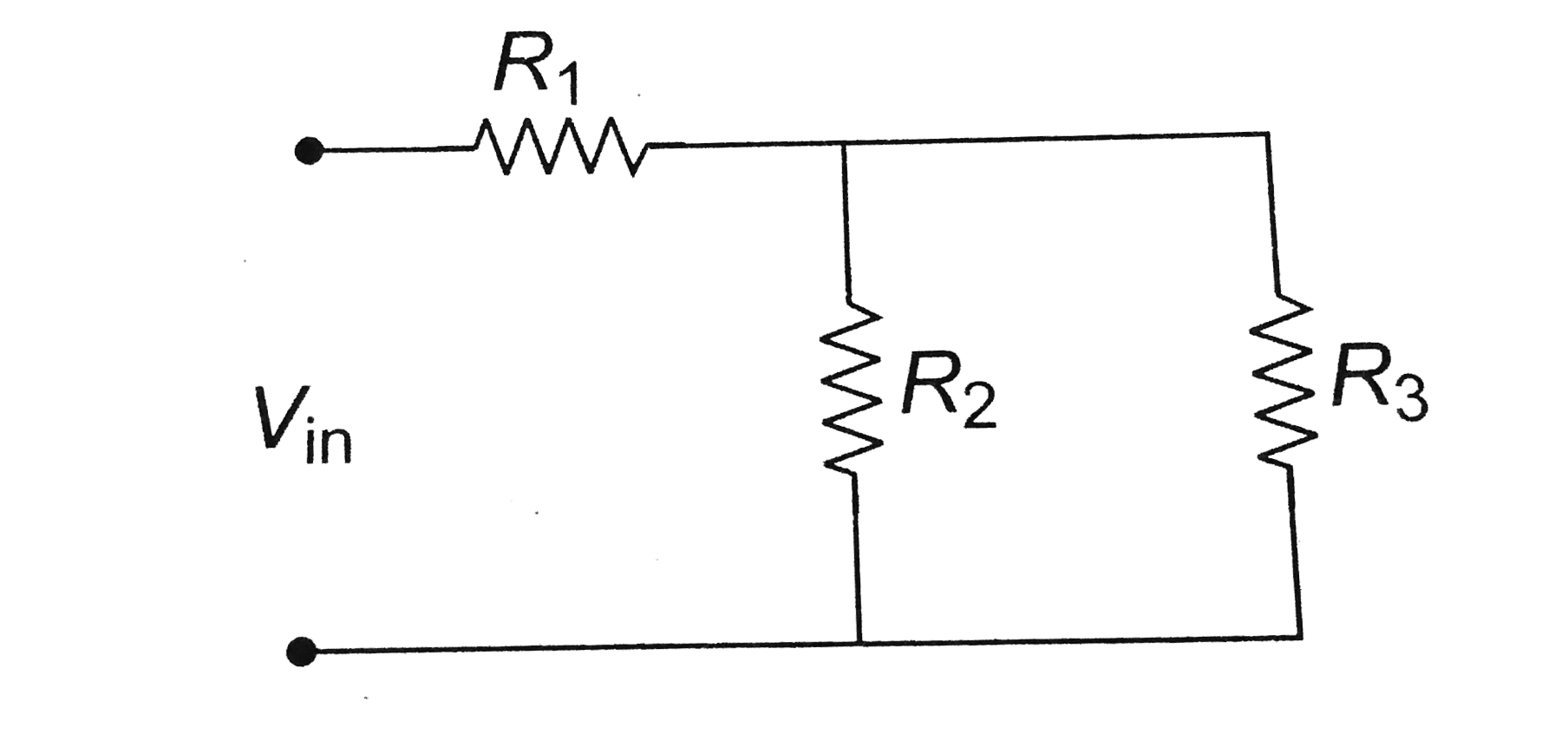
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- For ensuring dissipation of same energy in all three resistors (R(1), ...
Text Solution
|
- A resistor R(1) dissipates the power P when connected to a certain gen...
Text Solution
|
- For ensuring dissipation of same energy in all three resistors (R(1), ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows three resistor configurations R(1),R(2) and R(3) connecte...
Text Solution
|
- A resistor R(1) dissipates the power P when connected to a certain gen...
Text Solution
|
- For ensuring disspation of same energy in all three resistors (R1, R2,...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical resistors R(1) = R(2) = R(3) are connected as shown to...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र II.65 में दिखाए अनुसार जोड़े जाए सभी तीनों प्रतिरोधकों ( R(1)...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र में दिखाये गये सभी तीनों प्रतिरोधकों (R(1),R(2),R(3)) में समान ऊ...
Text Solution
|