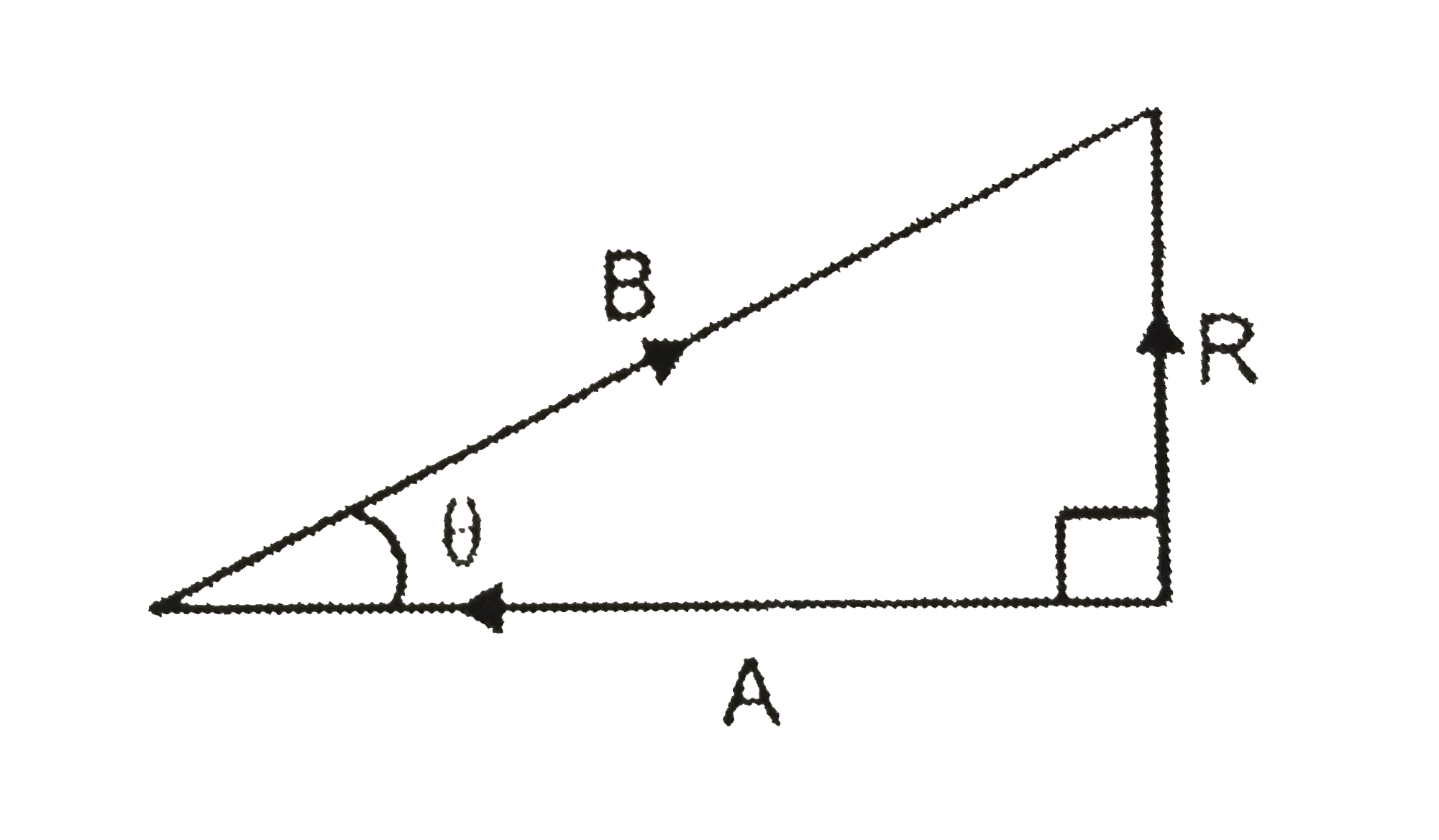
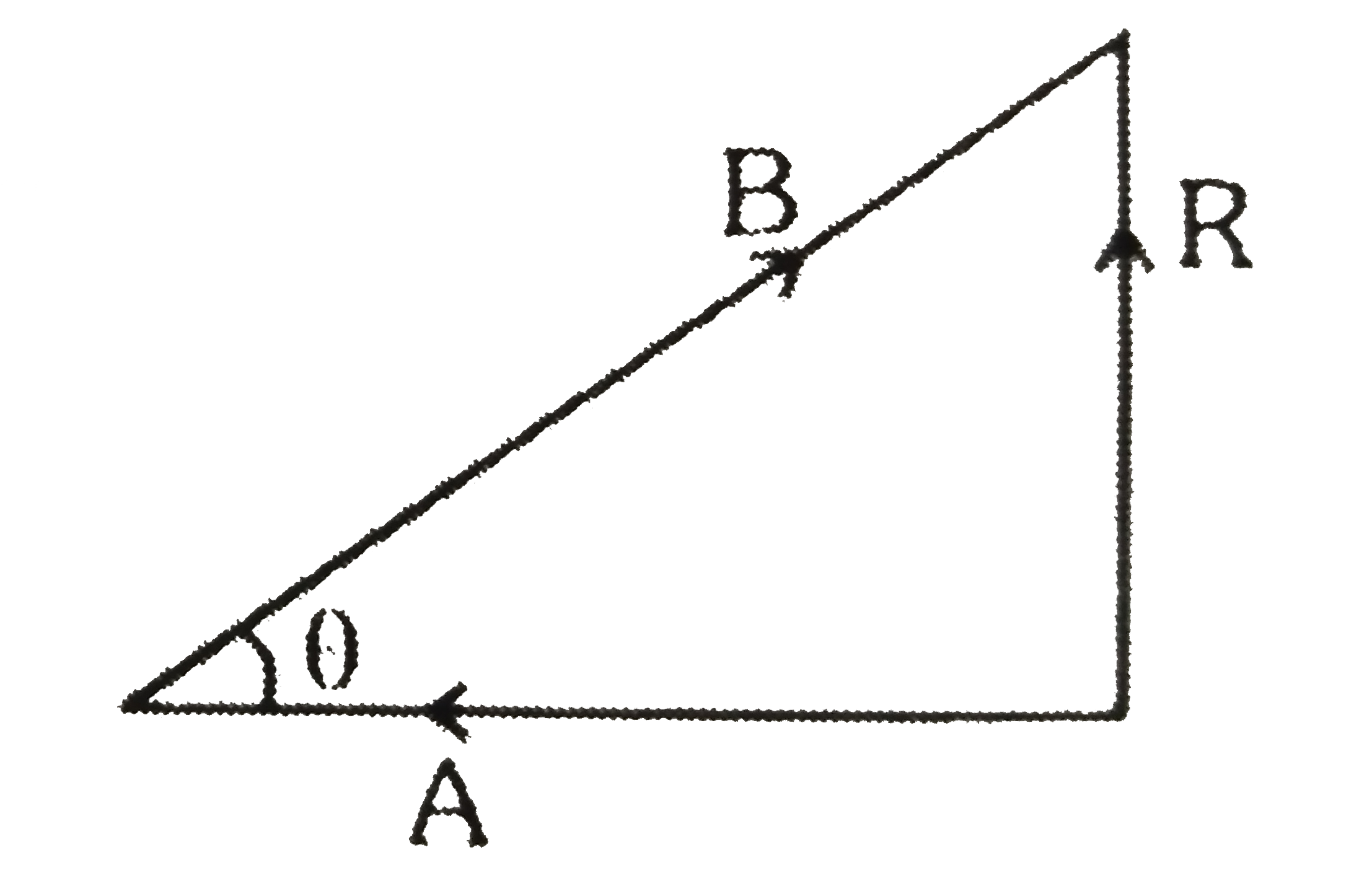
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS
ALLEN |Exercise RESOLUTION OF VECTOR|8 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS
ALLEN |Exercise DOT PRODUCT|20 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS
ALLEN |Exercise DEFINITION & TYPES OF VECTOR|5 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-V B|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -BASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS -ADDITON & SUBTRACTION, MULTIPLICATION & DIVISION OF A VECTOR BY A SCALAR
- Two vectors vec(A) and vec(B) lie in one plane. Vector vec(C ) lies in...
Text Solution
|
- In vector diagram shown in figure where (vecR) is the resultant of vec...
Text Solution
|
- The resultant of vecA and vecB makes an angle alpha with vecA and beta...
Text Solution
|
- Two vectors vecA and vecB are such that vecA+vecB=vecC and A^(2)+B^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- Minimum number of two coplanar vectors of equal magnitude whose v...
Text Solution
|
- Minimum number of coplanar vector having different magnitudes can be a...
Text Solution
|
- How many minimum numbers of non zero vectors in different planes can b...
Text Solution
|
- What are the maximum number of rectangular component in which a vecto...
Text Solution
|
- What are the maximum number of rectangular component in which a vecto...
Text Solution
|
- What are the maximum number of rectangular component in which a vecto...
Text Solution
|
- The vector sum of the forces of 10 newton and 6 newton can be:
Text Solution
|
- Vector sum of two forces of 10N and 6N cannot be:
Text Solution
|
- Which pair of the following forces will never give resultant force of ...
Text Solution
|
- If vecA+ vecB = vecC and A+B+C=0, then the angle between vecA and vec...
Text Solution
|
- The resultant of vec(A)+vec(B) is vec(R )(1). On reversing the vecto...
Text Solution
|
- Given that vecP + vecQ = vecP-vecQ,. This can be true when
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following sets of concurrent forces may be in equilibrium...
Text Solution
|
- If vectors vecA and vecB are such that |vecA+vecB|= |vecA|= |vecB| the...
Text Solution
|
- What happens, when we multiply a vector by (-3)
Text Solution
|
- If the magnitue of sum two vectors is equal to the magnitude of differ...
Text Solution
|