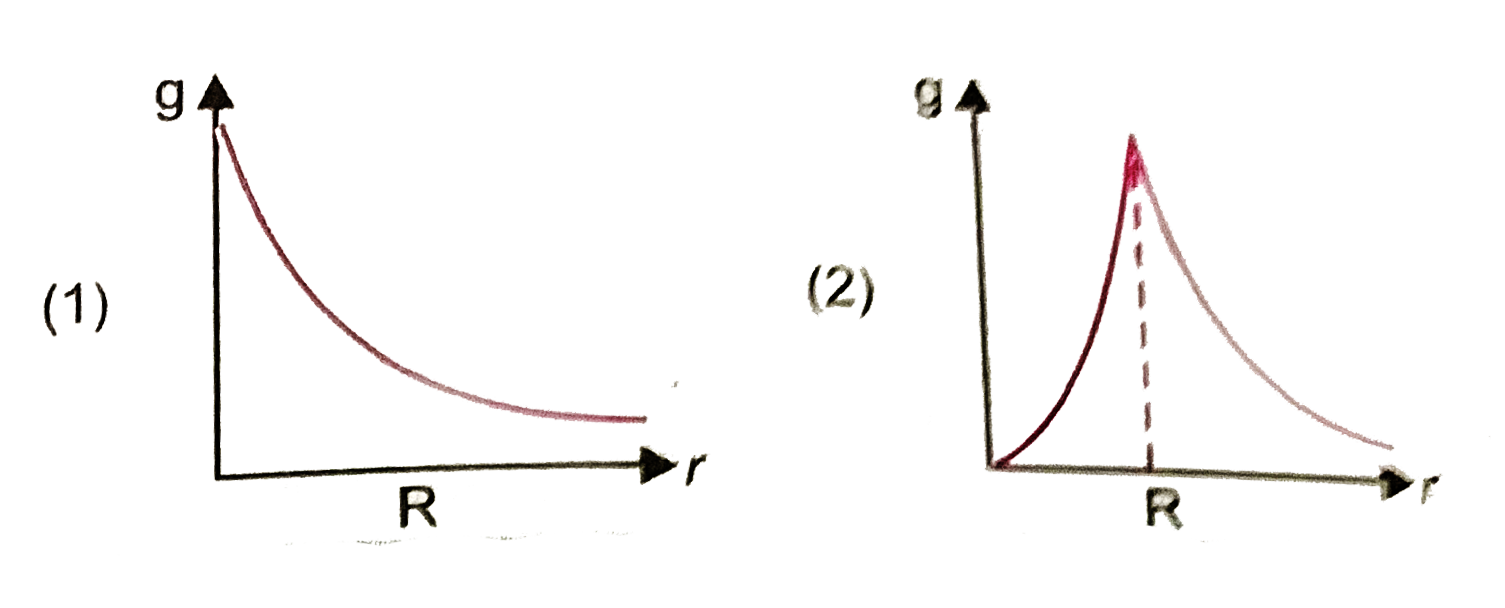
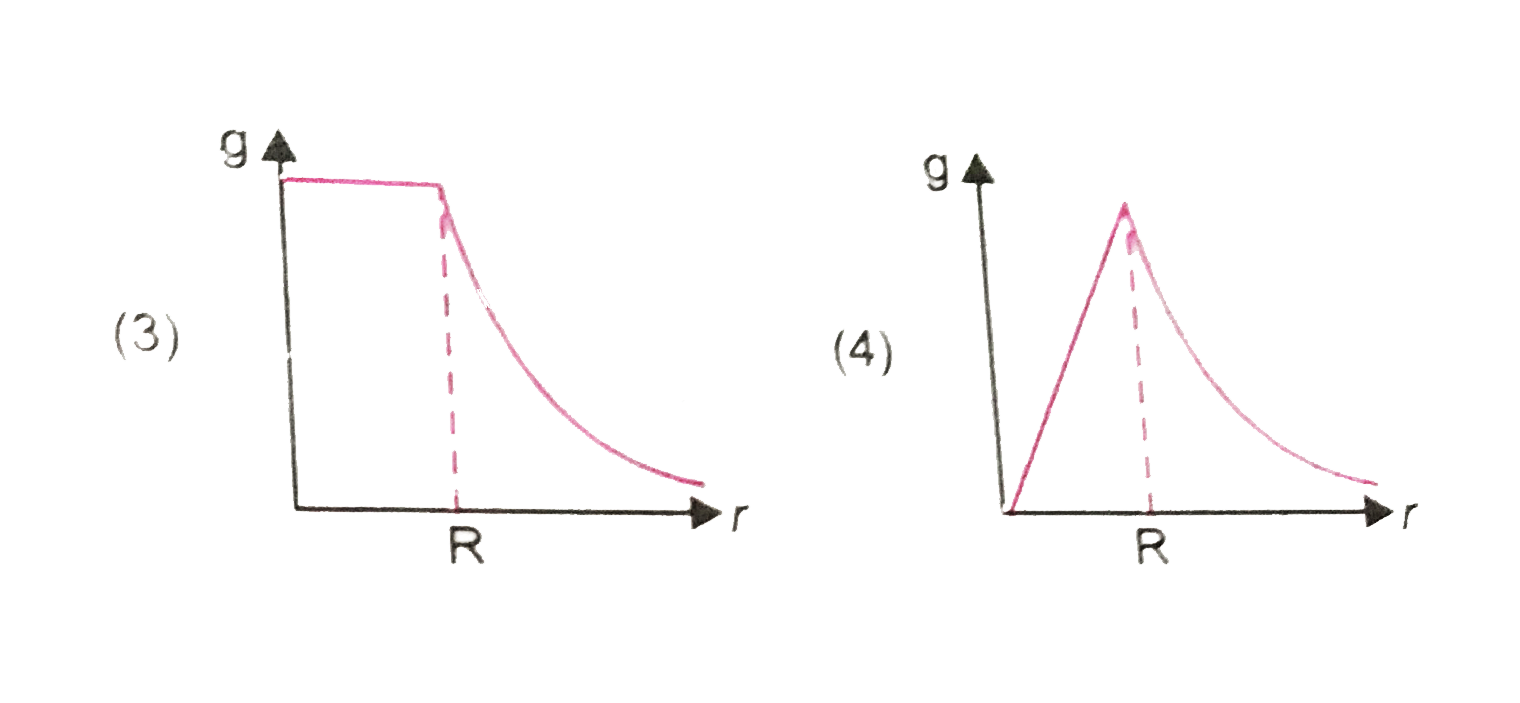
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -GRAVITATION-EXERCISE 2
- The radii of circular orbits of two satellite A and B of the earth are...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass M is placed at the centre of a spherical shell of s...
Text Solution
|
- The dependence of acceleration due to gravity g on the distance r from...
Text Solution
|
- The additional kinetic energy to be provided to a satellite of mass m ...
Text Solution
|
- A plenet moving along an elliptical orbit is closest to the sun at a d...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical planet far out in space has a mass M(p) and diameter D(p)....
Text Solution
|
- A geostationary satellite is orbiting the earth at a height of 5R abov...
Text Solution
|
- The height a which the weight of a body becomes 1//16th its weight on ...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following plots represents the variation of the gravi...
Text Solution
|
- If v(e) is escape velocity and v(0), is orbital velocity of satellite ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is thrown with escape velocity v(e) from the surface of ear...
Text Solution
|
- A black hole is an object whose gravitational field is so strong that ...
Text Solution
|
- Dependence of intensity of gravitational field (E) of earth with dista...
Text Solution
|
- Kepler's third law states that square of period revolution (T) of a pl...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite S is moving in an elliptical orbit around the earth. The m...
Text Solution
|
- A remote-sensing satellite of earth revolves in a circular orbit at a ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the velocity of a satellite at height 80 km from earth. If the ra...
Text Solution
|
- At what height from the surface of earth the gravitation potential and...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of escape velocity at earth (v(e)) to the escape velocity at...
Text Solution
|
- Starting from the centre of the earth having radius R, the variation o...
Text Solution
|