A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -AIIMS 2019-PHYSICS
- An equi-convex lens of focal length 10 cm and refractive index (mug=1....
Text Solution
|
- A boy of height 1.5m with his eye level at 1.4m stands before a plane ...
Text Solution
|
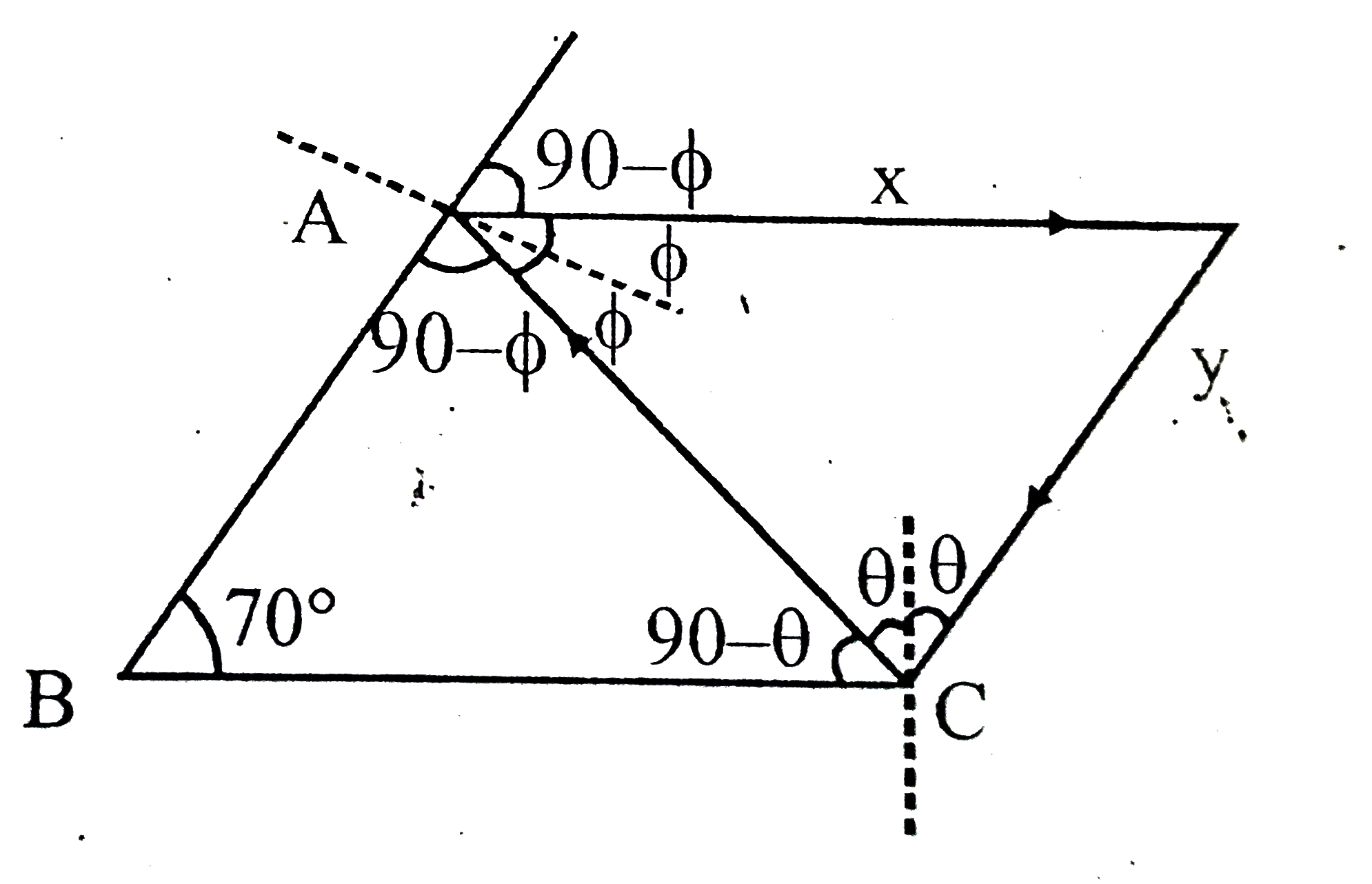
- Two plane mirror M(1) "and" M(2) are inclined to each other at 70^(@)....
Text Solution
|
- A beam of diameter 'd' is incident on a glass hemisphere. If the radiu...
Text Solution
|
- Two lenses in contact made of materials with dispersive powers in the ...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of monochromatic light is incident at i= 50^(@) on one face of ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the height of image in the following diagram.
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror is moving with velocity -2 hati - 3 hatj + 4hatk ....
Text Solution
|
- Find the lateral shift of a light ray while it passws through a paral...
Text Solution
|
- A thin convex lens from a real Image of a certain object 'p' times it ...
Text Solution
|
- The distance between the objective lens and the eye lens of an astrono...
Text Solution
|
- A far sighted person has a near point of 60"cm" . What power lens shou...
Text Solution
|
- If the potential at the center of a uniformly charged sphere of radius...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at the point P as shown in figure on the axis of ...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge Q is placed at the centre of a spherical conducting she...
Text Solution
|
- Two spherical, nonconducting, and very thin shells of uniformly distri...
Text Solution
|
- An infinite number of concentric rings carry a charge Q each alternate...
Text Solution
|
- If uniform electric field vec E = E 0 hati + 2 E 0 hatj ,...
Text Solution
|
- For an infinite line of charge having linear charge density lambda lyi...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m and charge +q approaches from a very large distan...
Text Solution
|