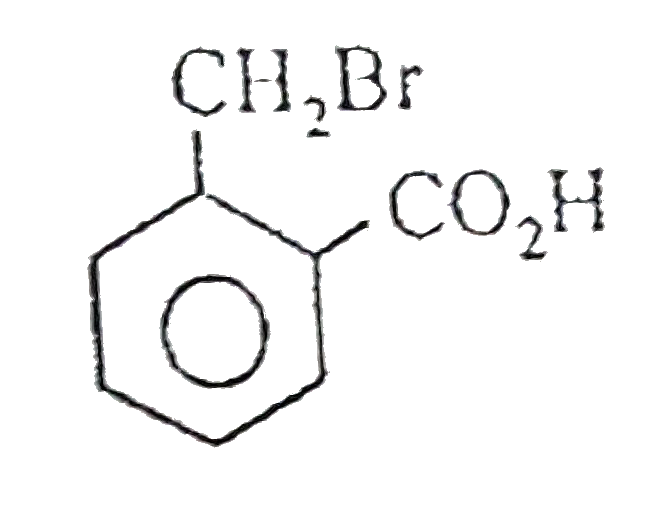
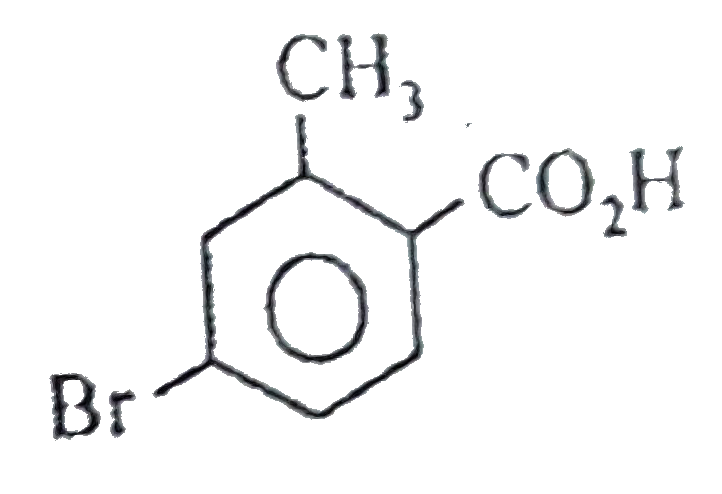
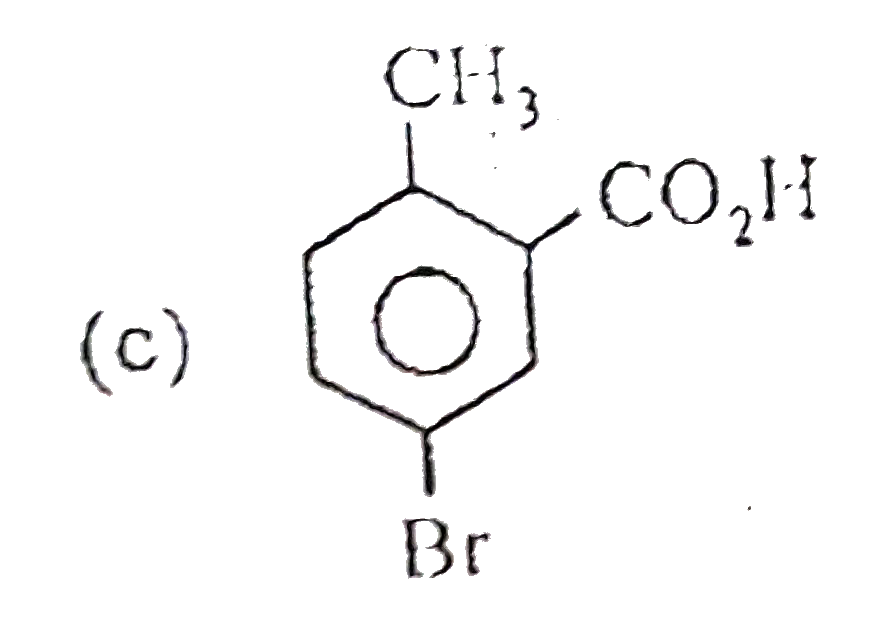
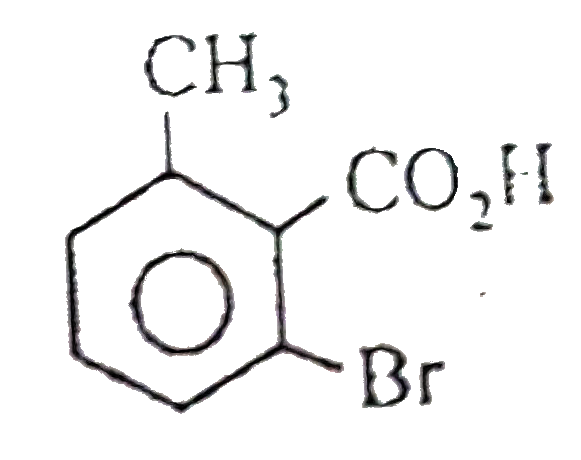
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- alpha-Toluic acid in reaction withBr(2)+Fe gives
Text Solution
|
- o-Toluic acid on reaction with Br(2) + Fe gives
Text Solution
|
- Carboxylic acids having at least one alpha -hydrogen react with Cl(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- Carboxylic acids having at least one alpha -hydrogen react with Cl(2)"...
Text Solution
|
- o-toluic acid on reaction with Br(2) +Fe gives
Text Solution
|
- The relative acidic strengths of benzoic acid, o-toluic acid and p-tol...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction of Br(2)//P or Cl(2)//P with carboxylic acid to form alp...
Text Solution
|
- alpha-Toluic acid in reaction withBr(2)+Fe gives
Text Solution
|
- IUPAC name m-toluic acid is
Text Solution
|