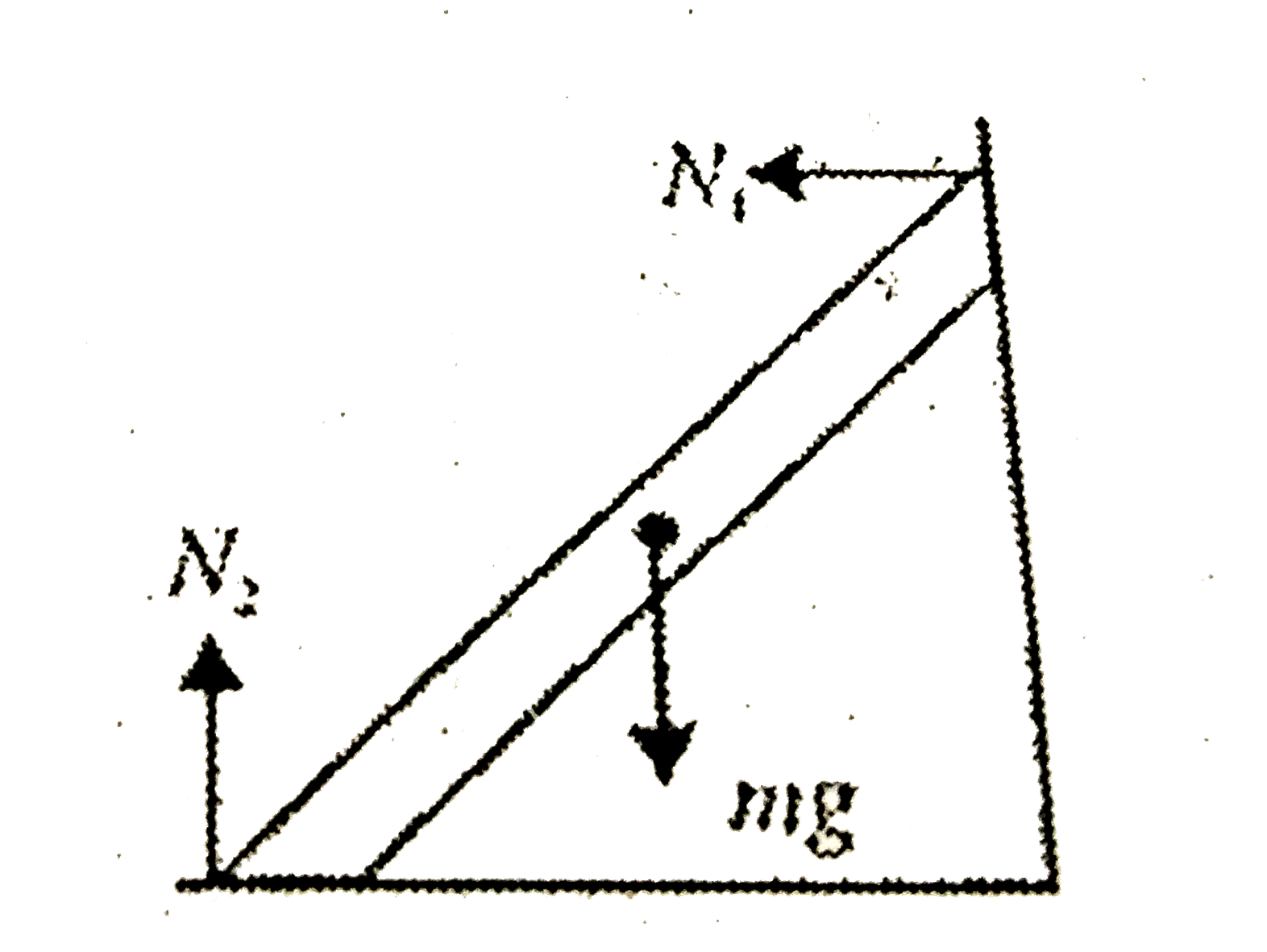
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A ladder is learned against a smooth wall and is allowed to slip on a ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform ladder of mass 10 kg leans against a smooth vertical wall ma...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, a ladder of mass m is shown leaning against a wall. It ...
Text Solution
|
- A ladder is leaned against a smooth wall and it is allowed to slip on ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform ladder of length l rests against a smooth, vertical wall (fi...
Text Solution
|
- A ladder of mass 10kg is held at reat against a smooth wall on a rough...
Text Solution
|
- A ladder weighing 20kg wt rests with its one end against a smooth vert...
Text Solution
|
- A ladder placed on a smooth floor slips. If at a given instant the vel...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform ladder is standing against a vertical smooth wall, resting o...
Text Solution
|