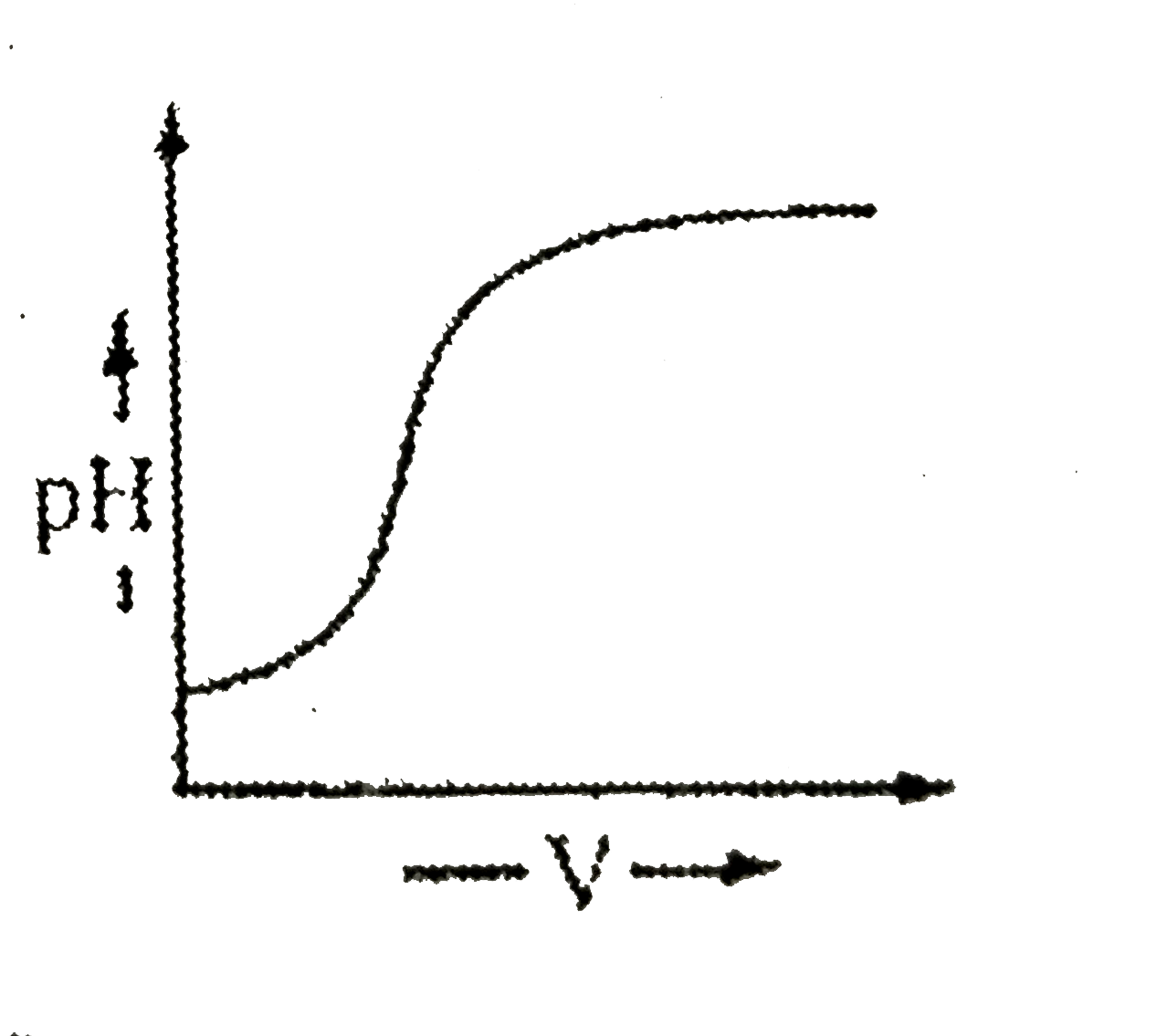
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- During titration of acetic acid with aq. NaOH solution, the neutralisa...
Text Solution
|
- When 0.2M solution of acetic acid is neutralised with 0.2M NaOH in 500...
Text Solution
|
- Calcualte the pH at the equivalence point when a solution of 0.1M acet...
Text Solution
|
- Acetic acid is titrated with NaOH solution. Which of the following sta...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following curves represents the graph pH during the t...
Text Solution
|
- which one of the following curves represents the graph of pH dur...
Text Solution
|
- During titration of acetic acid with aq. NaOH solution, the neutralisa...
Text Solution
|
- 100 mL of ( M / 1 0) aqueous solution of a monoprotic acid is titrated...
Text Solution
|
- 0.1 M acetic acid solution is titrated against 0.1M NaOH solution. Wha...
Text Solution
|