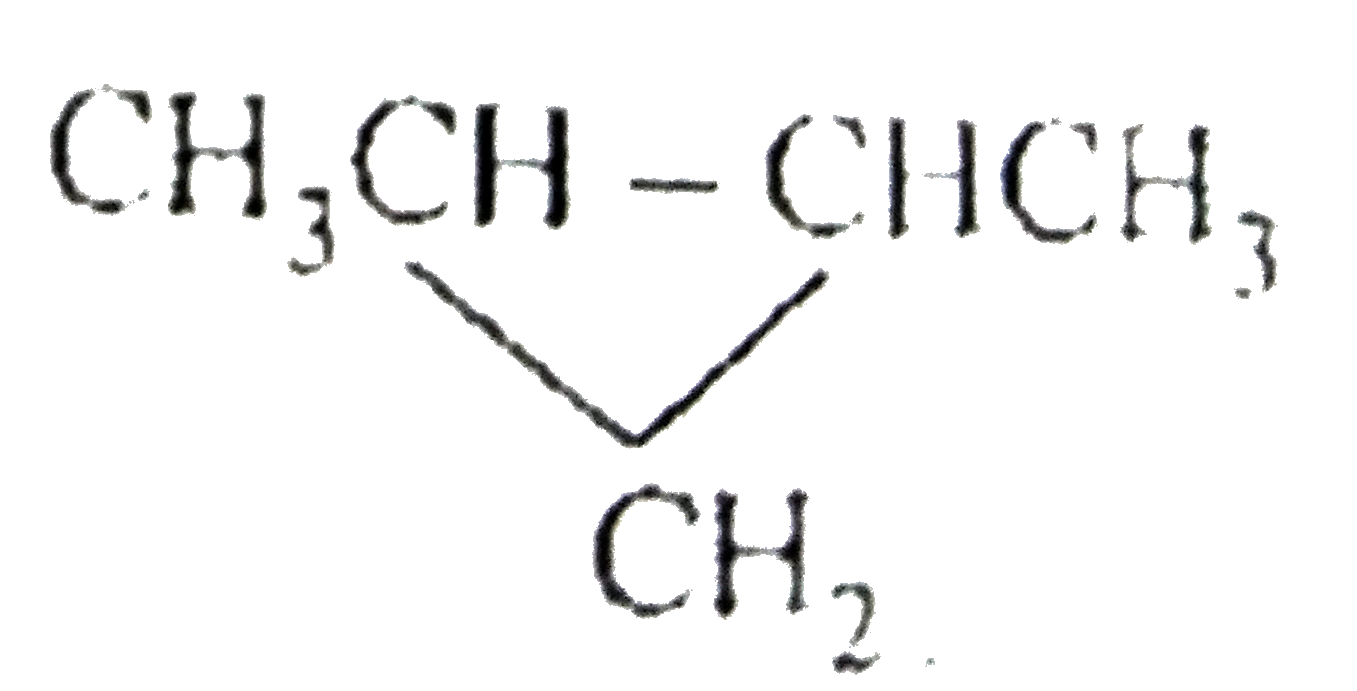
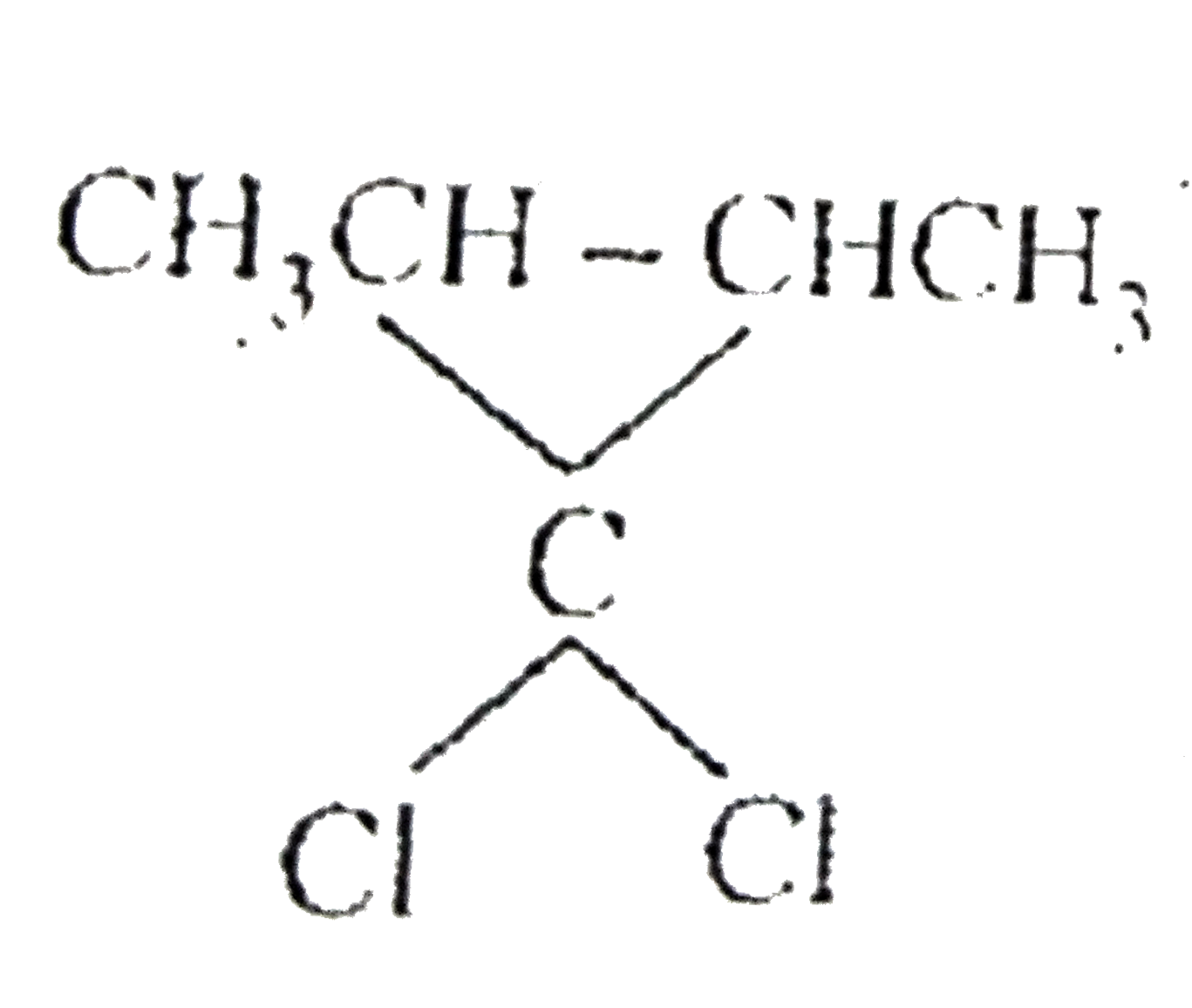
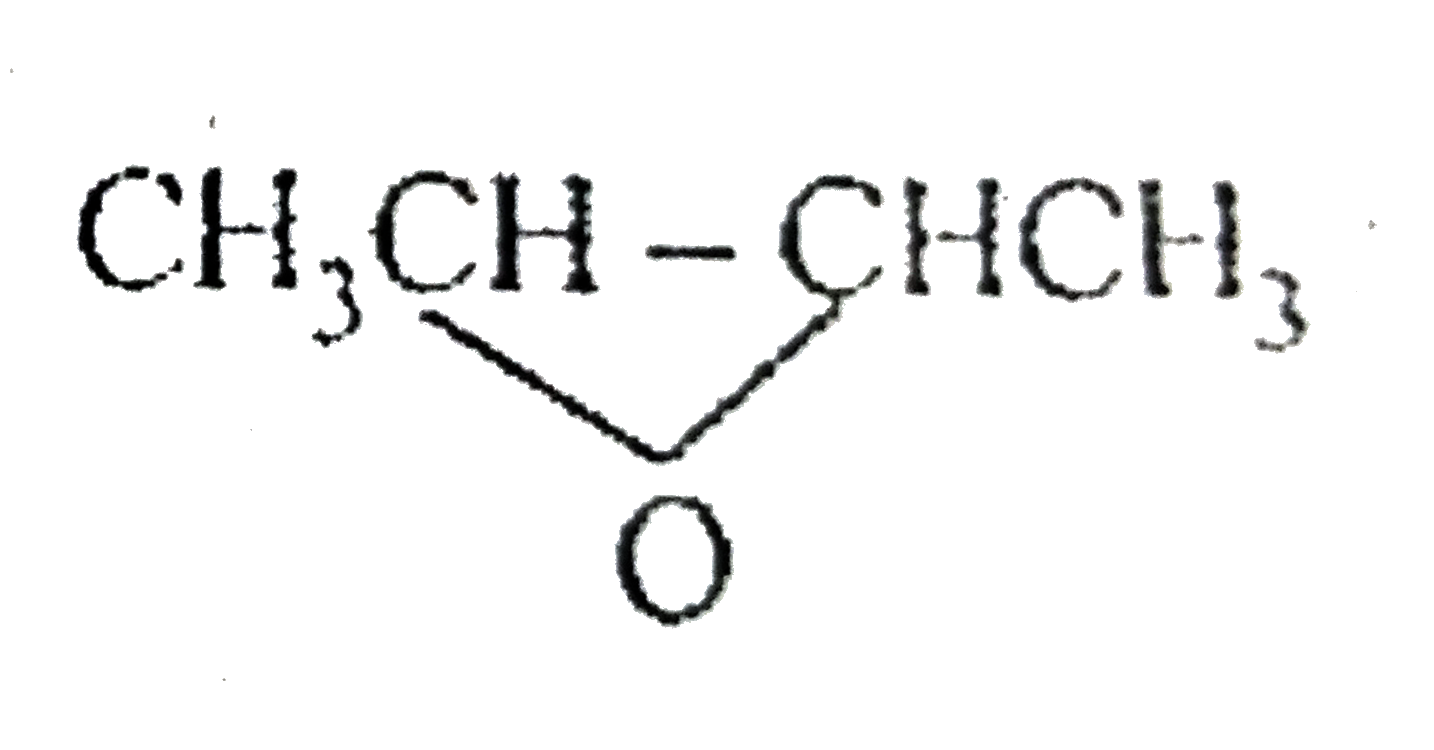
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- CH3CH=CHCH3+CHCl3+t-BuOK rarr A. A is
Text Solution
|
- What is A in the following reaction ? overset(t-BuOK)underset(t-BuOk)t...
Text Solution
|
- The compounds that will give an isomer of 2, 2-dimethyl propane on cat...
Text Solution
|
- The order of increasing reactivity towards HCI of the following compou...
Text Solution
|
- यौगिक के निम्लिखित युग्मो में कौन-सी समावयवता है ? कारण सहित स्पस्ट की...
Text Solution
|
- CH3CH=CHCH3+CHCl3+t-BuOK rarr A.A
Text Solution
|
- निम्नलिखित अभिक्रिया क्रम में एल्कीन यौगिक B उत्पन्न करती है- CH3CH=CH...
Text Solution
|
- निम्नलिखित अभिक्रियाओं के कर्म में एक एल्काइन यौगिक B बनती है CH3C...
Text Solution
|
- Write structures and names of the compounds A to Q in the following r...
Text Solution
|