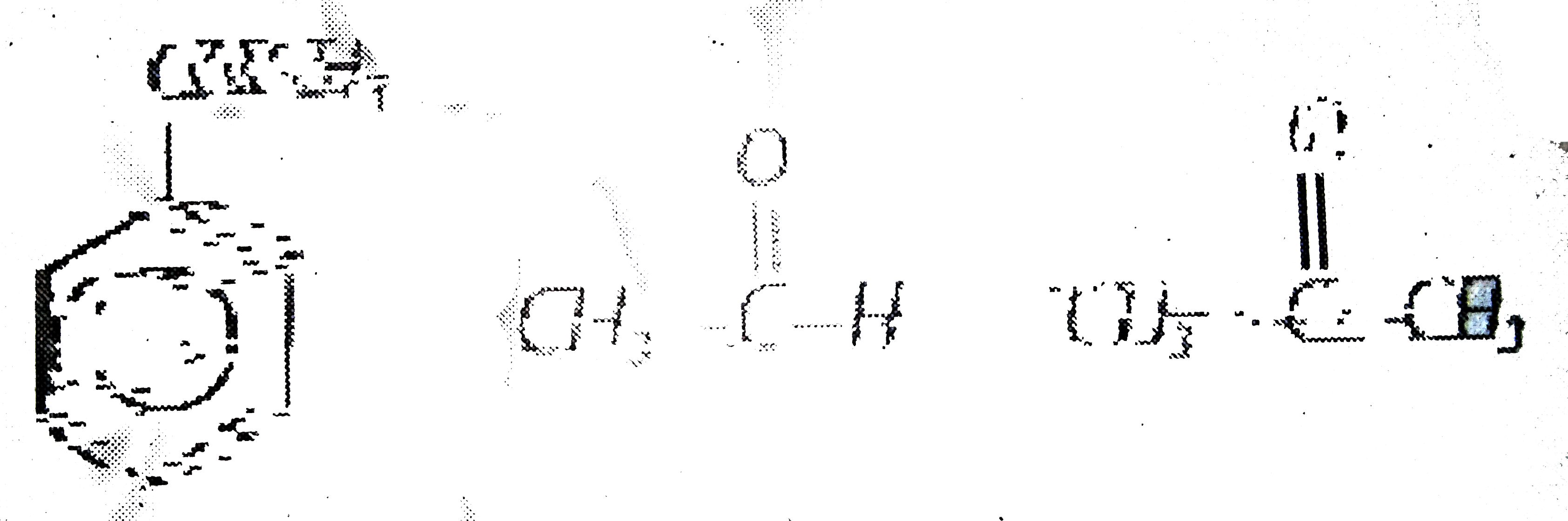A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Ease of nucleophilic addition in the given compounds is
Text Solution
|
- Which carbonyl group of the given compound is most reactive for nucleo...
Text Solution
|
- Carbonyl compounds undergo nucleophilic addition because of :
Text Solution
|
- Which compound is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition ?
Text Solution
|
- Ease of nucleophilic addition in the given compounds is
Text Solution
|
- The order of reactivity of carbonyl compounds for nucleophilic additio...
Text Solution
|
- Which carbonyl group of the given compound in most reactive for...
Text Solution
|
- Write the mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions of carbonyl com...
Text Solution
|
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo electrophilic addition and carbonyl c...
Text Solution
|