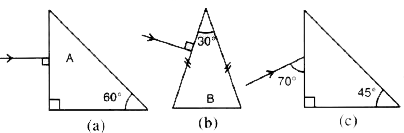
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Figure below shows a light ray of green colour incident on the prisms ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident at an angle of 60^@ on the face of a prism ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the path of light ray passing through a prism. Label angle of inc...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the graph of angle of deviation del versus angle of incid...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows graph of deviation delta versus angle of incidence for a ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a ray diagram to show a right angled isosceles prism may be used ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Draw the ray diagram showing refraction of ray of light through a ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a ray diagram to show the path of light that enters the glass pri...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a ray diagram showing the path of a ray of light entering through...
Text Solution
|